Intro
Compare the benefits of Active Duty vs Reserve military service. Discover the 5 key differences in education assistance, healthcare, retirement plans, and deployment policies. Learn how to choose the best option for your military career, weighing factors like length of service, deployment frequency, and access to on-base facilities and resources.
Serving in the military can be a rewarding and challenging experience, offering a range of benefits to those who choose to serve. However, the benefits and responsibilities can vary significantly depending on whether you serve on active duty or in the reserve. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between active duty and reserve benefits, helping you make an informed decision about your military career.
Overview of Active Duty and Reserve Benefits
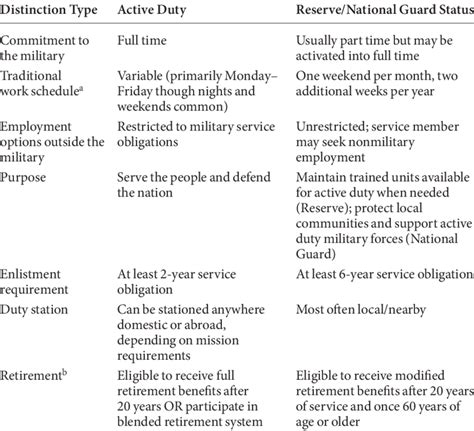
Before diving into the differences, it's essential to understand the basics of active duty and reserve benefits. Active duty personnel serve full-time in the military, while reserve personnel serve part-time, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year. Both active duty and reserve personnel are eligible for various benefits, including education assistance, healthcare, and home loan guarantees.
Difference 1: Education Benefits

One of the most significant differences between active duty and reserve benefits is education assistance. Active duty personnel are eligible for the Military Tuition Assistance (TA) program, which covers up to 100% of tuition costs for college courses. Reserve personnel, on the other hand, are eligible for the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) program, which provides a monthly stipend for education expenses.
In addition, active duty personnel may be eligible for the Post-9/11 GI Bill, which provides more comprehensive education benefits, including coverage for tuition, fees, and living expenses. Reserve personnel may also be eligible for the Post-9/11 GI Bill, but the benefits are typically less generous than those available to active duty personnel.
Education Benefits Comparison
| Benefit | Active Duty | Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition Assistance | Up to 100% coverage | MGIB-SR stipend |
| Post-9/11 GI Bill | Comprehensive benefits | Less generous benefits |
Difference 2: Healthcare Benefits
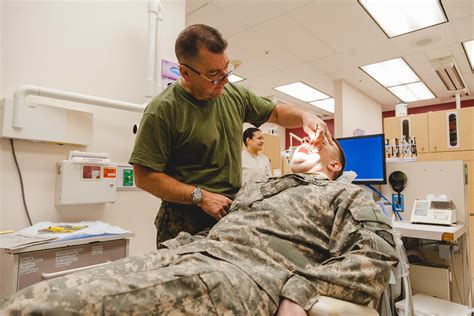
Active duty personnel and their families are eligible for comprehensive healthcare benefits through the Military Health System (MHS). Reserve personnel and their families may also be eligible for MHS benefits, but the coverage is typically less comprehensive.
Active duty personnel are automatically enrolled in the MHS, while reserve personnel must enroll in the TRICARE Reserve Select program, which requires a monthly premium payment. Additionally, active duty personnel may be eligible for special healthcare benefits, such as the Military Treatment Facility (MTF) system, which provides free or low-cost healthcare services.
Healthcare Benefits Comparison
| Benefit | Active Duty | Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Military Health System | Comprehensive benefits | Less comprehensive benefits |
| TRICARE Reserve Select | Not applicable | Monthly premium payment required |
| Military Treatment Facility | Eligible | Not eligible |
Difference 3: Home Loan Guarantees

Both active duty and reserve personnel are eligible for home loan guarantees through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). However, the benefits and requirements differ significantly.
Active duty personnel may be eligible for a zero-down mortgage with no private mortgage insurance (PMI) requirement, while reserve personnel may require a down payment and PMI. Additionally, active duty personnel may be eligible for lower interest rates and reduced funding fees.
Home Loan Guarantees Comparison
| Benefit | Active Duty | Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Down payment | Zero-down mortgage | Down payment required |
| Private mortgage insurance | Not required | Required |
| Interest rates | Lower interest rates | Higher interest rates |
| Funding fees | Reduced funding fees | Higher funding fees |
Difference 4: Retirement Benefits

Active duty personnel are eligible for retirement benefits after 20 years of service, while reserve personnel may be eligible for retirement benefits after 20 years of qualifying service. However, the retirement benefits and requirements differ significantly.
Active duty personnel are eligible for a pension and access to the Military Retirement System (MRS), while reserve personnel are eligible for a pension and access to the Reserve Retirement System (RRS). Additionally, active duty personnel may be eligible for the Career Status Bonus (CSB) and the Redefined Benefit Plan (RBP), which provide additional retirement benefits.
Retirement Benefits Comparison
| Benefit | Active Duty | Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Pension | Eligible after 20 years | Eligible after 20 years of qualifying service |
| Military Retirement System | Eligible | Not eligible |
| Reserve Retirement System | Not eligible | Eligible |
| Career Status Bonus | Eligible | Not eligible |
| Redefined Benefit Plan | Eligible | Not eligible |
Difference 5: Special Benefits

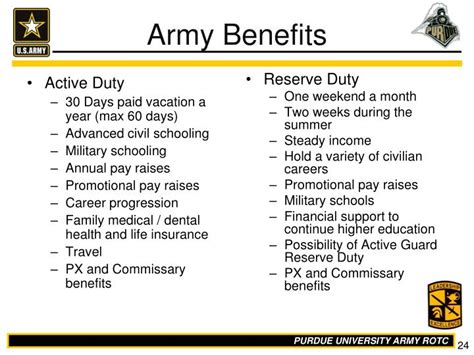
Active duty personnel may be eligible for special benefits, such as the Military Housing Allowance (MHA), the Subsistence Allowance (SA), and the Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS). Reserve personnel may also be eligible for special benefits, such as the Reserve Component (RC) drill pay and the Selected Reserve (SR) drill pay.
However, the benefits and requirements differ significantly. Active duty personnel may be eligible for more comprehensive special benefits, while reserve personnel may be eligible for less comprehensive benefits.
Special Benefits Comparison
| Benefit | Active Duty | Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Military Housing Allowance | Eligible | Not eligible |
| Subsistence Allowance | Eligible | Not eligible |
| Basic Allowance for Subsistence | Eligible | Not eligible |
| Reserve Component drill pay | Not eligible | Eligible |
| Selected Reserve drill pay | Not eligible | Eligible |
Military Benefits Image Gallery








What are the main differences between active duty and reserve benefits?
+The main differences between active duty and reserve benefits include education benefits, healthcare benefits, home loan guarantees, retirement benefits, and special benefits.
Are reserve personnel eligible for the same education benefits as active duty personnel?
+No, reserve personnel are not eligible for the same education benefits as active duty personnel. Reserve personnel are eligible for the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) program, which provides a monthly stipend for education expenses.
Can active duty personnel be eligible for special benefits, such as the Military Housing Allowance (MHA)?
+Yes, active duty personnel may be eligible for special benefits, such as the Military Housing Allowance (MHA), the Subsistence Allowance (SA), and the Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS).
In conclusion, while both active duty and reserve personnel are eligible for various military benefits, the benefits and requirements differ significantly. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision about your military career.
