Intro
Discover the key differences between active duty and reserve pay in the military. Learn how base pay, allowances, and benefits vary between active duty and reserve personnel, including Drill Pay, Basic Allowance for Housing, and Veterans benefits. Make informed decisions about your military career with our comprehensive comparison.
Serving in the military is a significant commitment, and compensation is a crucial aspect to consider. The pay structure for active duty and reserve personnel differs in several ways. Understanding these differences is essential for those considering a military career or transitioning between active duty and reserve roles.
The pay for active duty personnel is generally higher than that for reservists, but there are other factors to consider, such as benefits, bonuses, and education assistance. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of active duty vs reserve pay, exploring the differences in pay scales, allowances, and benefits.
Understanding Military Pay Scales
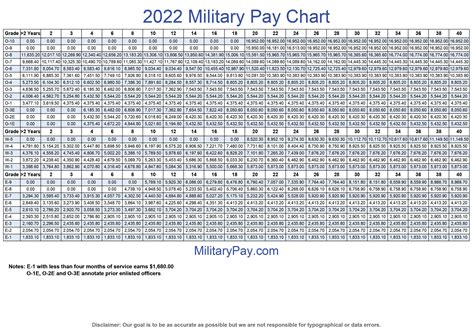
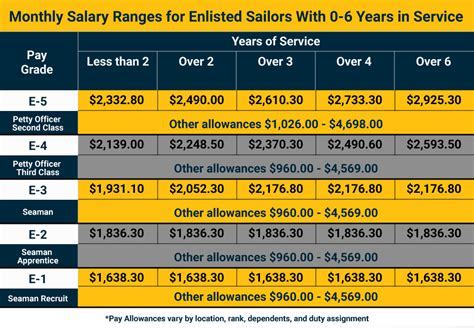
The military uses a pay scale system to determine compensation based on rank and time in service. The pay scale is divided into two main categories: enlisted and officer. Enlisted personnel are further divided into nine pay grades (E-1 to E-9), while officers are divided into 11 pay grades (O-1 to O-10).
Active duty personnel receive a base pay, which is taxable, and various allowances, such as basic allowance for housing (BAH) and basic allowance for subsistence (BAS). These allowances are non-taxable.
Active Duty Pay Scales
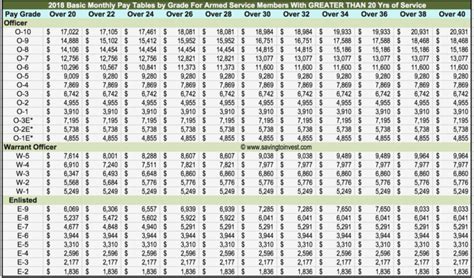
Active duty personnel receive a monthly base pay, which is determined by their rank and time in service. The pay scale is adjusted annually based on the Employment Cost Index (ECI), which measures changes in the cost of labor.
Here is an example of the 2022 active duty pay scale for enlisted personnel:
| Rank | Time in Service | Monthly Base Pay |
|---|---|---|
| E-1 | 0-2 years | $1,733.10 |
| E-2 | 2-3 years | $1,942.50 |
| E-3 | 3-4 years | $2,043.70 |
| E-4 | 4-6 years | $2,244.90 |
Officers receive a higher base pay, with the following example for 2022:
| Rank | Time in Service | Monthly Base Pay |
|---|---|---|
| O-1 | 0-2 years | $3,287.10 |
| O-2 | 2-3 years | $3,704.90 |
| O-3 | 3-4 years | $4,236.40 |
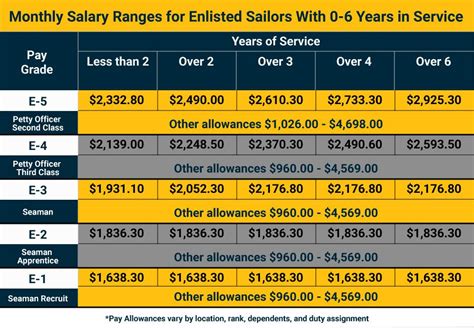
Reserve Pay Scales
Reservists receive a monthly base pay, but it is calculated differently than active duty pay. Reserve pay is based on the number of drills and annual training days attended.
Here is an example of the 2022 reserve pay scale for enlisted personnel:
| Rank | Drills per Month | Monthly Base Pay |
|---|---|---|
| E-1 | 1-2 drills | $278.40 |
| E-2 | 2-3 drills | $306.30 |
| E-3 | 3-4 drills | $334.20 |
Officers receive a higher base pay, with the following example for 2022:
| Rank | Drills per Month | Monthly Base Pay |
|---|---|---|
| O-1 | 1-2 drills | $541.80 |
| O-2 | 2-3 drills | $613.50 |
| O-3 | 3-4 drills | $685.20 |
Allowances and Benefits

In addition to base pay, military personnel receive various allowances and benefits. These include:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): a tax-free allowance to help cover housing costs.
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): a tax-free allowance to help cover food costs.
- Health insurance: military personnel and their families receive comprehensive health insurance through TRICARE.
- Education assistance: military personnel can receive education assistance, such as the GI Bill, to help pay for college or vocational training.
- Retirement benefits: military personnel are eligible for retirement benefits, including a pension and access to the Veterans Affairs healthcare system.
Active duty personnel receive these allowances and benefits, while reservists may receive them on a limited basis, depending on their drill schedule and deployment status.
Other Forms of Compensation
In addition to base pay and allowances, military personnel may receive other forms of compensation, such as:
- Bonuses: signing bonuses, reenlistment bonuses, and special duty pay.
- Special pays: hazardous duty pay, jump pay, and dive pay.
- Incentive pays: pays for proficiency in a foreign language, hazardous duty, or other specialized skills.
These forms of compensation can significantly impact a military member's overall pay.
Comparison of Active Duty and Reserve Pay
When comparing active duty and reserve pay, it is essential to consider the differences in pay scales, allowances, and benefits. Active duty personnel generally receive higher pay and more comprehensive benefits, including health insurance and education assistance.
However, reservists may receive other benefits, such as:
- Flexibility: reservists can balance military service with civilian life and careers.
- Education assistance: reservists may be eligible for education assistance, such as the GI Bill.
- Retirement benefits: reservists are eligible for retirement benefits, including a pension and access to the Veterans Affairs healthcare system.
Ultimately, the choice between active duty and reserve service depends on individual circumstances and priorities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between active duty and reserve pay is crucial for those considering a military career or transitioning between active duty and reserve roles. While active duty personnel generally receive higher pay and more comprehensive benefits, reservists may receive other benefits, such as flexibility and education assistance.
It is essential to weigh the pros and cons of each option and consider individual circumstances and priorities when making a decision.
Active Duty vs Reserve Pay Image Gallery







What is the main difference between active duty and reserve pay?
+The main difference between active duty and reserve pay is the pay scale. Active duty personnel receive a higher base pay and more comprehensive benefits, while reservists receive a lower base pay and limited benefits.
Do reservists receive the same benefits as active duty personnel?
+No, reservists do not receive the same benefits as active duty personnel. While reservists may be eligible for some benefits, such as education assistance and retirement benefits, they do not receive the same level of benefits as active duty personnel.
Can I transition from active duty to reserve service?
+How do I determine which type of service is best for me?
+To determine which type of service is best for you, consider your individual circumstances, priorities, and goals. You may also want to speak with a military recruiter or career counselor to get personalized advice.
