Intro
Discover effective agriculture food and natural resources management strategies to boost crop yields, conserve water, and reduce environmental impact. Learn about sustainable farming practices, soil conservation techniques, and innovative technologies to enhance food security and promote eco-friendly agriculture systems.
The importance of effective management strategies in agriculture, food, and natural resources cannot be overstated. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food, water, and energy increases, putting pressure on the world's natural resources. In order to meet this demand, it is essential to adopt sustainable and efficient management practices that ensure the long-term health and productivity of our planet. In this article, we will explore the various management strategies that can be employed in agriculture, food, and natural resources to promote sustainability and resilience.

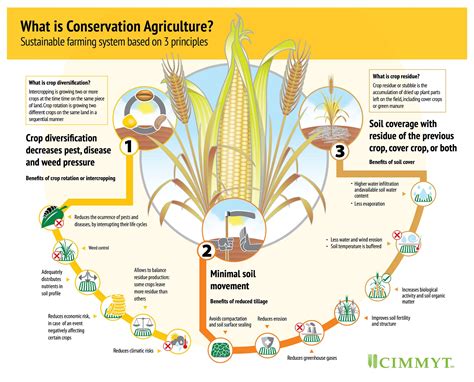
Soil Conservation and Management
Soil is a vital component of the ecosystem, providing the foundation for plant growth and filtering water. However, soil degradation and erosion are major concerns worldwide, resulting in decreased fertility and productivity. To combat this, several soil conservation and management strategies can be employed.
- Crop rotation: Rotating crops helps to break disease and pest cycles, improves soil structure, and increases nutrient availability.
- Cover cropping: Planting cover crops between crop cycles helps to reduce erosion, increase soil organic matter, and provide habitat for beneficial insects.
- Minimum tillage: Reducing tillage frequency and depth helps to minimize soil disturbance, reduce erosion, and promote soil biota.
- Integrated nutrient management: Managing soil nutrients through a combination of organic and inorganic fertilizers helps to optimize soil fertility and minimize environmental impact.
Water Management
Water is a limited resource, and its management is critical for agriculture, food, and natural resources. Several strategies can be employed to optimize water use and reduce waste.
- Irrigation management: Implementing precision irrigation systems and scheduling irrigation according to crop water requirements helps to reduce water waste and optimize water use.
- Water harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater for non-potable uses helps to reduce the demand on potable water sources.
- Water-efficient crops: Planting crops that are tolerant to drought or require less water helps to reduce water demand.

Pest and Disease Management
Pests and diseases can have a significant impact on crop yields and quality. Several management strategies can be employed to minimize the risk of pest and disease outbreaks.
- Integrated pest management: Managing pests through a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical controls helps to minimize environmental impact and optimize pest control.
- Crop monitoring: Regularly monitoring crops for signs of pests and diseases helps to detect problems early and implement control measures.
- Resistant varieties: Planting crop varieties that are resistant to pests and diseases helps to reduce the risk of outbreaks.
Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecosystem health and resilience. Several strategies can be employed to conserve biodiversity in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes helps to promote biodiversity, reduce soil erosion, and increase ecosystem services.
- Conservation agriculture: Implementing conservation agriculture practices such as reduced tillage and permanent soil cover helps to promote soil biota and reduce erosion.
- Ecological restoration: Restoring degraded ecosystems helps to promote biodiversity, improve ecosystem services, and enhance ecosystem resilience.

Farmers' Adoption of Sustainable Practices
The adoption of sustainable practices by farmers is critical for promoting sustainability in agriculture, food, and natural resources. Several factors can influence farmers' adoption of sustainable practices, including:
- Economic incentives: Providing economic incentives such as subsidies, tax breaks, or premium prices for sustainably produced products can encourage farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
- Extension services: Providing extension services such as training, technical assistance, and demonstration plots can help farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
- Social norms: Promoting social norms that value sustainability and environmental stewardship can encourage farmers to adopt sustainable practices.

Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the benefits of sustainable agriculture, food, and natural resources management, several challenges and opportunities exist.
- Climate change: Climate change poses a significant challenge to agriculture, food, and natural resources, requiring the adoption of climate-resilient practices.
- Population growth: The growing global population requires increased food production, putting pressure on natural resources and requiring the adoption of sustainable practices.
- Technological innovation: Technological innovation provides opportunities for improving the efficiency and sustainability of agriculture, food, and natural resources management.
Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources Management Image Gallery








What is sustainable agriculture?
+Sustainable agriculture refers to the production of food, fiber, and other plant and animal products using farming practices that protect the environment, public health, and animal welfare.
Why is biodiversity important in agriculture?
+Biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecosystem health and resilience, and is critical for ensuring the long-term sustainability of agriculture.
What is the importance of soil conservation in agriculture?
+Soil conservation is critical for maintaining soil health and fertility, reducing erosion, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of agriculture.
As we move forward, it is essential that we adopt sustainable and efficient management practices in agriculture, food, and natural resources to promote sustainability and resilience. By implementing strategies such as soil conservation, water management, pest and disease management, biodiversity conservation, and farmers' adoption of sustainable practices, we can ensure the long-term health and productivity of our planet.
