Intro
Uncover the cutting-edge capabilities of the AH-64 Apache, a premier attack helicopter. Learn about its advanced rotors, state-of-the-art avionics, and precision firepower. Discover its combat history, tactical significance, and role in modern warfare. Get inside the cockpit and explore 10 fascinating facts about this iconic aircraft.
The AH-64 Apache is one of the most iconic and feared military aircraft in the world. As a multi-role attack helicopter, it has been used in various combat missions across the globe. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the AH-64 Apache, exploring its history, design, and capabilities.

Origins and Development
The AH-64 Apache was first conceived in the 1970s as a replacement for the AH-1 Cobra. The United States Army sought a new attack helicopter that could provide close air support and anti-tank capabilities. In 1972, the Army awarded a contract to Hughes Aircraft (now Boeing) to develop the YAH-64, which would eventually become the AH-64 Apache.
Design and Features
The AH-64 Apache is a twin-engine, tandem-seat attack helicopter with a distinctive angular design. Its fuselage is made of aluminum and titanium, providing exceptional strength and durability. The Apache features a four-blade main rotor and a four-blade tail rotor, which provides improved stability and maneuverability.
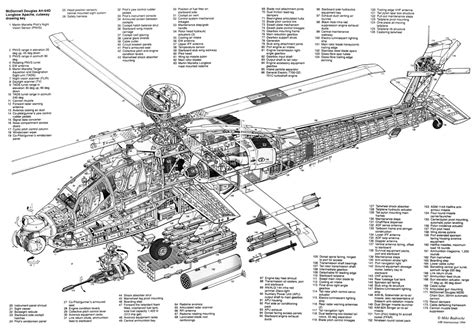
Armament and Avionics
The AH-64 Apache is equipped with a 30mm M230 Chain Gun, which can fire up to 650 rounds per minute. It also features four hardpoints for mounting rockets, missiles, and other ordnance. The Apache's avionics system includes a fire control radar, infrared and low-light TV cameras, and a missile guidance system.
Combat History
The AH-64 Apache has seen extensive combat in various conflicts, including the Gulf War, Operation Iraqi Freedom, and Operation Enduring Freedom. Its ability to provide close air support and conduct precision strikes has made it an invaluable asset on the battlefield.

Upgrades and Modernization
Over the years, the AH-64 Apache has undergone several upgrades and modernization programs. The latest variant, the AH-64E, features improved avionics, a more powerful engine, and enhanced survivability measures. The Apache has also been integrated with advanced precision-guided munitions, such as the AGM-114 Hellfire missile.
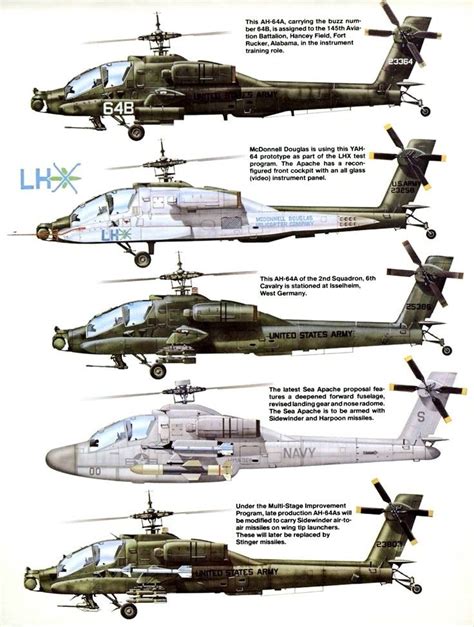
Operators and Variants
The AH-64 Apache has been exported to several countries, including Israel, the United Kingdom, and Japan. There are several variants of the Apache, including the AH-64A, AH-64D, and AH-64E. Each variant features unique upgrades and improvements.

Specifications
Here are some key specifications of the AH-64 Apache:
- Length: 58.17 feet (17.73 meters)
- Rotor Diameter: 48 feet (14.63 meters)
- Height: 15.24 feet (4.65 meters)
- Empty Weight: 11,000 pounds (5,000 kilograms)
- Maximum Takeoff Weight: 23,000 pounds (10,433 kilograms)
- Powerplant: 2 x General Electric T700-GE-701C turboshaft engines
- Speed: 227 mph (365 km/h)
- Range: 300 miles (483 kilometers)
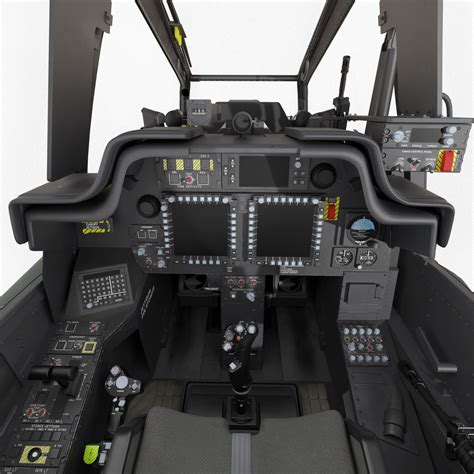
Crew and Training
The AH-64 Apache is crewed by two pilots: a left-seat pilot-in-command and a right-seat co-pilot/gunner. Apache pilots undergo extensive training, which includes simulator training, flight training, and combat training.

Gallery of AH-64 Apache Images
AH-64 Apache Image Gallery









What is the primary role of the AH-64 Apache?
+The primary role of the AH-64 Apache is to provide close air support and anti-tank capabilities to ground forces.
What is the difference between the AH-64A and AH-64E?
+The AH-64E is an upgraded variant of the AH-64A, featuring improved avionics, a more powerful engine, and enhanced survivability measures.
How many countries operate the AH-64 Apache?
+The AH-64 Apache is operated by several countries, including the United States, Israel, the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The AH-64 Apache is an iconic and formidable attack helicopter that has proven itself in combat time and time again. With its advanced avionics, precision-guided munitions, and exceptional maneuverability, the Apache remains a vital component of modern military forces.
