Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the US Air Force with our in-depth guide to 13 officer rankings. From Second Lieutenant to General, discover the responsibilities, requirements, and career paths for each rank. Learn about the different types of officers, including pilots, navigators, and non-rated officers, and how to advance through the ranks.
The United States Air Force is a branch of the US military that operates with a hierarchical structure, with various ranks and positions that define an officer's level of responsibility and authority. Understanding these rankings can provide insight into the career progression and roles of Air Force officers. In this article, we will delve into the 13 Air Force officer rankings, explaining the duties, responsibilities, and requirements for each rank.
Enlisted vs. Officer Ranks
Before we dive into the officer rankings, it's essential to distinguish between enlisted and officer ranks. Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the Air Force, comprising the majority of the force. They are responsible for executing the day-to-day tasks and operations. Officer ranks, on the other hand, are leadership positions that require a higher level of education, training, and experience.
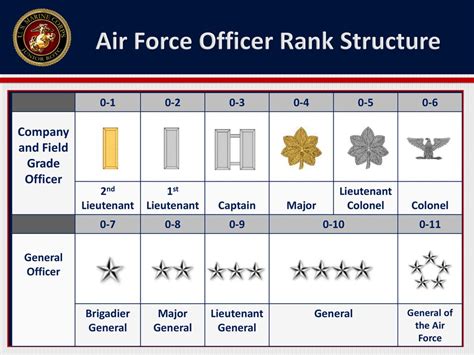
Company Grade Officer Ranks
Company grade officer ranks are the entry-level to mid-level positions in the Air Force officer hierarchy. These ranks are responsible for leading small teams and executing specific tasks.
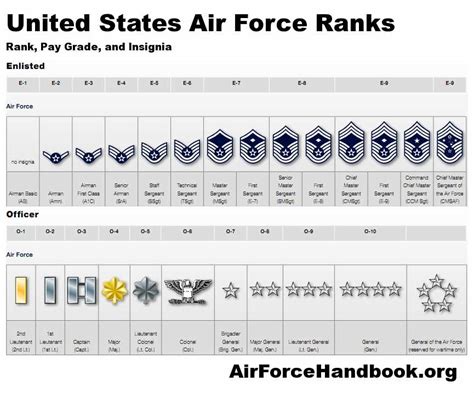
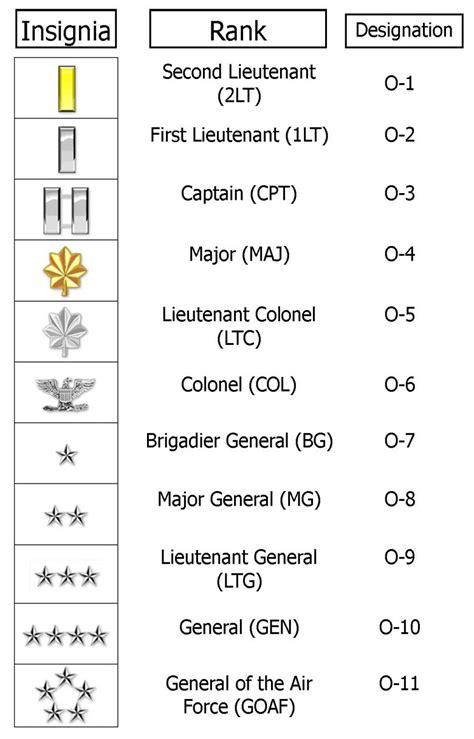
Second Lieutenant (2d Lt, O-1)
The second lieutenant is the most junior commissioned officer rank in the Air Force. They typically lead small teams and are responsible for executing specific tasks. To become a second lieutenant, one must complete a four-year degree and attend Officer Training School (OTS) or the Air Force Academy.
First Lieutenant (1st Lt, O-2)
First lieutenants have more experience and responsibility than second lieutenants. They often lead larger teams and are responsible for making tactical decisions. To become a first lieutenant, one must complete a minimum of two years of service as a second lieutenant.
Captain (Capt, O-3)
Captains are mid-level company grade officers who lead larger teams and are responsible for making strategic decisions. They often serve as flight commanders or executive officers. To become a captain, one must complete a minimum of three years of service as a first lieutenant.
Field Grade Officer Ranks
Field grade officer ranks are the mid-level to senior positions in the Air Force officer hierarchy. These ranks are responsible for leading larger units and making strategic decisions.
Major (Maj, O-4)
Majors are senior field grade officers who lead larger units and are responsible for making strategic decisions. They often serve as squadron commanders or deputy group commanders. To become a major, one must complete a minimum of six years of service as a captain.
Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col, O-5)
Lieutenant colonels are senior field grade officers who lead larger units and are responsible for making strategic decisions. They often serve as group commanders or deputy wing commanders. To become a lieutenant colonel, one must complete a minimum of eight years of service as a major.
Colonel (Col, O-6)
Colonels are senior field grade officers who lead larger units and are responsible for making strategic decisions. They often serve as wing commanders or deputy division commanders. To become a colonel, one must complete a minimum of 11 years of service as a lieutenant colonel.
General Officer Ranks
General officer ranks are the most senior positions in the Air Force officer hierarchy. These ranks are responsible for leading the entire Air Force and making strategic decisions.
Brigadier General (Brig Gen, O-7)
Brigadier generals are one-star generals who serve as deputy commanders or assistant deputy commanders. They are responsible for leading large units and making strategic decisions.
Major General (Maj Gen, O-8)
Major generals are two-star generals who serve as commanders or deputy commanders of large units. They are responsible for making strategic decisions and leading the Air Force.
Lieutenant General (Lt Gen, O-9)
Lieutenant generals are three-star generals who serve as deputy chiefs of staff or vice commanders. They are responsible for making strategic decisions and leading the Air Force.
General (Gen, O-10)
Generals are four-star generals who serve as the Chief of Staff of the Air Force or commanders of major commands. They are responsible for making strategic decisions and leading the Air Force.
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officer ranks are technical experts who serve as advisors and leaders in specific areas.
Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)
Warrant officers are technical experts who serve as advisors and leaders in specific areas. They are responsible for providing guidance and expertise to officers and enlisted personnel.
Gallery of Air Force Officer Ranks
Air Force Officer Ranks Image Gallery





What is the highest rank in the Air Force?
+The highest rank in the Air Force is General (Gen, O-10).
How do I become an Air Force officer?
+To become an Air Force officer, you must complete a four-year degree and attend Officer Training School (OTS) or the Air Force Academy.
What is the difference between enlisted and officer ranks?
+Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the Air Force, responsible for executing day-to-day tasks and operations. Officer ranks are leadership positions that require a higher level of education, training, and experience.
We hope this comprehensive guide to Air Force officer rankings has provided you with a deeper understanding of the hierarchy and career progression within the Air Force. Whether you're an aspiring officer or simply interested in learning more about the military, we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.
