Intro
Discover the crucial roles of an Aircraft Controller. Learn about the 7 key responsibilities, from ensuring safe takeoffs and landings to coordinating with pilots and ground staff. Get insights into air traffic control, radar operations, and emergency response procedures. Understand the high-stakes job of an Aircraft Controller and the skills required for success.
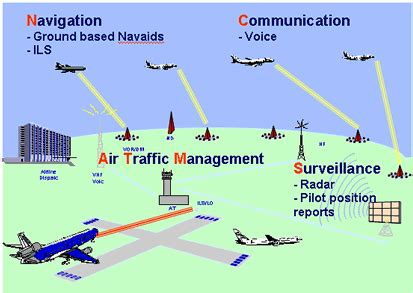
Air traffic control is a critical component of the aviation industry, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft through the skies. At the heart of this complex system are aircraft controllers, highly trained professionals responsible for coordinating the takeoff, landing, and travel of planes. Their role is multifaceted, requiring a unique blend of technical knowledge, situational awareness, and communication skills. Here, we delve into the seven key responsibilities of an aircraft controller, highlighting the complexity and importance of their job.

Responsibility 1: Maintaining Aircraft Separation
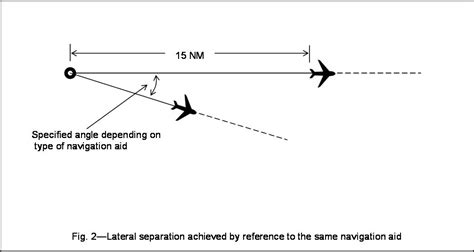
One of the most critical responsibilities of an aircraft controller is ensuring that aircraft maintain a safe distance from each other. This involves monitoring the movement of planes on radar screens and issuing clearances and instructions to pilots to prevent collisions. The safe separation of aircraft is a fundamental principle of air traffic control, and controllers must remain vigilant at all times to prevent accidents.
Techniques for Maintaining Separation
- Visual Separation: Controllers use visual references, such as the position of aircraft on radar screens, to estimate distances and ensure separation.
- Radar Separation: This involves using radar to monitor the distance between aircraft, often in instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) or at night.
- Procedural Separation: Controllers use standardized procedures, such as requiring aircraft to follow specific routes or altitudes, to maintain separation.
Responsibility 2: Issuing Clearances and Instructions
Aircraft controllers are responsible for providing pilots with clearances and instructions necessary for the safe operation of their aircraft. This includes authorizing takeoffs and landings, directing aircraft to specific runways, and issuing instructions for taxiing and departure procedures.
Elements of Clear Communications
- Clarity: Instructions must be clear and concise to avoid confusion.
- Brevity: Controllers must communicate efficiently, using standardized phrases and avoiding unnecessary information.
- Confirmation: Pilots must confirm receipt and understanding of instructions.
Responsibility 3: Coordinating with Other Controllers
Air traffic control is a team effort, with controllers working together to manage the flow of aircraft. This involves coordinating with other controllers in adjacent sectors, at neighboring airports, or in area control centers to ensure smooth transitions of aircraft.
Coordination Techniques
- Handovers: Controllers must transfer responsibility for an aircraft to another controller, ensuring a smooth transition.
- Coordination Messages: Standardized messages are used to communicate with other controllers about aircraft movements and intentions.
Responsibility 4: Handling Emergency Situations
Aircraft controllers must be prepared to handle emergency situations, such as medical emergencies on board, system failures, or severe weather conditions. This requires staying calm under pressure, making quick decisions, and coordinating with emergency services.
Emergency Procedures
- Emergency Declarations: Controllers must quickly identify and declare emergencies, alerting other controllers and emergency services.
- Coordination with Emergency Services: Controllers work closely with emergency services, such as fire and rescue teams, to ensure a swift and effective response.

Responsibility 5: Managing Air Traffic Flow
Aircraft controllers play a crucial role in managing the flow of air traffic, ensuring that aircraft are spaced correctly and that arrival and departure rates are managed efficiently. This involves adjusting flight plans, delaying departures, or redirecting aircraft to manage congestion.
Air Traffic Flow Management Techniques
- Flow Control: Controllers adjust the flow of aircraft to match available airspace and airport capacity.
- Route Modifications: Controllers may reroute aircraft to avoid congestion or adverse weather conditions.

Responsibility 6: Maintaining Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is critical for aircraft controllers, who must maintain a mental picture of the airspace, including the location and intentions of all aircraft. This involves monitoring radar screens, communicating with pilots, and staying alert for changes in weather or other conditions that could impact air traffic.
Techniques for Maintaining Situational Awareness
- Radar Monitoring: Controllers use radar to track the movement of aircraft.
- Weather Monitoring: Controllers stay informed about weather conditions that could impact air traffic.

Responsibility 7: Participating in Training and Development
Finally, aircraft controllers must participate in ongoing training and development to stay current with the latest technologies, procedures, and best practices. This includes regular training sessions, simulator training, and attending conferences and seminars.
Training and Development Opportunities
- Simulator Training: Controllers practice handling different scenarios in a simulated environment.
- Mentoring Programs: Experienced controllers mentor new recruits, providing guidance and support.

In conclusion, the role of an aircraft controller is complex and demanding, requiring a unique blend of technical knowledge, situational awareness, and communication skills. By understanding the seven key responsibilities of an aircraft controller, we can appreciate the critical role they play in ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft through the skies.
Aircraft Controller Image Gallery








What are the primary responsibilities of an aircraft controller?
+The primary responsibilities of an aircraft controller include maintaining aircraft separation, issuing clearances and instructions, coordinating with other controllers, handling emergency situations, managing air traffic flow, maintaining situational awareness, and participating in training and development.
How do aircraft controllers maintain situational awareness?
+Aircraft controllers maintain situational awareness by monitoring radar screens, communicating with pilots, and staying informed about weather conditions that could impact air traffic.
Why is training and development important for aircraft controllers?
+Training and development are crucial for aircraft controllers to stay current with the latest technologies, procedures, and best practices, ensuring they can perform their duties safely and efficiently.
