Intro
Discover the latest updates to the Army Fraternization Policy, governing romantic and social relationships between soldiers. Learn about the 5 key changes, including revised definitions of fraternization, new guidelines for online interactions, and stricter enforcement. Understand how these updates impact Army personnel, unit cohesion, and morale.
The United States Army has a long-standing tradition of maintaining a professional and respectful environment among its ranks. One aspect of this environment is governed by the Army's fraternization policy, which aims to prevent relationships that could compromise the chain of command, create favoritism, or undermine unit cohesion. Recently, the Army has made significant updates to its fraternization policy, reflecting the evolving needs of a modern military. In this article, we will explore five key updates to the Army fraternization policy.
Understanding the Army Fraternization Policy

The Army fraternization policy is outlined in Army Regulation 600-20, which provides guidance on relationships between soldiers of different ranks. The policy is designed to prevent relationships that could create a conflict of interest, undermine the chain of command, or compromise the professionalism of the Army.
The Importance of a Clear Policy
A clear and comprehensive fraternization policy is essential for maintaining a professional and respectful environment in the Army. Without such a policy, relationships between soldiers of different ranks could lead to favoritism, create conflicts of interest, or undermine unit cohesion.
Update 1: Expanded Definition of Fraternization
One of the key updates to the Army fraternization policy is the expansion of the definition of fraternization. Previously, the policy only addressed relationships between officers and enlisted soldiers. However, the updated policy now includes relationships between soldiers of different ranks, regardless of their military occupational specialty (MOS).
Implications of the Expanded Definition
The expanded definition of fraternization highlights the Army's commitment to maintaining a professional environment. By including relationships between soldiers of different ranks, the policy ensures that all soldiers are held to the same standards of professionalism, regardless of their MOS.
Update 2: Prohibited Relationships
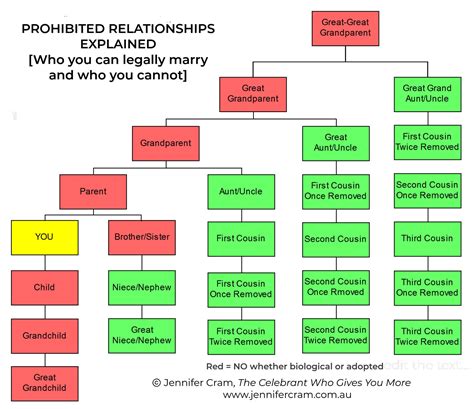
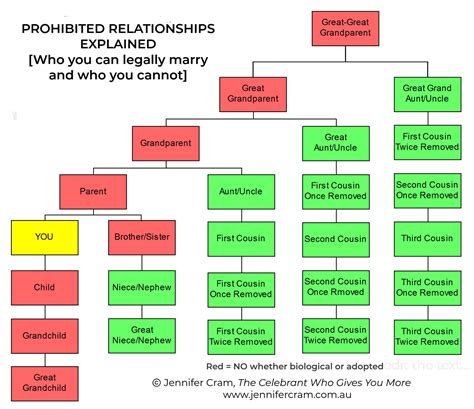
The updated policy also clarifies which relationships are prohibited. These include:
- Romantic relationships between soldiers of different ranks
- Business relationships between soldiers of different ranks
- Social relationships between soldiers of different ranks that could create a conflict of interest
Consequences of Prohibited Relationships
Soldiers who engage in prohibited relationships may face disciplinary action, including counseling, reprimand, or even court-martial. It is essential for soldiers to understand what constitutes a prohibited relationship and to avoid such relationships to maintain a professional environment.
Update 3: Reporting Requirements
The updated policy also outlines reporting requirements for soldiers who engage in relationships that may be prohibited. Soldiers are now required to report any relationships that could be perceived as fraternization to their chain of command.
Importance of Reporting
Reporting relationships that may be prohibited is essential for maintaining a professional environment. By reporting such relationships, soldiers can ensure that they are not compromising the chain of command or creating conflicts of interest.
Update 4: Commanders' Responsibilities

The updated policy also outlines the responsibilities of commanders in preventing and addressing fraternization. Commanders are now required to:
- Educate soldiers on the fraternization policy
- Monitor relationships between soldiers
- Take disciplinary action when necessary
Importance of Commanders' Roles
Commanders play a critical role in maintaining a professional environment. By educating soldiers on the fraternization policy, monitoring relationships, and taking disciplinary action when necessary, commanders can ensure that their units remain cohesive and effective.
Update 5: Consequences for Non-Compliance

Finally, the updated policy outlines the consequences for non-compliance. Soldiers who engage in prohibited relationships or fail to report such relationships may face disciplinary action, including counseling, reprimand, or even court-martial.
Importance of Consequences
Consequences for non-compliance are essential for maintaining a professional environment. By outlining the consequences for prohibited relationships, the Army can ensure that soldiers understand the importance of adhering to the fraternization policy.
Fraternization Policy Image Gallery








What is the purpose of the Army fraternization policy?
+The purpose of the Army fraternization policy is to prevent relationships that could compromise the chain of command, create favoritism, or undermine unit cohesion.
What types of relationships are prohibited under the Army fraternization policy?
+Prohibited relationships include romantic relationships between soldiers of different ranks, business relationships between soldiers of different ranks, and social relationships between soldiers of different ranks that could create a conflict of interest.
What are the consequences for non-compliance with the Army fraternization policy?
+Consequences for non-compliance may include counseling, reprimand, or even court-martial.
By understanding the five key updates to the Army fraternization policy, soldiers can ensure that they maintain a professional environment and avoid relationships that could compromise the chain of command or create conflicts of interest.
