Intro
Learn about the Army National Guard ranks and insignia in this comprehensive guide. Discover the different enlisted and officer ranks, from Private to General, and understand the symbols and emblems that represent each level of service. Find out how rank structures work and what it takes to advance through the ranks.
The Army National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces that consists of citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to serve in a variety of roles, from homeland security to overseas deployments. Understanding the Army National Guard ranks and insignia is essential for anyone interested in joining the organization or for those who want to learn more about the structure and hierarchy of the Guard.

The Army National Guard uses a similar ranking system to the regular Army, with some slight variations. The ranks are divided into three main categories: enlisted, warrant officer, and officer. Each rank has its own unique insignia, which is worn on the uniform to identify the soldier's rank and position.
Enlisted Ranks
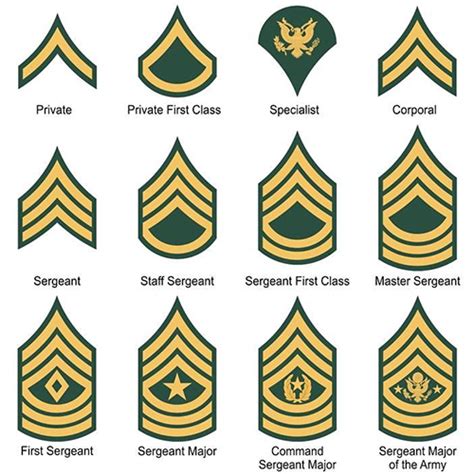
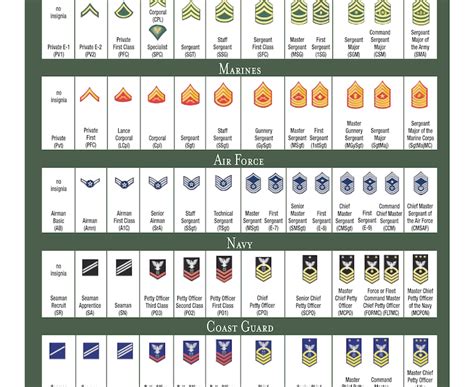
The enlisted ranks in the Army National Guard are the backbone of the organization, making up the majority of the Guard's personnel. These ranks range from Private (PVT) to Sergeant Major (SGM).
- Private (PVT): The lowest rank in the Army National Guard, privates are new recruits who are still in training.
- Private Second Class (PV2): A higher rank than private, PV2s have completed basic training and are assigned to a unit.
- Private First Class (PFC): PFCs are experienced soldiers who have demonstrated leadership potential and are often assigned to specialized roles.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): Specialists and corporals are technical experts in their field and often serve as team leaders.
- Sergeant (SGT): Sergeants are non-commissioned officers who serve as team leaders and are responsible for training and mentoring junior soldiers.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): Staff sergeants are senior non-commissioned officers who serve as squad leaders and are responsible for planning and executing missions.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): Sergeant first class is a senior enlisted rank that requires significant experience and leadership ability.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): Master sergeants and first sergeants are senior enlisted leaders who serve as senior advisors and mentors.
- Sergeant Major (SGM): The highest enlisted rank in the Army National Guard, sergeant majors serve as senior enlisted advisors to commanders and are responsible for leading and developing junior soldiers.

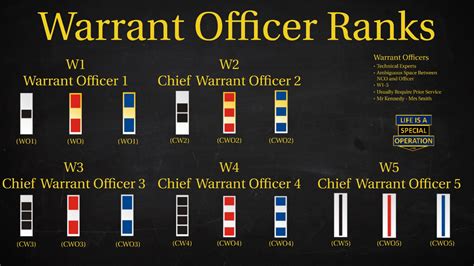
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers in the Army National Guard are technical experts in their field and serve as advisors and trainers. These ranks range from Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) to Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5).
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The lowest rank of warrant officer, WO1s are technical experts who serve as advisors and trainers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): CW2s are experienced warrant officers who serve as senior advisors and trainers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): CW3s are senior warrant officers who serve as senior advisors and trainers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): CW4s are experienced warrant officers who serve as senior advisors and trainers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The highest rank of warrant officer, CW5s serve as senior advisors and trainers.
Officer Ranks
The officer ranks in the Army National Guard are responsible for leading and commanding units. These ranks range from Second Lieutenant (2LT) to General (GEN).
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The lowest rank of officer, 2LTs are new officers who are still in training.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): 1LTs are experienced officers who serve as platoon leaders and are responsible for leading and training junior soldiers.
- Captain (CPT): Captains are company-level officers who serve as commanders and are responsible for leading and training junior officers.
- Major (MAJ): Majors are field-grade officers who serve as battalion-level officers and are responsible for leading and training junior officers.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): LTCs are senior field-grade officers who serve as battalion commanders and are responsible for leading and training junior officers.
- Colonel (COL): COLs are senior officers who serve as brigade commanders and are responsible for leading and training junior officers.
- Brigadier General (BG): BGs are one-star generals who serve as senior advisors and commanders.
- Major General (MG): MGs are two-star generals who serve as senior advisors and commanders.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): LTGs are three-star generals who serve as senior advisors and commanders.
- General (GEN): The highest rank in the Army National Guard, generals serve as senior advisors and commanders.
Insignia
Each rank in the Army National Guard has its own unique insignia, which is worn on the uniform to identify the soldier's rank and position. The insignia is worn on the sleeves, collar, or hat, depending on the rank and uniform.

In conclusion, understanding the Army National Guard ranks and insignia is essential for anyone interested in joining the organization or for those who want to learn more about the structure and hierarchy of the Guard. From enlisted to officer, each rank has its own unique insignia and responsibilities, and understanding these ranks can help individuals navigate the complex world of the Army National Guard.
Army National Guard Image Gallery








What is the highest rank in the Army National Guard?
+The highest rank in the Army National Guard is General (GEN).
What is the difference between enlisted and officer ranks?
+Enlisted ranks are the backbone of the Army National Guard, making up the majority of the Guard's personnel. Officer ranks are responsible for leading and commanding units.
What is the insignia for a Sergeant Major?
+The insignia for a Sergeant Major is three chevrons (V-shaped stripes) below two arcs.
