Intro
Discover the 5 key differences between Army Officer and Enlisted roles. Learn about the distinct responsibilities, education requirements, and career paths for both. Understand the variations in training, leadership roles, and promotions to make an informed decision about your military career.
The United States Army is a hierarchical organization with a clear distinction between its officer and enlisted personnel. While both play critical roles in the success of the Army, their responsibilities, training, and career paths are vastly different. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals considering a career in the Army, as well as for those who want to appreciate the unique contributions of each group.

Rank Structure and Responsibilities
The most obvious difference between Army officers and enlisted personnel is their rank structure and responsibilities. Officers are leaders who hold commissioned ranks, such as second lieutenant, captain, or colonel. They are responsible for making strategic decisions, leading units, and overseeing the execution of missions. Enlisted personnel, on the other hand, hold non-commissioned ranks, such as private, sergeant, or staff sergeant. They are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations of their unit.
Key Responsibilities of Officers
- Lead and manage units
- Make strategic decisions
- Oversee training and operations
- Develop and implement policies
- Represent the Army in official capacities
Key Responsibilities of Enlisted Personnel
- Carry out day-to-day tasks and operations
- Support unit leaders and officers
- Participate in training and professional development
- Maintain equipment and supplies
- Engage in combat and other military operations
Education and Training
Another significant difference between Army officers and enlisted personnel is their education and training. Officers typically require a bachelor's degree and complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or the United States Military Academy at West Point. Enlisted personnel, on the other hand, typically require a high school diploma or equivalent and complete Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training (AIT).

Officer Education and Training
- Bachelor's degree
- Officer Candidate School (OCS)
- United States Military Academy at West Point
- Branch-specific training (e.g., infantry, artillery, engineering)
Enlisted Education and Training
- High school diploma or equivalent
- Basic Combat Training (BCT)
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT)
- Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) training
Leadership and Career Advancement
Army officers and enlisted personnel have different leadership and career advancement opportunities. Officers are expected to lead and manage units, while enlisted personnel are expected to support and follow the leadership of their officers. Officers also have more opportunities for career advancement, as they can move up the ranks and take on more senior leadership positions.

Officer Leadership and Career Advancement
- Lead and manage units
- Take on senior leadership positions
- Participate in joint military operations
- Advise senior leaders and policymakers
- Pursue advanced education and training
Enlisted Leadership and Career Advancement
- Support unit leaders and officers
- Take on non-commissioned officer (NCO) roles
- Participate in professional development and training
- Advise junior enlisted personnel
- Pursue specialized skills and certifications
Work-Life Balance and Quality of Life
Army officers and enlisted personnel also have different work-life balance and quality of life. Officers often work long hours and are required to be on call 24/7. They may also be required to deploy to combat zones or other high-stress environments. Enlisted personnel also work long hours, but they may have more predictable schedules and fewer deployments.

Officer Work-Life Balance and Quality of Life
- Long hours and 24/7 on-call requirements
- Frequent deployments to combat zones or other high-stress environments
- High-stress leadership positions
- Opportunities for advanced education and training
- Access to senior leadership and policymakers
Enlisted Work-Life Balance and Quality of Life
- Long hours, but more predictable schedules
- Fewer deployments to combat zones or other high-stress environments
- Supportive unit leadership and camaraderie
- Opportunities for specialized skills and certifications
- Access to unit-level leadership and decision-making
Compensation and Benefits
Finally, Army officers and enlisted personnel have different compensation and benefits. Officers typically earn higher salaries and have access to more comprehensive benefits, such as education assistance and healthcare. Enlisted personnel also earn competitive salaries and have access to benefits, but they may not be as comprehensive as those offered to officers.
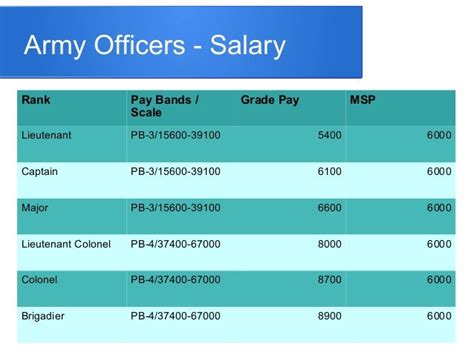
Officer Compensation and Benefits
- Higher salaries
- Comprehensive education assistance
- Access to healthcare and medical benefits
- Opportunities for advanced education and training
- Access to senior leadership and policymakers
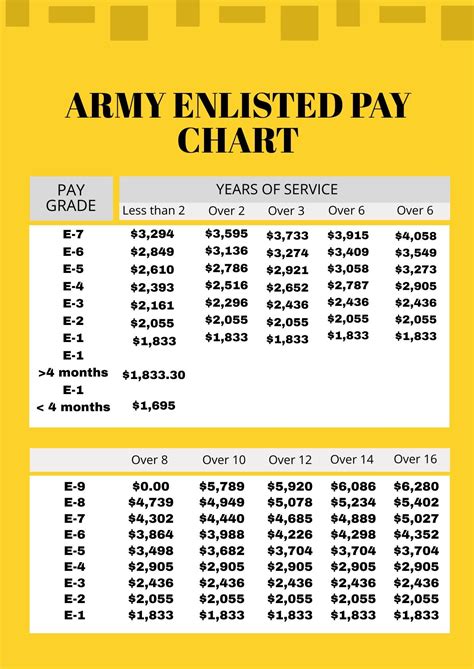
Enlisted Compensation and Benefits
- Competitive salaries
- Access to education assistance and training
- Healthcare and medical benefits
- Opportunities for specialized skills and certifications
- Access to unit-level leadership and decision-making
Army Officer vs Enlisted Image Gallery





What is the main difference between Army officers and enlisted personnel?
+The main difference between Army officers and enlisted personnel is their rank structure and responsibilities. Officers are leaders who hold commissioned ranks and are responsible for making strategic decisions, while enlisted personnel hold non-commissioned ranks and are responsible for carrying out day-to-day tasks and operations.
What kind of education and training do Army officers receive?
+Army officers typically require a bachelor's degree and complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or the United States Military Academy at West Point. They also receive branch-specific training and may pursue advanced education and training throughout their careers.
What kind of compensation and benefits do Army officers receive?
+Army officers typically earn higher salaries and have access to more comprehensive benefits, such as education assistance and healthcare. They also have opportunities for advanced education and training, and may receive special allowances and bonuses.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the key differences between Army officers and enlisted personnel. Whether you're considering a career in the Army or simply want to learn more about the military, we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.

