Intro
Discover the Army Officer Recruiting Office, your gateway to a life of service and leadership. Learn about the various career paths, requirements, and opportunities for commissioned officers in the US Army. From education benefits to career advancement, find your path to serving your country with honor and distinction.
The thrill of serving one's country, the camaraderie of brotherhood, and the pride of leadership – these are just a few aspects that draw individuals to the esteemed profession of an Army officer. However, the journey to becoming an officer is not without its challenges. For those who aspire to join the ranks of the bravest and most dedicated, the Army Officer Recruiting Office is here to guide you every step of the way.

Pursuing a career as an Army officer requires more than just physical prowess and mental toughness; it demands a deep understanding of oneself, one's values, and one's motivations. It is a calling that requires dedication, perseverance, and a strong sense of purpose. As you consider this noble profession, it is essential to ask yourself: what drives me to serve? What qualities do I possess that would make me an effective leader? And what kind of impact do I hope to make in the world?
Understanding the Role of an Army Officer
An Army officer is more than just a leader; they are a symbol of hope, a beacon of strength, and a guardian of freedom. As a commissioned officer, you will be responsible for leading, training, and mentoring soldiers in various capacities. You will be called upon to make critical decisions, often under intense pressure, and to inspire your troops to perform at their best. Whether you choose to specialize in a specific branch, such as infantry, engineering, or medicine, your role will be crucial to the success of the mission.

Key Responsibilities of an Army Officer
- Leading and training soldiers in various capacities
- Making critical decisions under pressure
- Developing and executing plans to achieve mission objectives
- Mentoring and guiding junior officers and enlisted personnel
- Collaborating with other branches and units to achieve strategic goals
Education and Training
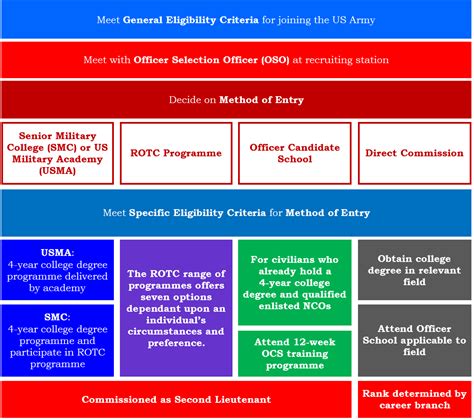
To become an Army officer, you will need to complete a rigorous education and training program. This typically involves attending a service academy, such as West Point, or completing a Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) program at a university. Additionally, you will need to complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) and receive specialized training in your chosen branch.

Types of Army Officer Education and Training Programs
- Service academies (e.g., West Point)
- Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) programs
- Officer Candidate School (OCS)
- Branch-specific training programs
Recruitment Process
The recruitment process for Army officers typically involves several steps:
- Meet the basic qualifications: age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness
- Take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test
- Complete a physical fitness test
- Apply for a commission through the Army's recruitment website or a recruiter
- Attend an interview with a recruiter or selection board
- Receive a commission as an Army officer
Tips for Success in the Recruitment Process
- Meet the basic qualifications and prepare for the ASVAB test
- Stay physically fit and prepare for the physical fitness test
- Research and understand the different branches and specialties
- Develop strong leadership and communication skills
- Be prepared to discuss your motivations and goals during the interview
Benefits and Rewards
As an Army officer, you will receive a comprehensive compensation package, including:
- Competitive salary and benefits
- Education assistance and tuition reimbursement
- Housing and food allowance
- Access to cutting-edge technology and training
- Opportunities for advancement and promotion

Personal and Professional Growth Opportunities
- Leadership development and mentorship
- Specialized training and certification
- Opportunities for advanced education and degrees
- Chance to serve in various capacities and locations
- Development of transferable skills and experience
Army Officer Image Gallery









What are the basic qualifications for becoming an Army officer?
+To become an Army officer, you must be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35, have a high school diploma or equivalent, and meet the physical fitness standards.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a non-commissioned officer?
+A commissioned officer is a leader who has completed a four-year college degree and has received a commission through a service academy, ROTC, or OCS. A non-commissioned officer is an enlisted soldier who has advanced through the ranks through experience and training.
What are the benefits of serving as an Army officer?
+As an Army officer, you will receive a comprehensive compensation package, including a competitive salary, education assistance, and access to cutting-edge technology and training. You will also have opportunities for advancement and promotion, as well as personal and professional growth.
