Intro
Unlock the latest Army salary facts for 2013. Discover the average military pay, salary ranges, and benefits for enlisted personnel and officers. Learn how ranks, time in service, and deployments impact Army salary. Get informed about special pays, allowances, and bonuses that boost take-home pay.
The Army is one of the most respected and esteemed institutions in the world, providing a sense of purpose and camaraderie to its members. Serving in the Army can be a rewarding and challenging experience, but it's essential to understand the compensation package that comes with it. In this article, we'll delve into the key Army salary facts for 2013, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of what to expect.
For many, the decision to join the Army is driven by a desire to serve their country, gain valuable skills, and be part of a proud tradition. However, it's crucial to consider the financial aspects of military service. The Army offers a competitive salary, benefits, and allowances that can significantly impact your lifestyle and long-term financial goals.
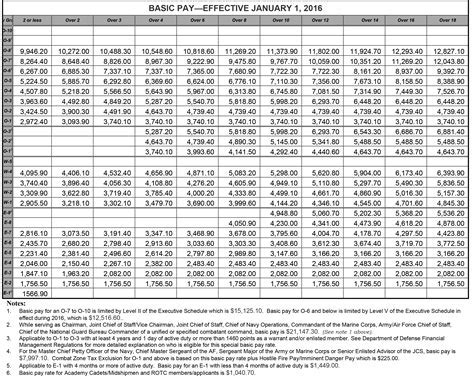
Understanding Army Ranks and Pay Grades
Before we dive into the specifics of Army salaries, it's essential to understand the rank structure and pay grades. The Army uses a pay grade system, which is based on the individual's rank and time in service. The pay grades range from E-1 (Private) to E-9 (Sergeant Major), with corresponding rank titles and responsibilities.
Army Salary Facts 2013
Here are five key Army salary facts for 2013:
1. Base Pay
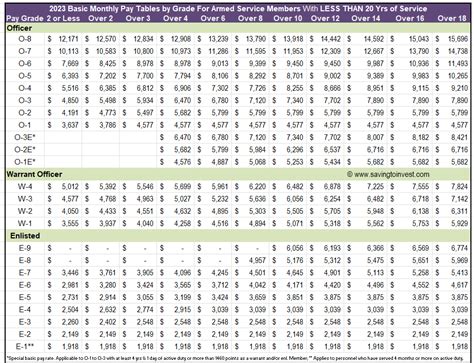
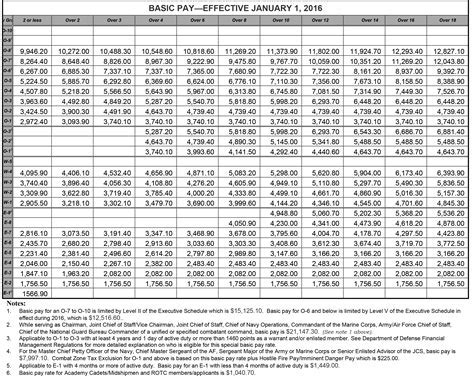
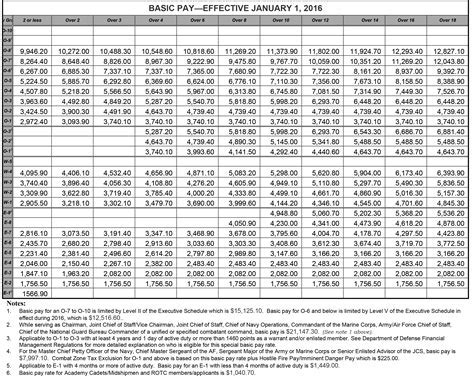
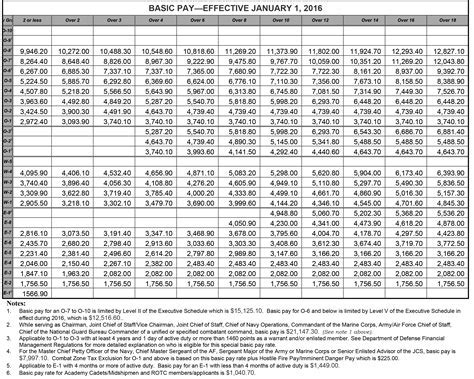
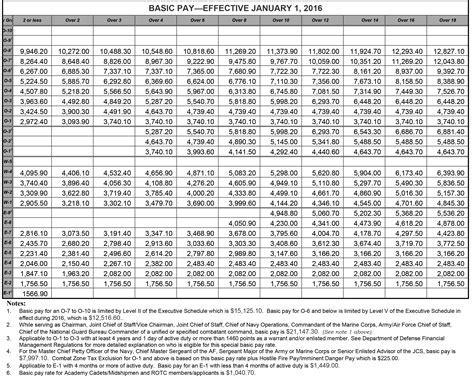
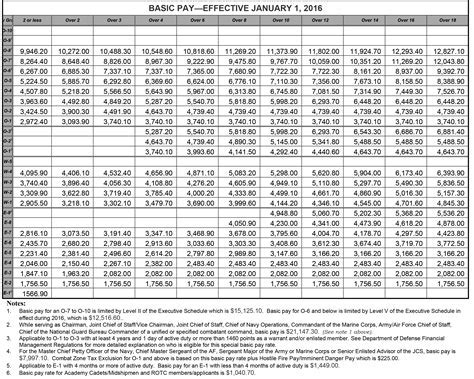
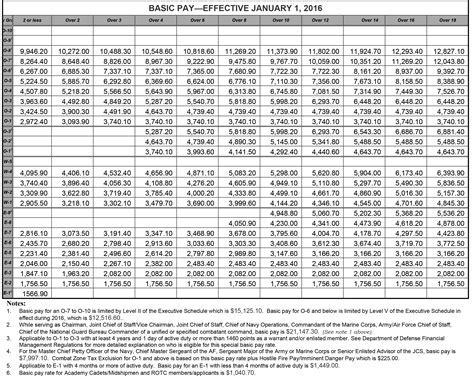
The base pay for Army personnel in 2013 ranged from $1,733.40 per month for a Private (E-1) to $7,869.90 per month for a Sergeant Major (E-9). The base pay is the primary component of an Army member's salary and is based on their pay grade and time in service.
2. Allowances
In addition to base pay, Army personnel receive various allowances to cover expenses such as housing, food, and clothing. The most common allowances include:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): This allowance helps cover the cost of housing, whether on or off base.
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): This allowance provides a stipend for food expenses.
- Clothing Allowance: This allowance helps cover the cost of uniforms and other clothing expenses.
3. Special Pays
The Army offers various special pays to compensate for unique circumstances, such as:
- Hazardous Duty Pay: This pay is awarded to personnel who perform hazardous duties, such as parachute duty or demolition duty.
- Diving Duty Pay: This pay is awarded to personnel who perform diving duties.
- Jump Pay: This pay is awarded to personnel who perform parachute duties.
4. Bonuses
The Army offers various bonuses to incentivize personnel to enlist, reenlist, or take on specific roles. Some of the most common bonuses include:
- Enlistment Bonus: This bonus is awarded to new recruits who enlist in the Army.
- Reenlistment Bonus: This bonus is awarded to personnel who reenlist in the Army.
- Special Duty Pay: This bonus is awarded to personnel who take on specific roles, such as recruiters or drill sergeants.
5. Tax-Free Benefits
The Army offers various tax-free benefits, including:
- Education Assistance: The Army offers education assistance, such as the GI Bill, to help personnel pay for college or vocational training.
- Healthcare: The Army provides comprehensive healthcare to personnel and their families.
- Shopping Privileges: Personnel have access to on-base shopping facilities, such as commissaries and exchanges, which offer discounted prices on groceries and other essentials.
How Army Salaries Compare to Civilian Salaries
When comparing Army salaries to civilian salaries, it's essential to consider the total compensation package, including benefits and allowances. While Army salaries may be lower than some civilian salaries, the benefits and allowances can make up for the difference.
For example, a Private (E-1) in the Army may earn a base salary of $1,733.40 per month, but with allowances and benefits, their total compensation package could be significantly higher.
Army Salary vs. Civilian Salary: A Comparison
| Rank | Army Salary | Civilian Salary |
|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | $1,733.40 | $2,000 - $3,000 |
| Corporal (E-4) | $2,343.90 | $3,500 - $5,000 |
| Sergeant (E-5) | $2,734.90 | $4,500 - $6,500 |
| Staff Sergeant (E-6) | $3,315.90 | $6,000 - $9,000 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the Army salary facts for 2013 is crucial for anyone considering a career in the military. While the base pay may be lower than some civilian salaries, the benefits and allowances can make up for the difference. It's essential to consider the total compensation package when evaluating Army salaries.
If you're considering joining the Army, we encourage you to research and understand the compensation package, including base pay, allowances, special pays, bonuses, and tax-free benefits.
Army Salary Facts 2013 Image Gallery
What is the average salary for an Army soldier?
+The average salary for an Army soldier varies based on rank and time in service. However, the average annual salary for an Army soldier is around $40,000.
What benefits do Army soldiers receive?
+Army soldiers receive a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare, shopping privileges, and tax-free allowances.
How do Army salaries compare to civilian salaries?
+Army salaries may be lower than some civilian salaries, but the benefits and allowances can make up for the difference. It's essential to consider the total compensation package when evaluating Army salaries.
