Intro
Discover the intricacies of the Soviet Unions administrative divisions with our 5 fascinating facts about Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics (ASSRs). Learn how ASSRs functioned within the Soviet federal system, their unique characteristics, and the implications of autonomy on Soviet politics, culture, and regional identity.
Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics (ASSRs) played a significant role in the Soviet Union's governance structure. Despite their dissolution following the Soviet Union's collapse, understanding the ASSRs is crucial for grasping the complexities of the Soviet state. Here are five key facts about Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics.
The Concept of ASSRs Was First Introduced in the 1920s
The concept of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics was first introduced in the 1920s as part of the Soviet Union's policy of korenizatsiya, or "indigenization." This policy aimed to promote the cultural and linguistic development of the Soviet Union's diverse ethnic groups by creating autonomous regions that would allow them to govern themselves.
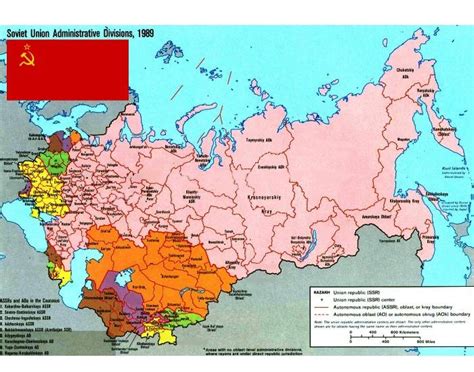
There Were 20 ASSRs in the Soviet Union at Its Peak

At its peak, the Soviet Union had 20 Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics, each with its own government and a degree of autonomy. These ASSRs were established to recognize the distinct cultural and linguistic identities of the Soviet Union's ethnic groups.
ASSRs Had a Degree of Autonomy, But Were Still Subject to Soviet Authority

While ASSRs had a degree of autonomy, they were still subject to Soviet authority. The Soviet government maintained control over key areas such as defense, foreign policy, and economic planning. ASSRs were also required to adhere to Soviet laws and policies.
ASSRs Were Established to Promote Ethnic Equality and Cultural Development

One of the primary goals of establishing ASSRs was to promote ethnic equality and cultural development. By recognizing the distinct cultural and linguistic identities of the Soviet Union's ethnic groups, the Soviet government aimed to create a more inclusive and equitable society.
ASSRs Were Abolished Following the Collapse of the Soviet Union

Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics were abolished. Many of the ASSRs were transformed into federal subjects of the Russian Federation, while others became independent countries.
Characteristics of ASSRs
Key Features of ASSRs
- Autonomous governance structure
- Degree of autonomy, but subject to Soviet authority
- Established to promote ethnic equality and cultural development
- Recognized distinct cultural and linguistic identities of ethnic groups
- Had their own governments and a degree of self-governance
Types of ASSRs
Examples of ASSRs
- Bashkir ASSR
- Buryat ASSR
- Chechen-Ingush ASSR
- Dagestan ASSR
- Kabardino-Balkar ASSR
Gallery of ASSRs
ASSRs Image Gallery



FAQs
What were the main goals of establishing ASSRs?
+The main goals of establishing ASSRs were to promote ethnic equality and cultural development, recognize the distinct cultural and linguistic identities of the Soviet Union's ethnic groups, and create a more inclusive and equitable society.
How many ASSRs were there in the Soviet Union at its peak?
+At its peak, the Soviet Union had 20 Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics.
What happened to the ASSRs following the collapse of the Soviet Union?
+Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics were abolished. Many of the ASSRs were transformed into federal subjects of the Russian Federation, while others became independent countries.
In conclusion, Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics played a significant role in the Soviet Union's governance structure. By understanding the concept of ASSRs, their characteristics, and their significance in the Soviet Union's history, we can gain a deeper insight into the complexities of the Soviet state. If you have any further questions or would like to share your thoughts on ASSRs, please feel free to comment below.
