Intro
Discover how Army salaries compare to civilian pay in our in-depth analysis. Learn the differences in compensation, benefits, and career growth opportunities between military and civilian careers. From enlistment bonuses to veterans preference, we explore 5 key ways Army pay measures up to its civilian counterpart.
The idea of joining the army is often associated with a sense of patriotism, adventure, and service to one's country. However, for many potential recruits, the decision to enlist is also influenced by the promise of a steady income and benefits. But how do army salaries compare to civilian pay? In this article, we'll delve into the details of army compensation and explore five key ways it stacks up against civilian pay.
Understanding Army Salaries
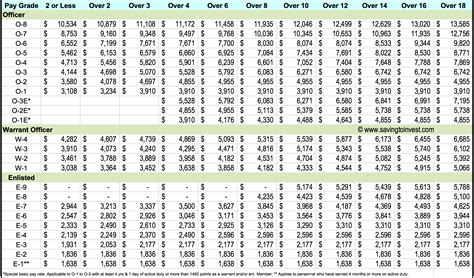
Army salaries are based on a combination of factors, including rank, time in service, and job specialty. The military uses a pay grade system, which consists of nine enlisted pay grades (E-1 to E-9) and eleven officer pay grades (O-1 to O-10). Within each pay grade, salaries can vary depending on the individual's level of experience and qualifications.
5 Ways Army Salaries Compare to Civilian Pay
1. Base Pay vs. Civilian Salaries
When comparing army salaries to civilian pay, it's essential to consider the base pay for each group. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for all occupations in the United States was $41,693 in May 2020. In contrast, the base pay for an army private (E-1) with less than two years of service is $1,733.10 per month, or approximately $20,797 per year.
However, as army personnel advance in rank and gain experience, their salaries can increase significantly. For example, an army sergeant (E-5) with four years of service can earn a base pay of $2,774.90 per month, or approximately $33,299 per year.
2. Benefits and Allowances
One of the most significant advantages of army salaries is the comprehensive benefits package, which includes:
- Free or low-cost medical, dental, and vision care
- Access to on-base shopping and recreational facilities
- Subsidized housing or a housing allowance
- Food allowance or access to on-base dining facilities
- Education assistance and tuition reimbursement
- Retirement benefits, including a pension and Thrift Savings Plan (TSP) matching contributions
When these benefits are factored into the overall compensation package, army salaries can be quite competitive with civilian pay.
3. Job Security and Stability
Another key advantage of army salaries is the high level of job security and stability. Once enlisted, army personnel can expect to have a steady income and benefits for the duration of their service contract, which can range from three to six years or more. In contrast, many civilian jobs are subject to layoffs, downsizing, and economic uncertainty.
4. Opportunities for Advancement
The army offers a clear path for advancement and career progression, with opportunities for promotion to higher ranks and specialized roles. As army personnel gain experience and develop new skills, they can move up the ranks and increase their earning potential. In contrast, civilian career advancement can be more uncertain and may require additional education or training.
5. Tax-Free Allowances and Bonuses
Army personnel may be eligible for various tax-free allowances and bonuses, including:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH)
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS)
- Combat Zone Tax Exclusion (CZTE)
- Hazardous Duty Pay (HDP)
- Special Duty Pay (SDP)
These allowances and bonuses can significantly increase an army member's take-home pay, making their overall compensation package more competitive with civilian salaries.
Army Salaries Image Gallery
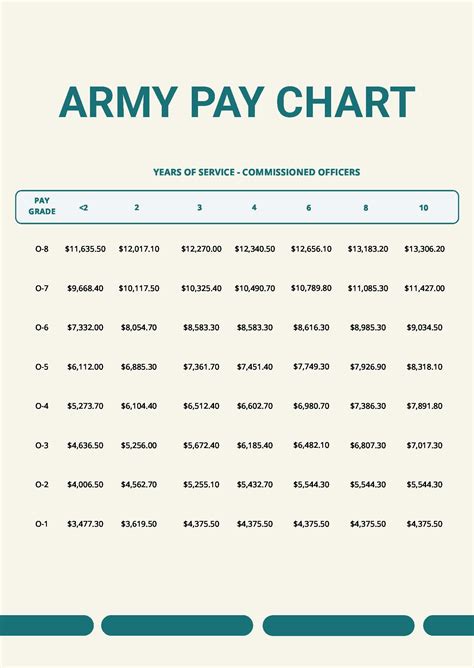






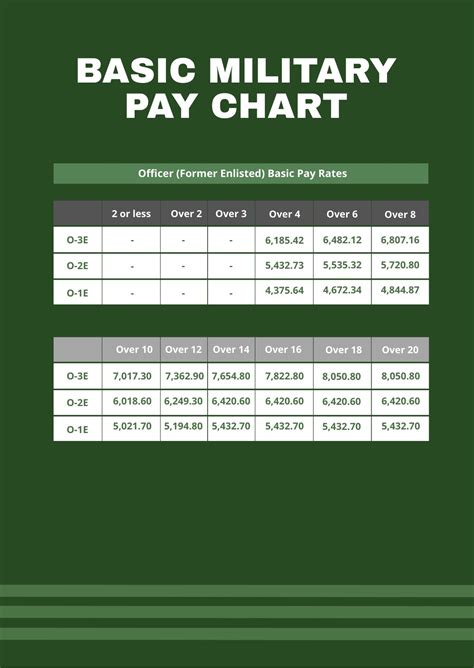
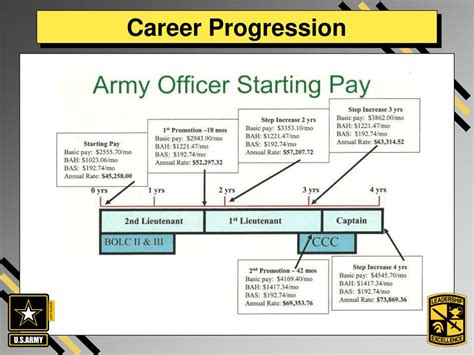

What is the average salary for an army soldier?
+The average salary for an army soldier varies depending on rank and time in service. According to the U.S. Army, the average annual salary for an army private (E-1) is approximately $20,797, while an army sergeant (E-5) can earn up to $33,299 per year.
What benefits do army personnel receive?
+Army personnel receive a comprehensive benefits package, including free or low-cost medical, dental, and vision care, access to on-base shopping and recreational facilities, subsidized housing or a housing allowance, food allowance or access to on-base dining facilities, education assistance, and retirement benefits.
How does army pay compare to civilian pay?
+Army pay can be competitive with civilian pay, especially when considering the comprehensive benefits package. However, base pay for lower-ranking army personnel may be lower than civilian salaries. As army personnel advance in rank and gain experience, their salaries can increase significantly.
What is the highest-paying job in the army?
+The highest-paying job in the army is typically held by high-ranking officers, such as generals and colonels. These positions can earn upwards of $200,000 per year, depending on experience and qualifications.
How does army pay affect taxes?
+Army pay can affect taxes in various ways. Some allowances and bonuses are tax-free, while others may be subject to taxation. Additionally, army personnel may be eligible for tax credits and deductions, such as the Combat Zone Tax Exclusion (CZTE).
In conclusion, army salaries offer a unique combination of benefits, allowances, and job security that can make them competitive with civilian pay. While base pay for lower-ranking army personnel may be lower than civilian salaries, the comprehensive benefits package and opportunities for advancement can make up for this difference. As army personnel advance in rank and gain experience, their salaries can increase significantly, making their overall compensation package more attractive.
