Intro
Explore the crucial distinctions between ballistic and cruise missiles in this in-depth analysis. Discover the 5 key differences that set these two types of missiles apart, including propulsion systems, range, accuracy, and payload capacity. Uncover the advantages and limitations of each, from nuclear deterrence to modern warfare tactics.
The world of modern warfare is complex and multifaceted, with various types of missiles playing a crucial role in military strategy. Two of the most commonly discussed types of missiles are ballistic missiles and cruise missiles. While both are designed to destroy targets, they differ significantly in terms of their design, functionality, and purpose. In this article, we will delve into the world of missiles and explore the 5 key differences between ballistic and cruise missiles.

1. Trajectory and Flight Path
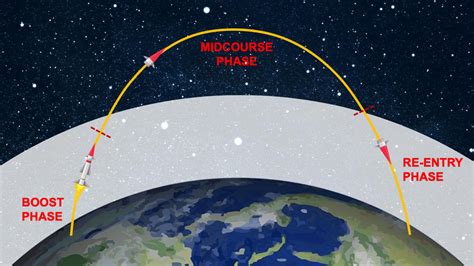
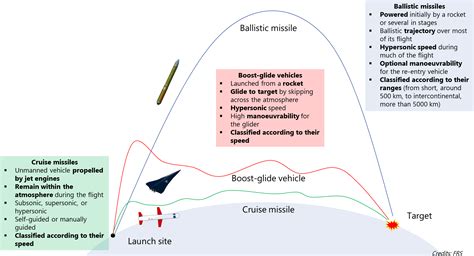
One of the primary differences between ballistic and cruise missiles lies in their trajectory and flight path. Ballistic missiles follow a predictable, parabolic trajectory, which is influenced by gravity and air resistance. Once launched, a ballistic missile will travel along a curved path, eventually returning to earth and striking its target.
On the other hand, cruise missiles fly at low altitudes, often using terrain-following radar to navigate and avoid obstacles. Their flight path is more flexible and can be adjusted mid-flight to ensure accurate targeting.

2. Propulsion and Speed
Ballistic missiles are typically powered by rocket engines, which provide a high-speed boost during the initial stages of flight. This allows ballistic missiles to reach speeds of up to Mach 20 (around 12,000 mph) or more. However, once the rocket engine is extinguished, the missile will begin to decelerate and eventually re-enter the earth's atmosphere.
In contrast, cruise missiles are powered by jet engines or turbofans, which provide a more sustained and efficient source of propulsion. While cruise missiles are generally slower than ballistic missiles, with speeds ranging from Mach 0.5 to Mach 3 (around 600-2,000 mph), they can maintain their speed over longer distances and navigate through dense air defenses.

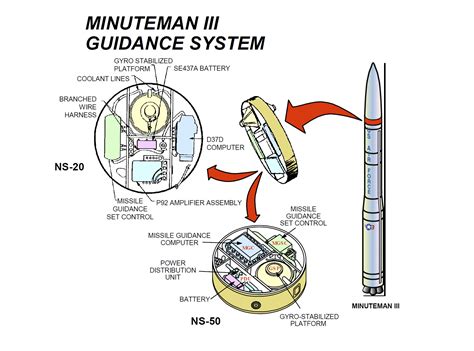
3. Guidance Systems and Accuracy
Ballistic missiles often rely on inertial guidance systems, which use a combination of gyroscopes, accelerometers, and computers to calculate the missile's position and velocity. While these systems can provide reasonable accuracy, they are limited by the missile's speed and altitude.
Cruise missiles, on the other hand, employ more sophisticated guidance systems, including GPS, terrain-following radar, and infrared seekers. These systems enable cruise missiles to navigate through complex terrain and engage targets with high accuracy.
4. Warhead and Payload
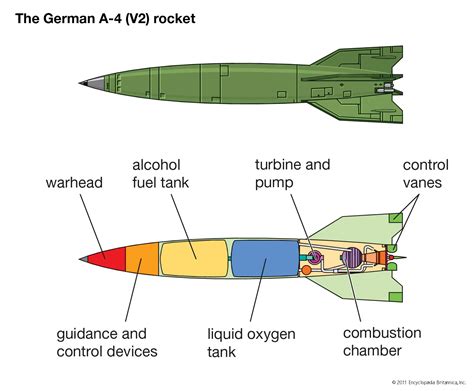
Ballistic missiles are often designed to carry large warheads, including nuclear, chemical, or biological payloads. These warheads are typically designed to inflict maximum damage on a target, with yields ranging from a few kilotons to several megatons.
Cruise missiles, while capable of carrying smaller warheads, are often designed to deliver precision-guided munitions (PGMs) or submunitions. These payloads are optimized for accuracy and effectiveness against specific targets, such as armored vehicles, bunkers, or buildings.

5. Countermeasures and Defense
Due to their high speed and altitude, ballistic missiles are challenging to intercept and defend against. However, various countermeasures have been developed, including ballistic missile defense (BMD) systems, which use radar, sensors, and interceptor missiles to detect and destroy incoming threats.
Cruise missiles, on the other hand, are more susceptible to air defenses, such as surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) and anti-aircraft artillery (AAA). However, their low-flying profile and ability to navigate through terrain make them more difficult to detect and engage.

Ballistic and Cruise Missile Image Gallery







What is the primary difference between ballistic and cruise missiles?
+The primary difference between ballistic and cruise missiles lies in their trajectory and flight path. Ballistic missiles follow a predictable, parabolic trajectory, while cruise missiles fly at low altitudes and use terrain-following radar to navigate.
What type of propulsion do ballistic missiles use?
+Ballistic missiles are typically powered by rocket engines, which provide a high-speed boost during the initial stages of flight.
What is the advantage of cruise missiles over ballistic missiles?
+Cruise missiles have the advantage of being more accurate and flexible, with the ability to navigate through terrain and engage targets with precision-guided munitions.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive understanding of the differences between ballistic and cruise missiles. These two types of missiles play a crucial role in modern warfare, and their design, functionality, and purpose are shaped by various factors, including trajectory, propulsion, guidance systems, warheads, and countermeasures. By understanding these differences, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and nuance of modern military strategy.
Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and don't forget to like and share this article with others.
