Intro
Discover the 7 essential parts of a house base, crucial for a sturdy and secure foundation. Learn about footings, walls, slabs, piers, beams, joists, and sill plates, and how they work together to support your home. Ensure a solid base for your dream house with our comprehensive guide on house foundation essentials.
A house base, also known as a foundation, is the structural element of a building that transfers loads from the walls and floors to the ground. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability, safety, and durability of a house. In this article, we will explore the 7 essential parts of a house base, their functions, and why they are vital for a strong and reliable foundation.
The Importance of a Strong House Base
A house base is more than just a platform that supports the weight of a building. It is a complex system that must withstand various external forces, such as soil pressure, water, and weather conditions. A weak or poorly designed foundation can lead to structural damage, safety hazards, and costly repairs. On the other hand, a well-designed and constructed house base can ensure the longevity and value of a property.

1. Footings
Footings are the lowest part of a house base, typically made of concrete, that transfer the weight of the building to the ground. They are usually wider than the walls they support and are designed to distribute the load evenly. Footings can be shallow or deep, depending on the soil conditions and the weight of the building.
Types of Footings
- Shallow footings: suitable for buildings with a low weight-bearing capacity
- Deep footings: suitable for buildings with a high weight-bearing capacity or unstable soil conditions
2. Walls
Walls are the vertical elements of a house base that support the weight of the building and transfer it to the footings. They can be made of concrete, masonry, or insulated concrete forms (ICFs). Walls must be strong, durable, and able to resist soil pressure and water infiltration.
Types of Walls
- Concrete walls: suitable for buildings with a high weight-bearing capacity
- Masonry walls: suitable for buildings with a low to moderate weight-bearing capacity
- ICF walls: suitable for buildings with high energy efficiency requirements

3. Slabs
Slabs are the horizontal elements of a house base that support the weight of the building and transfer it to the walls. They can be made of concrete, typically 4-6 inches thick, and are designed to provide a smooth and level surface for flooring.
Types of Slabs
- Monolithic slabs: suitable for buildings with a low to moderate weight-bearing capacity
- T-beam slabs: suitable for buildings with a high weight-bearing capacity
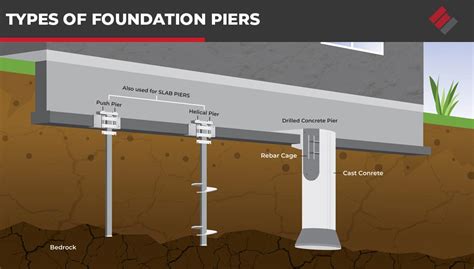
4. Piers
Piers are the vertical elements of a house base that support the weight of the building and transfer it to the footings. They are typically made of concrete and are used to support heavy loads, such as columns or walls.
Types of Piers
- Isolated piers: suitable for buildings with a low to moderate weight-bearing capacity
- Combined piers: suitable for buildings with a high weight-bearing capacity
5. Tie Beams
Tie beams are the horizontal elements of a house base that connect the walls and piers, providing additional support and stability to the foundation. They are typically made of concrete and are used to resist soil pressure and water infiltration.
Types of Tie Beams
- Solid tie beams: suitable for buildings with a low to moderate weight-bearing capacity
- Hollow tie beams: suitable for buildings with a high weight-bearing capacity
6. Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolts are the metal fasteners that connect the walls and piers to the footings, providing additional support and stability to the foundation. They are typically made of steel and are used to resist soil pressure and water infiltration.
Types of Anchor Bolts
- J-bolts: suitable for buildings with a low to moderate weight-bearing capacity
- L-bolts: suitable for buildings with a high weight-bearing capacity

7. Waterproofing
Waterproofing is the process of preventing water from entering the foundation of a building, which can cause damage and structural issues. It is typically achieved through the use of waterproofing membranes, such as bitumen or polyethylene, which are applied to the walls and footings.
Types of Waterproofing
- Positive-side waterproofing: suitable for buildings with a low to moderate water table
- Negative-side waterproofing: suitable for buildings with a high water table
In conclusion, a house base is a complex system that requires careful design and construction to ensure the stability, safety, and durability of a building. The 7 essential parts of a house base, including footings, walls, slabs, piers, tie beams, anchor bolts, and waterproofing, work together to provide a strong and reliable foundation for a building.
Gallery of House Base Foundations
House Base Foundations Image Gallery









FAQs
What is the purpose of a house base?
+The purpose of a house base is to transfer the weight of a building to the ground and provide a stable and level surface for the walls and floors.
What are the different types of house bases?
+There are several types of house bases, including slab-on-grade, crawl space, and full basement foundations.
How do I maintain my house base?
+To maintain your house base, ensure proper drainage, inspect for cracks and damage, and perform regular repairs and maintenance.
