Intro
Explore the 6 branches of the US Army, including the Active Army, Army Reserve, Army National Guard, Army Civilian Corps, and more. Discover their roles, responsibilities, and differences. Learn about the unique missions and contributions of each branch, and find out how they work together to defend the nation.
The United States Army is one of the most respected and formidable military forces in the world. With a rich history dating back to 1775, the Army has evolved over the centuries to become a technologically advanced and highly trained fighting force. The Army is divided into six branches, each with its own unique mission, responsibilities, and specialized skills. In this article, we will explore the six branches of the US Army, their roles, and the requirements for joining each branch.
Overview of the US Army
Before diving into the six branches, it's essential to understand the Army's overall mission and structure. The US Army is a branch of the US Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. The Army's primary mission is to protect the United States and its interests by fighting and winning wars, as well as promoting peace and stability around the world. The Army is led by the Secretary of the Army and the Chief of Staff of the Army, who oversee the various branches and their operations.
1. Infantry Branch
The Infantry Branch is the largest branch of the US Army, with over 200,000 active-duty soldiers. The Infantry is responsible for conducting land-based combat operations, including urban warfare, jungle warfare, and desert warfare. Infantry soldiers are trained to engage enemy forces using a variety of tactics, including patrols, ambushes, and raids.
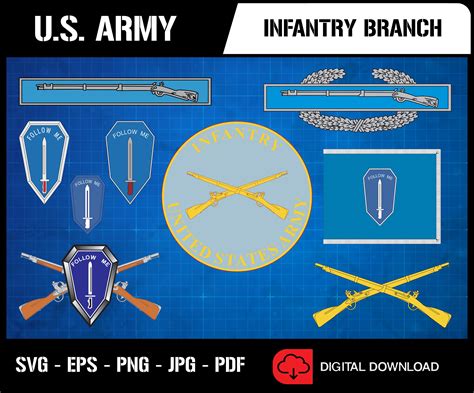
To join the Infantry Branch, soldiers must complete Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training (AIT). Infantry soldiers can specialize in various Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), including rifleman, machine gunner, and mortarman.
2. Armor Branch
The Armor Branch is responsible for operating and maintaining armored vehicles, including tanks and armored personnel carriers. Armor soldiers are trained to conduct armored warfare, including reconnaissance, security, and combat operations.

To join the Armor Branch, soldiers must complete BCT and AIT. Armor soldiers can specialize in various MOS, including tank commander, gunner, and loader.
3. Artillery Branch
The Artillery Branch is responsible for conducting indirect fire operations using artillery systems, including howitzers, mortars, and rockets. Artillery soldiers are trained to provide supporting fire to infantry and armored units.

To join the Artillery Branch, soldiers must complete BCT and AIT. Artillery soldiers can specialize in various MOS, including cannon crewmember, fire direction specialist, and rocket artillery specialist.
4. Aviation Branch
The Aviation Branch is responsible for operating and maintaining aircraft, including helicopters, airplanes, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Aviation soldiers are trained to conduct air reconnaissance, transportation, and medical evacuation operations.

To join the Aviation Branch, soldiers must complete BCT and AIT. Aviation soldiers can specialize in various MOS, including helicopter pilot, fixed-wing pilot, and UAV operator.
5. Signal Corps
The Signal Corps is responsible for establishing and maintaining communication systems, including radios, satellites, and networks. Signal soldiers are trained to provide communication support to Army units.

To join the Signal Corps, soldiers must complete BCT and AIT. Signal soldiers can specialize in various MOS, including radio operator, satellite communication specialist, and network administrator.
6. Engineer Branch
The Engineer Branch is responsible for conducting engineering operations, including construction, demolition, and reconnaissance. Engineer soldiers are trained to provide engineering support to Army units.

To join the Engineer Branch, soldiers must complete BCT and AIT. Engineer soldiers can specialize in various MOS, including combat engineer, construction engineer, and engineer surveyor.
Gallery of US Army Branches
US Army Branches Image Gallery





Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary mission of the US Army?
+The primary mission of the US Army is to protect the United States and its interests by fighting and winning wars, as well as promoting peace and stability around the world.
What are the six branches of the US Army?
+The six branches of the US Army are: Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Aviation, Signal Corps, and Engineer.
What is the role of the Infantry Branch?
+The Infantry Branch is responsible for conducting land-based combat operations, including urban warfare, jungle warfare, and desert warfare.
In conclusion, the US Army is a highly trained and technologically advanced fighting force, with six branches that specialize in various aspects of land-based military operations. Each branch has its own unique mission, responsibilities, and specialized skills, and soldiers can choose to join the branch that best suits their interests and skills. Whether you're interested in combat, aviation, or engineering, the US Army has a branch that can provide you with a challenging and rewarding career.
