Intro
Discover the rank and responsibilities of a Colonel in the Air Force. Learn about the insignia, pay grade, and requirements for this senior leadership position. Understand the Colonels role in commanding units, making strategic decisions, and leading airmen. Explore the career path to becoming a Colonel and the significance of this rank in the US Air Force hierarchy.
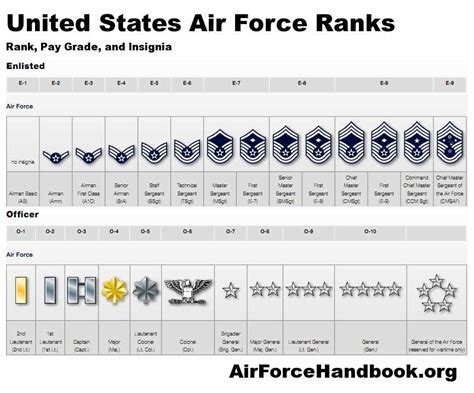
The rank of Colonel is a prestigious and highly respected position in the United States Air Force. It is the third-highest rank in the officer ranks, below the ranks of Brigadier General and Major General. A Colonel is a senior field-grade officer who has achieved a high level of leadership and expertise in their field.
The role of a Colonel in the Air Force is multifaceted and demanding. They are responsible for leading and managing large teams of personnel, making strategic decisions, and overseeing the planning and execution of complex operations. Colonels are also expected to be experts in their field, with a deep understanding of the Air Force's mission, vision, and values.

To become a Colonel in the Air Force, an officer must have a minimum of 20-25 years of service, including 10-15 years as a commissioned officer. They must also have completed advanced training and education, including a Master's degree or higher. Colonels are selected for promotion through a competitive process, which evaluates their leadership abilities, technical expertise, and potential for future success.
The rank of Colonel is denoted by the insignia of an eagle, which is worn on the officer's uniform. Colonels are addressed as "Colonel" or "Col," and they are entitled to a number of privileges and benefits, including a higher salary, additional allowances, and increased responsibility.
In terms of responsibilities, Colonels in the Air Force can serve in a variety of roles, including:
- Wing Commander: A Colonel may serve as the commander of a wing, which is a large organization that includes multiple squadrons and support units.
- Group Commander: A Colonel may serve as the commander of a group, which is a smaller organization that includes multiple squadrons.
- Squadron Commander: A Colonel may serve as the commander of a squadron, which is a unit that includes multiple flights and sections.
- Staff Officer: A Colonel may serve as a staff officer at the wing, group, or squadron level, where they provide advice and guidance to senior leaders.
- Professor or Instructor: A Colonel may serve as a professor or instructor at the Air Force Academy or other educational institutions.
Overall, the rank of Colonel is a significant achievement in the Air Force, and it requires a high level of leadership, technical expertise, and dedication to the service.
History of the Rank of Colonel in the Air Force
The rank of Colonel has a long and distinguished history in the United States military. The rank was first established in 1775, during the American Revolution, when George Washington was appointed as the Colonel of the Virginia Regiment. Over time, the rank of Colonel has evolved and been modified, but its core responsibilities and values have remained the same.
In the Air Force, the rank of Colonel was established in 1947, when the Air Force was separated from the Army and became a separate branch of the military. Since then, the rank of Colonel has become an integral part of the Air Force's leadership structure, with Colonels serving in key roles at the wing, group, and squadron levels.

Throughout its history, the rank of Colonel has been associated with a number of notable figures, including military leaders, politicians, and celebrities. Some notable examples of Colonels in the Air Force include:
- General Curtis LeMay, who served as a Colonel during World War II and later became the Chief of Staff of the Air Force.
- Colonel Chuck Yeager, who was the first person to break the sound barrier and served as a Colonel in the Air Force.
- Colonel John Glenn, who was the first American to orbit the Earth and served as a Colonel in the Air Force.
Responsibilities of a Colonel in the Air Force
As a senior field-grade officer, a Colonel in the Air Force has a wide range of responsibilities, including:
- Leadership: A Colonel is responsible for leading and managing large teams of personnel, including officers, enlisted personnel, and civilians.
- Strategic Planning: A Colonel is responsible for developing and implementing strategic plans, which involve setting goals and objectives, allocating resources, and evaluating progress.
- Operations: A Colonel is responsible for overseeing the planning and execution of complex operations, including combat, humanitarian, and disaster relief missions.
- Training and Education: A Colonel is responsible for providing training and education to personnel, including officers, enlisted personnel, and civilians.
- Logistics: A Colonel is responsible for managing logistics, including supply chain management, maintenance, and transportation.

In addition to these responsibilities, a Colonel in the Air Force is also expected to:
- Be an expert in their field, with a deep understanding of the Air Force's mission, vision, and values.
- Be a leader and a role model, with a strong sense of integrity, ethics, and professionalism.
- Be able to communicate effectively, both verbally and in writing.
- Be able to make strategic decisions, which involve analyzing complex information, evaluating options, and selecting a course of action.
- Be able to work effectively with others, including officers, enlisted personnel, and civilians.
Requirements for Becoming a Colonel in the Air Force
To become a Colonel in the Air Force, an officer must meet certain requirements, including:
- Education: A Colonel must have a Bachelor's degree or higher, with a Master's degree or higher preferred.
- Experience: A Colonel must have a minimum of 20-25 years of service, including 10-15 years as a commissioned officer.
- Training: A Colonel must have completed advanced training and education, including the Air War College, the Air Command and Staff College, and the Squadron Officer School.
- Performance: A Colonel must have a strong performance record, with a history of leadership, technical expertise, and achievement.
- Selection: A Colonel must be selected for promotion through a competitive process, which evaluates their leadership abilities, technical expertise, and potential for future success.
In addition to these requirements, a Colonel in the Air Force must also be willing to serve in a variety of roles, including leadership, staff, and operational positions.
Gallery of Colonel Insignia
Colonel Insignia Gallery






Frequently Asked Questions
What is the rank of Colonel in the Air Force?
+The rank of Colonel is the third-highest rank in the officer ranks, below the ranks of Brigadier General and Major General.
What are the responsibilities of a Colonel in the Air Force?
+A Colonel is responsible for leading and managing large teams of personnel, making strategic decisions, and overseeing the planning and execution of complex operations.
How do I become a Colonel in the Air Force?
+To become a Colonel in the Air Force, an officer must meet certain requirements, including education, experience, training, performance, and selection through a competitive process.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the rank of Colonel in the Air Force. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences as a Colonel, please leave a comment below.

