Intro
Discover the crucial role of Army Medics in combat situations and their relationship with firearms. Learn about their training, responsibilities, and the weapons they use to protect themselves and others. Get the inside scoop on the top 5 facts about Army Medics and firearms, including their history, tactics, and protocols.
The role of army medics is often misunderstood, with many people assuming that their sole responsibility is to provide medical care to wounded soldiers. While this is a critical aspect of their job, army medics are also trained to use firearms in combat situations. Here are five facts about army medics and firearms that highlight the complexity and importance of their role.
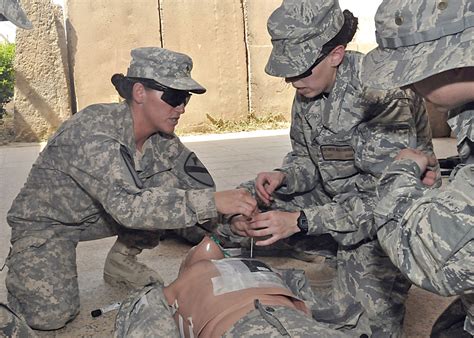
Firstly, army medics are trained to use a variety of firearms, including pistols, rifles, and machine guns. This training is designed to ensure that they can protect themselves and their patients in combat situations. While their primary role is to provide medical care, they must also be able to defend themselves and others when necessary.
The Role of Army Medics in Combat
Army medics play a critical role in combat situations, providing medical care to wounded soldiers and helping to stabilize them for evacuation. However, they are also expected to be able to defend themselves and their patients, which requires them to be proficient in the use of firearms.

In combat situations, army medics are often exposed to extreme danger, and their ability to use firearms effectively can be the difference between life and death. Despite this, they are still expected to provide high-quality medical care, even in the most challenging environments.
Firearms Training for Army Medics
Army medics receive extensive training in the use of firearms, which includes both classroom instruction and hands-on practice. This training is designed to ensure that they can use their firearms safely and effectively, even in high-stress combat situations.
Some of the specific skills that army medics learn during firearms training include:
- How to handle and maintain their firearms
- How to load and unload their firearms
- How to aim and fire their firearms accurately
- How to use cover and concealment to protect themselves and their patients
- How to engage multiple targets quickly and effectively
Secondly, army medics are not just limited to using firearms in combat situations. They may also be required to use their firearms in other situations, such as when providing security for medical convoys or when protecting patients from harm.
The Importance of Firearms Training for Army Medics
Firearms training is an essential part of an army medic's education, as it allows them to protect themselves and their patients in a variety of situations. Without this training, army medics would be unable to provide the high level of care that is expected of them, and their patients would be put at greater risk.

Thirdly, army medics are not just limited to using firearms; they are also trained in hand-to-hand combat and other forms of self-defense. This training is designed to ensure that they can protect themselves and their patients, even in situations where firearms are not available.
Hand-to-Hand Combat Training for Army Medics
Army medics receive extensive training in hand-to-hand combat, which includes techniques such as punching, kicking, and grappling. This training is designed to ensure that they can defend themselves and their patients in close-quarters combat situations.
Some of the specific skills that army medics learn during hand-to-hand combat training include:
- How to use their body weight and positioning to defend themselves
- How to use their arms and legs to strike and defend
- How to use grappling techniques to take down opponents
- How to use choke holds and other submission techniques to incapacitate opponents

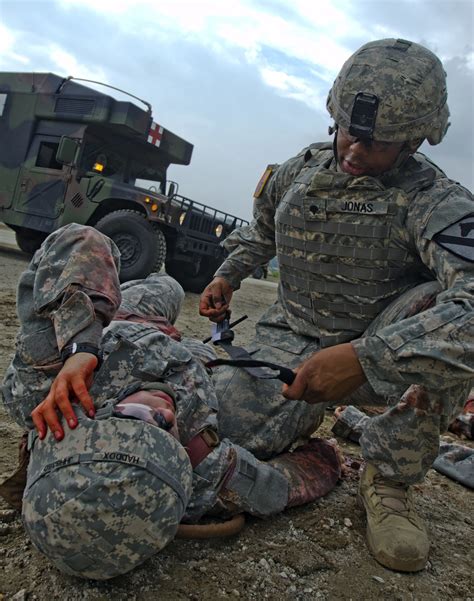
Fourthly, army medics are often deployed to remote or hostile areas, where they may not have access to backup or support. In these situations, their ability to use firearms and defend themselves is critical to their survival and the survival of their patients.
The Challenges of Deploying Army Medics
Deploying army medics to remote or hostile areas can be challenging, as they may not have access to backup or support. In these situations, their ability to use firearms and defend themselves is critical to their survival and the survival of their patients.

Finally, army medics play a critical role in the military, providing medical care to wounded soldiers and helping to stabilize them for evacuation. Their ability to use firearms and defend themselves is essential to their role, and they receive extensive training in both firearms and hand-to-hand combat.
The Critical Role of Army Medics
Army medics play a critical role in the military, providing medical care to wounded soldiers and helping to stabilize them for evacuation. Their ability to use firearms and defend themselves is essential to their role, and they receive extensive training in both firearms and hand-to-hand combat.

In conclusion, army medics play a critical role in the military, providing medical care to wounded soldiers and helping to stabilize them for evacuation. Their ability to use firearms and defend themselves is essential to their role, and they receive extensive training in both firearms and hand-to-hand combat.
Army Medics and Firearms Image Gallery









What is the role of an army medic?
+The role of an army medic is to provide medical care to wounded soldiers and help stabilize them for evacuation.
Do army medics receive firearms training?
+Yes, army medics receive extensive training in the use of firearms, including pistols, rifles, and machine guns.
Why is firearms training important for army medics?
+Firearms training is essential for army medics, as it allows them to protect themselves and their patients in combat situations.
Do army medics receive hand-to-hand combat training?
+Yes, army medics receive training in hand-to-hand combat, which includes techniques such as punching, kicking, and grappling.
What are some of the challenges of deploying army medics?
+Deploying army medics can be challenging, as they may not have access to backup or support in remote or hostile areas.
