Intro
Discover the role of Army Medics in combat situations. Learn about their primary responsibility of providing medical care, while also understanding their potential involvement in combat zones. Explore the challenges they face, their training, and the importance of their skills in saving lives on the battlefield.
The role of Army medics in combat situations is often misunderstood. While their primary responsibility is to provide medical care to wounded soldiers, they are also trained to operate in combat environments and may be required to engage in fighting when necessary.
Army medics, also known as combat medics, are trained to work in a variety of situations, from treating wounds on the battlefield to providing medical care in hospitals and clinics. However, their training also includes combat skills, such as marksmanship and first aid, in order to enable them to survive and provide medical care in hostile environments.
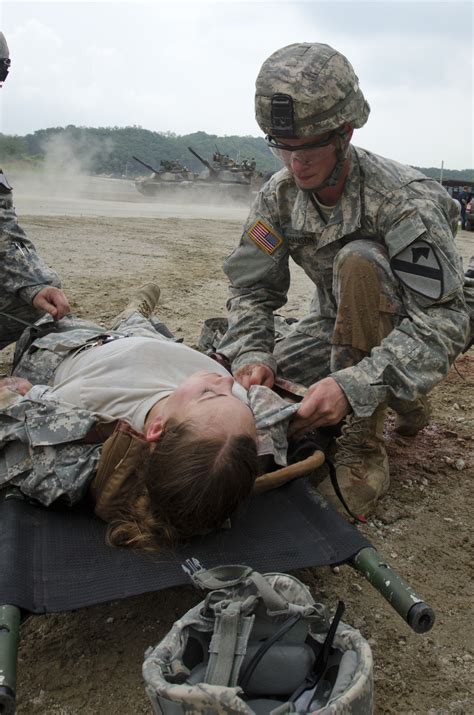

While Army medics are not typically considered front-line combat troops, they are often embedded with combat units and may be required to engage in fighting when necessary to protect themselves and their patients. In fact, the Army's medical corps has a long history of producing decorated heroes who have demonstrated exceptional bravery and selflessness in combat.
One notable example is Desmond Doss, a conscientious objector who served as a medic in World War II and became the first conscientious objector to receive the Medal of Honor. Doss's bravery and selflessness in the face of intense enemy fire are an inspiration to many, and his story has been immortalized in the film "Hacksaw Ridge."
Training and Responsibilities
Army medics undergo rigorous training to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat environments. This training includes:
- Basic combat training: Army medics receive the same basic combat training as other soldiers, including marksmanship, first aid, and combat tactics.
- Advanced individual training: After completing basic training, Army medics attend advanced individual training (AIT) where they learn medical skills such as wound treatment, trauma care, and patient assessment.
- Combat medic specialist training: Army medics who specialize in combat medicine attend additional training where they learn skills such as tactical combat casualty care and combat medic procedures.
Army medics are responsible for providing medical care to wounded soldiers in a variety of settings, from the battlefield to hospitals and clinics. Their responsibilities include:
- Treating wounds and injuries: Army medics are trained to treat a wide range of wounds and injuries, including gunshot wounds, shrapnel wounds, and blunt trauma.
- Providing emergency care: Army medics are trained to provide emergency care, including CPR, bleeding control, and shock management.
- Administering medications: Army medics are trained to administer medications and vaccinations to prevent and treat diseases.
Combat Medic Jobs
There are several combat medic jobs in the Army, each with its own unique responsibilities and requirements. Some of the most common combat medic jobs include:
- 68W Health Care Specialist: This is the most common combat medic job in the Army. 68W health care specialists provide medical care to wounded soldiers in a variety of settings.
- 25U Signal Support Systems Specialist: This job involves providing communication support to medical units in the field.
- 42A Human Resources Specialist: This job involves providing administrative support to medical units, including personnel management and supply management.

Deployment and Combat Experience
Army medics may be deployed to combat zones around the world, where they provide medical care to wounded soldiers in a variety of settings. Some of the most common deployment locations for Army medics include:
- Afghanistan: Army medics have been deployed to Afghanistan since 2001, where they have provided medical care to wounded soldiers in combat zones.
- Iraq: Army medics have been deployed to Iraq since 2003, where they have provided medical care to wounded soldiers in combat zones.
- Syria: Army medics have been deployed to Syria since 2015, where they have provided medical care to wounded soldiers in combat zones.
Army medics may also be deployed to humanitarian missions around the world, where they provide medical care to civilians in need. Some of the most common humanitarian mission locations for Army medics include:
- Haiti: Army medics were deployed to Haiti in 2010 to provide medical care to civilians after a devastating earthquake.
- Philippines: Army medics were deployed to the Philippines in 2013 to provide medical care to civilians after a devastating typhoon.
Personal Qualities and Skills
Army medics require a unique set of personal qualities and skills, including:
- Compassion: Army medics must be able to provide compassionate care to wounded soldiers, often in high-stress environments.
- Calm under pressure: Army medics must be able to remain calm under pressure, even in the face of intense enemy fire.
- Strong communication skills: Army medics must be able to communicate effectively with patients, colleagues, and commanders.
- Physical stamina: Army medics must be physically fit and able to work in challenging environments.
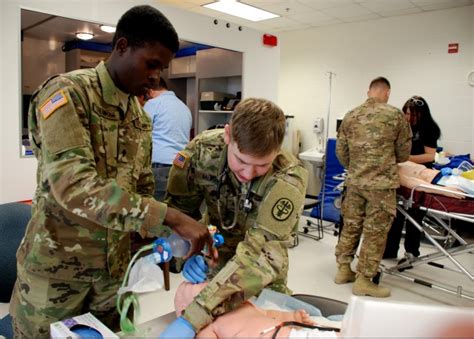
Education and Training
Army medics receive comprehensive education and training to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat environments. This training includes:
- Basic training: Army medics attend basic training, where they learn basic combat skills and medical procedures.
- Advanced individual training: After completing basic training, Army medics attend AIT, where they learn advanced medical skills and procedures.
- Combat medic specialist training: Army medics who specialize in combat medicine attend additional training where they learn skills such as tactical combat casualty care and combat medic procedures.
Army medics may also receive specialized training in areas such as:
- Tactical combat casualty care (TCCC)
- Combat medic procedures
- Trauma care
- Patient assessment
Combat Medic Certification
Army medics may become certified as combat medics through the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT). To become certified, Army medics must:
- Complete a combat medic training program
- Pass a written exam
- Pass a practical exam

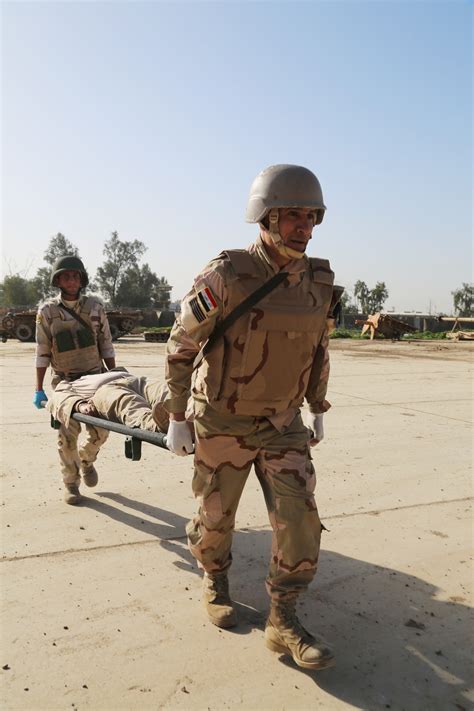
Gallery of Army Medics in Combat Situations
Army Medics in Combat Situations






Frequently Asked Questions
Do Army medics fight in combat situations?
+Yes, Army medics may be required to engage in fighting when necessary to protect themselves and their patients.
What is the role of an Army medic?
+Army medics provide medical care to wounded soldiers in a variety of settings, from the battlefield to hospitals and clinics.
How do Army medics receive training?
+Army medics receive comprehensive education and training to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat environments.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the role of Army medics in combat situations. These brave men and women play a critical role in providing medical care to wounded soldiers, often in high-stress environments. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
