Intro
Discover the truth about military officers and combat. Do they see action often? Learn about the roles, deployments, and combat experiences of military officers, including the risks and realities of their careers, to help you decide if a life of service is right for you.
The image of a military officer is often associated with combat and the front lines of war. However, the reality is that many military officers spend their careers in roles that are far removed from direct combat. While some officers may see combat frequently, others may never experience it at all.
The frequency of combat for military officers depends on a variety of factors, including their branch of service, Military Occupational Specialty (MOS), and the specific needs of their unit. For example, officers in the infantry or special operations forces are more likely to see combat than those in support roles such as logistics or administration.

In fact, a study by the RAND Corporation found that only about 10% of military officers serve in combat roles. The majority of officers serve in support roles, such as intelligence, communications, or logistics. Even among those who do serve in combat roles, the frequency of combat can vary greatly.
Some officers may see combat frequently, while others may go years without experiencing it. Additionally, the nature of modern warfare has changed, with many conflicts involving asymmetric warfare, counterinsurgency, and peacekeeping operations. These types of operations often require officers to perform duties that are far removed from traditional combat roles.
Types of Military Officers and Their Combat Experience
Different types of military officers have varying levels of combat experience. For example:
-
Infantry Officers
Infantry officers are the most likely to see combat. They are responsible for leading infantry units and are often deployed to combat zones. Infantry officers may see combat frequently, especially during intense fighting.
-
Special Operations Officers
Special operations officers, such as those in the Navy SEALs or Army Rangers, are trained to conduct unconventional warfare and counterterrorism operations. They may see combat frequently, often in small, specialized units.
-
Logistics Officers
Logistics officers are responsible for managing the supply chain and providing support to combat units. They may not see combat directly, but may be deployed to combat zones to provide support.
-
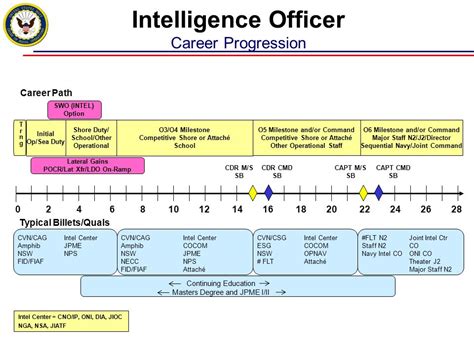
Intelligence Officers
Intelligence officers are responsible for gathering and analyzing information about the enemy. They may not see combat directly, but may be deployed to combat zones to provide intelligence support.
The Reality of Modern Warfare
Modern warfare has changed the nature of combat for military officers. Many conflicts now involve asymmetric warfare, counterinsurgency, and peacekeeping operations. These types of operations often require officers to perform duties that are far removed from traditional combat roles.
In addition, advances in technology have changed the way wars are fought. Drones, precision-guided munitions, and other technologies have reduced the need for direct combat. Many officers may spend their careers in roles that involve operating and maintaining these technologies, rather than engaging in direct combat.

Career Paths for Military Officers
Military officers have a variety of career paths to choose from, both within and outside of combat roles. Some officers may choose to specialize in a particular area, such as intelligence or logistics, while others may choose to pursue command roles.
Command roles involve leading units and making strategic decisions. These roles can be challenging and require strong leadership and decision-making skills. Officers who pursue command roles may see combat, but may also be responsible for making decisions that affect the outcome of battles.
Other career paths for military officers include:
-
Staff Roles
Staff roles involve supporting commanders and making strategic decisions. These roles can be challenging and require strong analytical and communication skills.
-
Trainer Roles
Trainer roles involve teaching and mentoring junior officers. These roles can be rewarding and require strong teaching and leadership skills.
-
Policy Roles
Policy roles involve developing and implementing policies that affect the military. These roles can be challenging and require strong analytical and communication skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, military officers do not always see combat. While some officers may see combat frequently, others may go years without experiencing it. The frequency of combat depends on a variety of factors, including the officer's branch of service, MOS, and the specific needs of their unit.
Modern warfare has changed the nature of combat for military officers, with many conflicts involving asymmetric warfare, counterinsurgency, and peacekeeping operations. These types of operations often require officers to perform duties that are far removed from traditional combat roles.
Military officers have a variety of career paths to choose from, both within and outside of combat roles. Whether they choose to pursue command roles, staff roles, trainer roles, or policy roles, military officers play a critical role in defending their country and upholding the values of their service.
We hope this article has provided you with a better understanding of the role of military officers and the frequency of combat in their careers. If you have any questions or comments, please let us know.
Military Officer Image Gallery








Do all military officers see combat?
+No, not all military officers see combat. The frequency of combat depends on a variety of factors, including the officer's branch of service, MOS, and the specific needs of their unit.
What types of military officers are most likely to see combat?
+Infantry officers and special operations officers are the most likely to see combat. They are responsible for leading infantry units and conducting unconventional warfare and counterterrorism operations.
What are some career paths for military officers outside of combat roles?
+Military officers have a variety of career paths to choose from, including staff roles, trainer roles, and policy roles. These roles can be challenging and require strong analytical and communication skills.
