Intro
Explore the nuances of Japans nuclear stance with our in-depth analysis. Discover the truth behind Japans nuclear ambitions, its Three Non-Nuclear Principles, and the countrys reliance on the US nuclear umbrella. Learn about Japans nuclear power generation, plutonium stockpiles, and the controversy surrounding its nuclear fuel cycle.
Japan's nuclear status has long been a topic of interest and debate, particularly given its history and geographical location. The country's unique relationship with nuclear power and its potential to develop nuclear weapons is multifaceted. Understanding this complex issue requires a look at the historical, political, and strategic factors at play.
Japan is one of the few nations that has been directly affected by nuclear warfare, with the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945 leading to the end of World War II. This experience has deeply ingrained a strong anti-nuclear sentiment within the country. Japan's commitment to non-proliferation is underscored by its being the only country to have suffered from nuclear attacks, yet choosing not to pursue nuclear armament.
Historical Background

The aftermath of World War II and the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki left Japan with a profound anti-nuclear stance. The Three Non-Nuclear Principles, which were enshrined in 1968, state that Japan shall not possess, produce, or permit the introduction of nuclear weapons. This policy reflects the country's commitment to nuclear disarmament and its role as a leading voice in international efforts against nuclear proliferation.
International Treaties and Agreements
Japan's nuclear policies are also guided by its adherence to international treaties and agreements. The country ratified the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) in 1976, reaffirming its commitment to non-proliferation and disarmament. Additionally, Japan has signed and ratified the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), further solidifying its stance against nuclear weapons.
Nuclear Power and Energy Policy
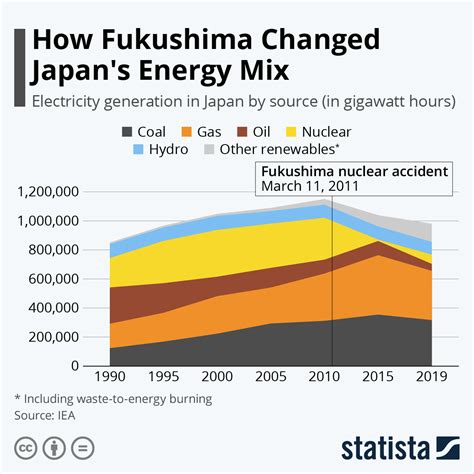
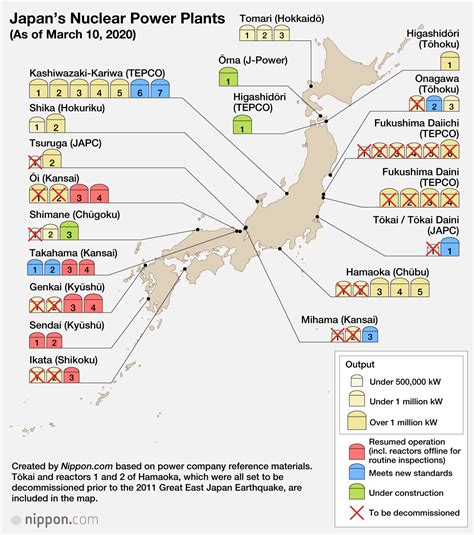
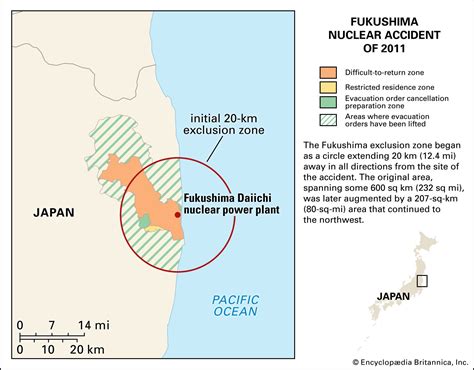
Despite its anti-nuclear stance, Japan has a significant nuclear power program aimed at reducing its reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. The country's energy policy emphasizes the importance of nuclear power as a clean and efficient source of electricity. This dichotomy between nuclear power for energy and the rejection of nuclear weapons highlights the complexity of Japan's nuclear policy.
Economic and Strategic Considerations
Economic and strategic factors also play a crucial role in shaping Japan's nuclear policy. The country's reliance on imported fossil fuels makes nuclear power an attractive option for energy security. Furthermore, Japan's strategic location in East Asia, where tensions with neighboring countries like North Korea and China are evident, necessitates a robust defense policy. However, this does not extend to the development of nuclear weapons, as Japan continues to rely on its alliance with the United States for nuclear deterrence.
Public Opinion and Debate

Public opinion in Japan is largely in favor of maintaining the country's non-nuclear status. However, there are debates among policymakers and scholars about the potential benefits of nuclear deterrence, especially in the context of regional security threats. The discussion centers around whether Japan's commitment to non-proliferation is sufficient in the face of growing nuclear arsenals among its neighbors.
International Implications and Future Directions


Japan's stance on nuclear issues has significant international implications. The country's commitment to non-proliferation serves as a model for other nations and reinforces global efforts towards disarmament. As the international landscape evolves, Japan will likely continue to play a key role in promoting peace and security, leveraging its unique experience to advocate for a world free of nuclear weapons.
Gallery of Japan's Nuclear Issues






Does Japan have nuclear weapons?
+No, Japan does not possess nuclear weapons. It has adhered to a non-nuclear policy since the aftermath of World War II.
What is Japan's stance on nuclear power?
+Japan supports the use of nuclear power for energy generation, considering it a clean and efficient source of electricity.
Is Japan a signatory to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)?
+Yes, Japan ratified the NPT in 1976, reaffirming its commitment to non-proliferation and disarmament.
What are the implications of Japan's nuclear policy for international security?
+Japan's commitment to non-proliferation and disarmament serves as a model for other nations and contributes to global efforts towards peace and security.
How does Japan's history influence its nuclear policy?
+The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki have deeply ingrained a strong anti-nuclear sentiment in Japan, guiding its nuclear policy and commitment to non-proliferation.
As you have read through this comprehensive article, it's clear that Japan's nuclear policy is rooted in its unique history, commitment to non-proliferation, and the pursuit of a safe and secure energy future. Share your thoughts and insights on this critical topic, and let's continue the conversation towards a safer and more peaceful world.
