Intro
Discover if military pay is sufficient for servicemembers, considering factors like base pay, allowances, and benefits. Explore the military pay scale, how pay is calculated, and the impact of deployments and promotions. Get an honest look at whether military compensation can support a comfortable lifestyle, and what servicemembers can expect in terms of salary and benefits.
Military service is a noble and selfless career path that requires immense dedication, sacrifice, and hard work. While the emotional rewards of serving one's country are immeasurable, the financial compensation is a critical aspect of a servicemember's life. The question on many minds is: does military pay well enough for servicemembers?
The answer to this question is complex and depends on various factors, including the individual's rank, time in service, education level, and occupation. In this article, we will delve into the world of military compensation, exploring the different components of military pay, the pros and cons of military service, and whether the pay is sufficient for the sacrifices made by servicemembers.
Components of Military Pay
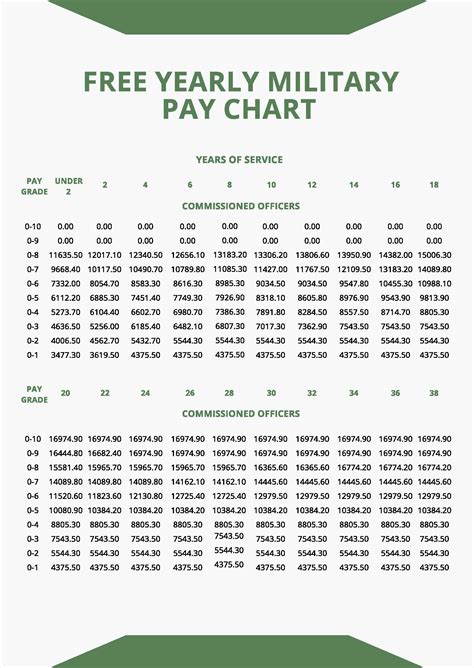
Military pay consists of several components, including:
- Basic Pay: This is the servicemember's base salary, which varies depending on their rank and time in service.
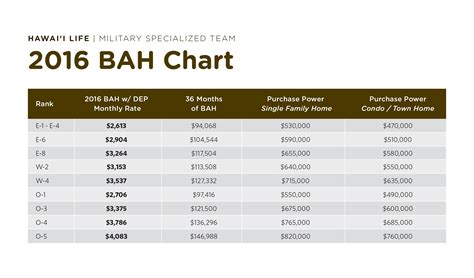
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): This is a tax-free allowance that helps cover the cost of housing, whether on or off base.
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): This is a tax-free allowance that helps cover the cost of food.
- Special Pay: This includes additional pay for special duties, such as hazardous duty pay, dive pay, or jump pay.
- Bonus Pay: This includes one-time bonuses for enlistment, reenlistment, or special skills.
Pros of Military Service
While military pay may not be the highest compared to civilian careers, there are many benefits that come with serving in the military. Some of the pros include:
- Education Benefits: The military offers various education benefits, including the GI Bill, which can help cover the cost of college tuition.
- Health Insurance: Military personnel and their families receive comprehensive health insurance, including medical, dental, and pharmacy coverage.
- Retirement Benefits: Military personnel can retire after 20 years of service and receive a pension, which can provide a steady income stream in retirement.
- Career Advancement: The military offers a wide range of career opportunities, from technical fields like engineering and cybersecurity to leadership roles and management positions.
- Camaraderie and Esprit de Corps: Military service provides a sense of belonging and camaraderie that is hard to find in civilian careers.
Cons of Military Service

While military service has many benefits, there are also significant sacrifices that come with serving in the military. Some of the cons include:
- Time Away from Family: Military personnel often have to deploy or relocate, which can be tough on families and relationships.
- Physical and Emotional Demands: Military service can be physically and emotionally demanding, with long hours, intense training, and exposure to combat.
- Limited Job Security: Military personnel can be subject to deployment, relocation, or changes in their military occupational specialty (MOS), which can impact their job security.
- Limited Career Flexibility: Military personnel often have limited career flexibility, as they are bound by their service contract and may have limited opportunities for career advancement.
Is Military Pay Enough?
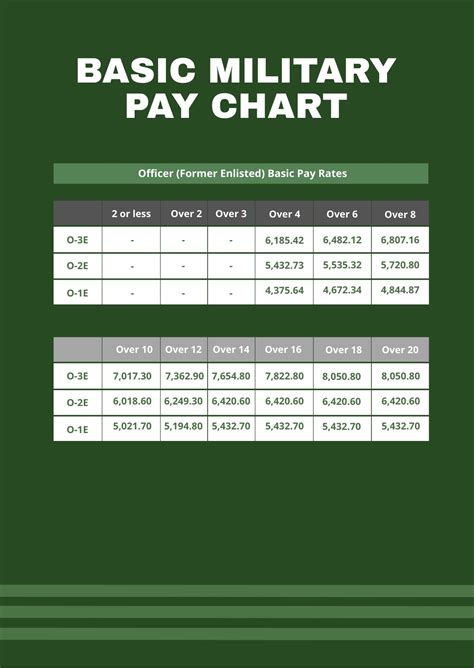
Whether military pay is enough depends on individual circumstances and expectations. According to the Military Pay Chart, the basic pay for an E-1 (Private) with less than two years of service is $1,733.10 per month, while the basic pay for an O-10 (General) with over 20 years of service is $19,762.80 per month.
While these figures may seem high, they do not reflect the total compensation package, which includes benefits like housing allowance, food allowance, and special pay. Additionally, military personnel often have to pay for their own uniforms, equipment, and travel expenses, which can add up quickly.
To give you a better idea, here are some approximate annual salary ranges for military personnel:
- E-1 (Private): $20,796 - $24,960
- E-5 (Sergeant): $34,464 - $44,784
- E-7 (Sergeant First Class): $44,784 - $59,520
- O-1 (Second Lieutenant): $39,444 - $53,520
- O-3 (Captain): $53,520 - $74,760
In comparison, civilian careers in similar fields can offer higher salaries, especially in fields like engineering, cybersecurity, and data science. For example:
- Software Engineer: $70,000 - $110,000 per year
- Data Scientist: $80,000 - $140,000 per year
- Cybersecurity Specialist: $60,000 - $120,000 per year
Gallery of Military Pay
Military Pay Gallery




FAQs
How much does the military pay?
+The military pay varies depending on rank, time in service, and occupation. Basic pay ranges from $20,796 per year for an E-1 (Private) to $19,762.80 per month for an O-10 (General).
What are the benefits of military service?
+Military service offers a wide range of benefits, including education benefits, health insurance, retirement benefits, and career advancement opportunities.
Is military pay enough?
+Whether military pay is enough depends on individual circumstances and expectations. While the basic pay may not be the highest, the total compensation package includes benefits like housing allowance, food allowance, and special pay.
In conclusion, while military pay may not be the highest compared to civilian careers, the total compensation package, including benefits and education opportunities, can make military service a fulfilling and rewarding career path. However, individual circumstances and expectations can vary greatly, and it's essential to weigh the pros and cons before making a decision.
If you have any thoughts or questions about military pay, please share them in the comments below. We would love to hear from you!
