Intro
Discover the unexpected twists in military pay that surprise new recruits. Learn about the top 5 financial surprises, including allowance variations, tax implications, and benefits beyond basic pay. Understand military compensation, including Base Pay, BAH, and BAS, to make informed decisions about your military career.
The allure of military service is strong for many young people. The promise of serving one's country, learning valuable skills, and enjoying a sense of camaraderie with fellow service members can be a powerful draw. However, one aspect of military life that often surprises new recruits is the pay. While the pay may not be the primary motivator for many who join the military, it is an important consideration, especially for those who are supporting families or have significant financial obligations.
Here are five ways that military pay can surprise new recruits:
1. Basic Pay vs. Total Compensation
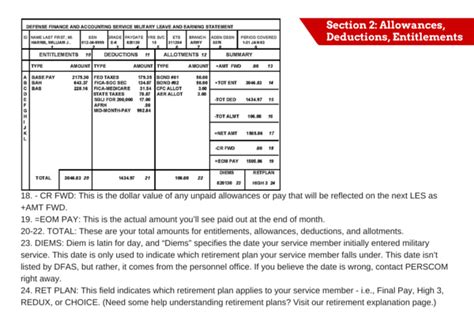
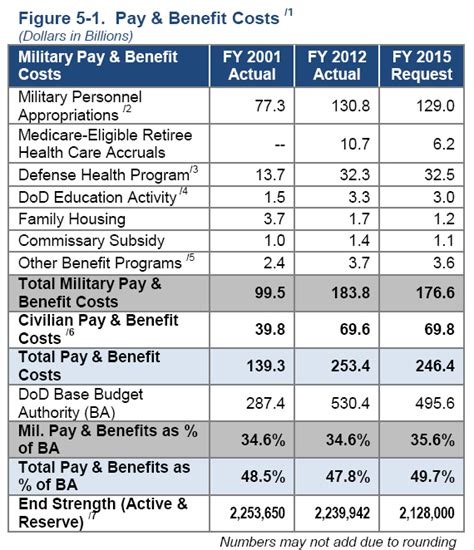
One of the biggest surprises for new recruits is the difference between basic pay and total compensation. Basic pay is the monthly salary that service members receive, and it is based on their rank and time in service. However, total compensation includes a range of additional benefits, such as housing allowance, food allowance, and access to on-base facilities like grocery stores and gyms. When these benefits are factored in, the total compensation package can be significantly higher than the basic pay.
For example, a private in the Army with two years of service might receive a basic pay of around $1,733 per month. However, with housing and food allowances, their total compensation could be closer to $2,500 per month. This can be a welcome surprise for new recruits who may not have realized the full extent of their compensation package.
Understanding the Military Pay Chart
The military pay chart is a complex document that outlines the various pay grades and corresponding salaries for each branch of the military. New recruits may find it difficult to navigate this chart and understand how their pay will be calculated. However, with a little practice, it becomes easier to understand how the pay chart works and how to use it to estimate total compensation.
2. Special Pays and Allowances

In addition to basic pay and total compensation, service members may also be eligible for special pays and allowances. These can include things like jump pay for paratroopers, dive pay for Navy divers, and hazardous duty pay for service members who work in high-risk environments. These special pays can add hundreds or even thousands of dollars to a service member's monthly salary, and they can be a welcome surprise for new recruits.
For example, a Navy diver who is stationed on a submarine might receive an additional $150 per month in dive pay. This can be a significant bonus for service members who are already receiving a competitive salary.
Types of Special Pays and Allowances
There are many different types of special pays and allowances that service members may be eligible for. Some examples include:
- Hazardous duty pay for service members who work in high-risk environments
- Jump pay for paratroopers
- Dive pay for Navy divers
- Submarine duty pay for service members who serve on submarines
- Aviation bonus for pilots and aviation crew members
3. Tax Benefits

One of the biggest surprises for new recruits is the tax benefits that come with military service. Service members do not have to pay taxes on their housing allowance or food allowance, and they may also be eligible for other tax breaks. This can result in significant savings for service members, especially those who are stationed overseas.
For example, a service member who is stationed in a combat zone may not have to pay taxes on their income, which can result in thousands of dollars in savings per year.
Understanding Military Tax Benefits
Military tax benefits can be complex and difficult to understand, but they can result in significant savings for service members. Some things to keep in mind include:
- Housing allowance and food allowance are tax-free
- Service members may be eligible for other tax breaks, such as the earned income tax credit
- Service members who are stationed overseas may not have to pay taxes on their income
4. Education Benefits
Another surprise for new recruits is the education benefits that come with military service. Service members may be eligible for programs like the GI Bill, which can help pay for college tuition and other education expenses. These benefits can be a significant bonus for service members who are looking to further their education.
For example, the GI Bill can provide up to 100% of tuition and fees for service members who attend college, which can result in thousands of dollars in savings per year.
Understanding Military Education Benefits
Military education benefits can be complex and difficult to understand, but they can result in significant savings for service members. Some things to keep in mind include:
- The GI Bill can provide up to 100% of tuition and fees for service members who attend college
- Service members may also be eligible for other education benefits, such as the Military Tuition Assistance Program
- Education benefits can be used for a variety of education expenses, including tuition, fees, and books
5. Veterans' Preference

Finally, new recruits may be surprised to learn about veterans' preference, which is a program that provides preference to veterans when they apply for federal jobs. This can be a significant bonus for service members who are looking to transition to a civilian career after their military service.
For example, veterans who apply for federal jobs may receive preference over non-veterans, which can increase their chances of being hired.
Understanding Veterans' Preference
Veterans' preference can be a complex and confusing topic, but it can result in significant benefits for service members. Some things to keep in mind include:
- Veterans' preference applies to federal jobs, not private sector jobs
- Veterans may receive preference over non-veterans when they apply for federal jobs
- Veterans' preference can be used for a variety of federal jobs, including administrative, technical, and professional positions
Military Pay Surprises Image Gallery








How is military pay calculated?
+Military pay is calculated based on rank and time in service. The military pay chart outlines the various pay grades and corresponding salaries for each branch of the military.
What are special pays and allowances?
+Special pays and allowances are additional forms of compensation that service members may be eligible for, such as jump pay, dive pay, and hazardous duty pay.
How do tax benefits work for military service members?
+Military service members do not have to pay taxes on their housing allowance or food allowance, and they may also be eligible for other tax breaks.
What are education benefits for military service members?
+Military service members may be eligible for programs like the GI Bill, which can help pay for college tuition and other education expenses.
How does veterans' preference work?
+Veterans' preference provides preference to veterans when they apply for federal jobs, which can increase their chances of being hired.
Now that you've learned more about the five ways military pay can surprise new recruits, we hope you have a better understanding of the complex and often misunderstood world of military compensation. Whether you're a new recruit or a seasoned veteran, it's essential to stay informed about the various pay and benefits that are available to you.
