Intro
Uncover the ultimate showdown between two top-tier fighter jets: the F-16 and Su-35. Explore the 5 key differences that set these aircraft apart, including maneuverability, range, armament, radar systems, and stealth capabilities. Discover which jet reigns supreme in this comprehensive comparison of speed, agility, and combat prowess.
The world of military aviation is filled with cutting-edge technology and impressive aircraft designs. Two of the most notable fighter jets in the world are the F-16 Fighting Falcon and the Su-35 Flanker-E. Both aircraft have their unique features, capabilities, and histories, which set them apart from one another. In this article, we will delve into the 5 key differences between the F-16 and the Su-35, exploring their design, performance, armament, avionics, and operational history.

Design and Aerodynamics
The F-16 and Su-35 have distinct design philosophies, reflecting their different development backgrounds and operational requirements. The F-16, designed by General Dynamics (now Lockheed Martin), is a single-engine, multi-role fighter with a focus on agility and maneuverability. Its sleek, delta-wing design provides exceptional roll rates and a high angle of attack. In contrast, the Su-35, developed by Sukhoi, is a twin-engine, air superiority fighter with a emphasis on speed and range. Its canard design and thrust-vectoring engines enable the aircraft to achieve remarkable agility and stability at high angles of attack.
Key Design Differences:
- Single-engine (F-16) vs. twin-engine (Su-35) design
- Delta-wing (F-16) vs. canard design (Su-35)
- Different materials and manufacturing techniques used in construction
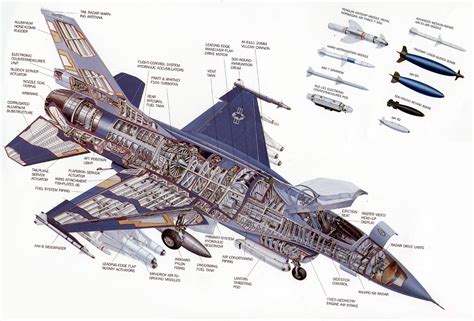
Performance and Capabilities
The F-16 and Su-35 exhibit different performance characteristics, influenced by their design and engine configurations. The F-16, powered by a single General Electric F110 or Pratt & Whitney F100 engine, has a maximum speed of around Mach 2.0 (1,470 mph) and a service ceiling of 50,000 feet. The Su-35, equipped with two Saturn AL-41F1S engines, can reach speeds of up to Mach 2.25 (1,700 mph) and has a service ceiling of 59,000 feet.
Key Performance Differences:
- Maximum speed: Mach 2.0 (F-16) vs. Mach 2.25 (Su-35)
- Service ceiling: 50,000 feet (F-16) vs. 59,000 feet (Su-35)
- Rate of climb: 50,000 ft/min (F-16) vs. 55,000 ft/min (Su-35)

Armament and Payload
The F-16 and Su-35 have different armament configurations, reflecting their intended roles and operational environments. The F-16 can carry a variety of air-to-air and air-to-ground munitions, including the AIM-120 AMRAAM, AIM-9 Sidewinder, and AGM-88 HARM. The Su-35 is also capable of carrying a range of missiles and bombs, including the R-77 and R-73 air-to-air missiles, as well as the KAB-500 and KAB-1500 guided bombs.
Key Armament Differences:
- Air-to-air missiles: AIM-120 and AIM-9 (F-16) vs. R-77 and R-73 (Su-35)
- Air-to-ground munitions: AGM-88 and GBU-31 (F-16) vs. KAB-500 and KAB-1500 (Su-35)
- Payload capacity: 20,000 pounds (F-16) vs. 26,000 pounds (Su-35)

Avionics and Electronics
The F-16 and Su-35 have advanced avionics and electronics systems, which provide their pilots with critical information and enhance their combat effectiveness. The F-16 features the AN/APG-66 radar system, which offers air-to-air and air-to-ground modes, as well as the ALR-69 radar warning receiver. The Su-35 is equipped with the Irbis-E radar system, which provides long-range detection and tracking capabilities, as well as the L175M Khibiny electronic warfare system.
Key Avionics Differences:
- Radar systems: AN/APG-66 (F-16) vs. Irbis-E (Su-35)
- Electronic warfare systems: ALR-69 (F-16) vs. L175M Khibiny (Su-35)
- Communication systems: HAVE QUICK II (F-16) vs. S-108 (Su-35)

Operational History
The F-16 and Su-35 have different operational histories, reflecting their development timelines and deployment patterns. The F-16, first introduced in 1978, has been widely exported and operated by numerous countries, including the United States, Israel, and Turkey. The Su-35, which began development in the 1980s, has been primarily operated by Russia and China.
Key Operational Differences:
- Introduction year: 1978 (F-16) vs. 2014 (Su-35)
- Primary operators: United States, Israel, and Turkey (F-16) vs. Russia and China (Su-35)
- Export history: Widespread exports (F-16) vs. Limited exports (Su-35)

Gallery of F-16 and Su-35 Images
F-16 and Su-35 Image Gallery






What is the main difference between the F-16 and Su-35?
+The main difference between the F-16 and Su-35 is their design philosophy and operational requirements. The F-16 is a single-engine, multi-role fighter with a focus on agility and maneuverability, while the Su-35 is a twin-engine, air superiority fighter with a emphasis on speed and range.
Which aircraft has a higher service ceiling?
+The Su-35 has a higher service ceiling, at 59,000 feet, compared to the F-16's service ceiling of 50,000 feet.
What is the difference in armament capacity between the two aircraft?
+The Su-35 has a higher payload capacity, at 26,000 pounds, compared to the F-16's payload capacity of 20,000 pounds.
In conclusion, the F-16 and Su-35 are two distinct fighter jets with unique characteristics, capabilities, and operational histories. While both aircraft have their strengths and weaknesses, they reflect the different design philosophies and requirements of their respective countries of origin. As the world of military aviation continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how these two aircraft adapt and improve to meet the changing needs of modern warfare.
