Intro
Explore the differences between F-35 variants A, B, and C. Discover the unique features, capabilities, and advantages of each model, including stealth technology, short takeoff and landing, and carrier-based operations. Learn how the F-35A, F-35B, and F-35C cater to different military needs, from air-to-air combat to ground attack and reconnaissance missions.
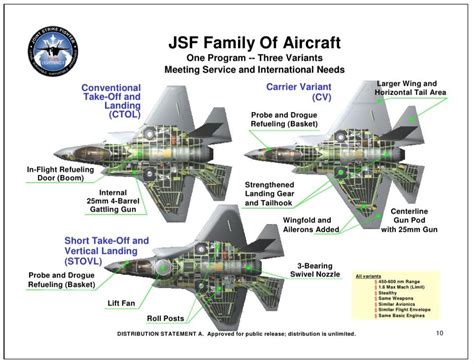
The F-35 Lightning II is a fifth-generation multirole fighter aircraft developed by Lockheed Martin. The F-35 program has three main variants: the F-35A (Conventional Takeoff and Landing, CTOL), the F-35B (Short Takeoff and Vertical Landing, STOVL), and the F-35C (Carrier Variant, CV). Each variant is designed to meet the specific needs of different branches of the military and foreign countries.

Overview of F-35 Variants
The F-35A is the most common variant, used by the US Air Force and several foreign countries. It is designed for conventional takeoff and landing operations from land-based runways. The F-35B is used by the US Marine Corps and the UK Royal Navy, and features a unique STOVL capability that allows it to take off from short runways and land vertically. The F-35C is designed for carrier operations, with a stronger wing and tailhook for catapult launches and arrested landings.
Key Differences Between F-35 Variants
- Takeoff and Landing: The F-35A is designed for conventional takeoff and landing, while the F-35B features STOVL capability, and the F-35C is designed for carrier operations.
- Wing Design: The F-35C has a stronger wing and tailhook to withstand the stresses of carrier operations, while the F-35A and F-35B have lighter wings.
- Engine: The F-35B has a unique engine nozzle that can rotate downward for vertical takeoff and landing, while the F-35A and F-35C have a standard engine nozzle.
- Range and Payload: The F-35A has the longest range and payload capacity, while the F-35B has a shorter range and payload capacity due to its STOVL capability.

F-35A (CTOL) Variant
The F-35A is the most common variant of the F-35, used by the US Air Force and several foreign countries. It is designed for conventional takeoff and landing operations from land-based runways. The F-35A has a range of over 1,200 nautical miles and a payload capacity of up to 18,000 pounds.
Features of the F-35A
- Conventional Takeoff and Landing: The F-35A is designed for conventional takeoff and landing operations from land-based runways.
- Long Range and Payload Capacity: The F-35A has a range of over 1,200 nautical miles and a payload capacity of up to 18,000 pounds.
- Advanced Avionics: The F-35A features advanced avionics, including a helmet-mounted display and a advanced sensor suite.

F-35B (STOVL) Variant
The F-35B is used by the US Marine Corps and the UK Royal Navy, and features a unique STOVL capability that allows it to take off from short runways and land vertically. The F-35B has a range of over 900 nautical miles and a payload capacity of up to 15,000 pounds.
Features of the F-35B
- Short Takeoff and Vertical Landing: The F-35B features a unique STOVL capability that allows it to take off from short runways and land vertically.
- Advanced Engine Nozzle: The F-35B has a unique engine nozzle that can rotate downward for vertical takeoff and landing.
- Reduced Range and Payload Capacity: The F-35B has a shorter range and payload capacity due to its STOVL capability.

F-35C (CV) Variant
The F-35C is designed for carrier operations, with a stronger wing and tailhook for catapult launches and arrested landings. The F-35C has a range of over 1,200 nautical miles and a payload capacity of up to 18,000 pounds.
Features of the F-35C
- Carrier Operations: The F-35C is designed for carrier operations, with a stronger wing and tailhook for catapult launches and arrested landings.
- Advanced Arresting Gear: The F-35C features advanced arresting gear, including a tailhook and a drag chute.
- Long Range and Payload Capacity: The F-35C has a range of over 1,200 nautical miles and a payload capacity of up to 18,000 pounds.

F-35 Variants Image Gallery








What are the main differences between F-35 variants?
+The main differences between F-35 variants are takeoff and landing capabilities, wing design, engine nozzle, range, and payload capacity.
Which F-35 variant has the longest range and payload capacity?
+The F-35A has the longest range and payload capacity, with a range of over 1,200 nautical miles and a payload capacity of up to 18,000 pounds.
Which F-35 variant is used by the US Marine Corps?
+The F-35B is used by the US Marine Corps and the UK Royal Navy, featuring a unique STOVL capability.
If you're interested in learning more about the F-35 variants, we encourage you to share this article with others and leave a comment below with any questions or thoughts you may have.
