Intro
Discover the strategies military recruiters use to hire health professionals. Learn about the 5 ways they attract and recruit top talent, from competitive salaries to specialized training programs. Explore how military recruiters identify and target skilled healthcare workers, and what sets military healthcare careers apart from civilian opportunities.
Joining the military as a health professional can be a fulfilling and rewarding career path. Not only do you get to serve your country, but you also have the opportunity to make a difference in the lives of others. If you're a health professional considering a career in the military, you might be wondering how military recruiters hire health professionals. In this article, we'll explore the top 5 ways military recruiters hire health professionals.

What Do Military Recruiters Look for in Health Professionals?
Before we dive into the top 5 ways military recruiters hire health professionals, it's essential to understand what they're looking for in a candidate. Military recruiters typically look for health professionals who are:
- Licensed and certified in their field
- Have a strong academic record
- Possess excellent communication and leadership skills
- Are physically fit and meet the military's medical standards
- Are willing to commit to a minimum of 2-4 years of service
Education and Certification Requirements
To be considered for a health professional role in the military, you typically need to have a degree from an accredited institution and be licensed and certified in your field. For example, if you're a nurse, you'll need to have a Bachelor's degree in nursing and be licensed as a registered nurse (RN). If you're a doctor, you'll need to have a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree and be licensed to practice medicine.
Top 5 Ways Military Recruiters Hire Health Professionals
Now that we've covered what military recruiters look for in health professionals, let's explore the top 5 ways they hire them:
1. Military Recruiting Offices
One of the most common ways military recruiters hire health professionals is through military recruiting offices. These offices are located throughout the country and are staffed by recruiters who specialize in recruiting health professionals. To get started, you can visit a recruiting office in person or schedule an appointment with a recruiter.

2. Online Applications
Another way military recruiters hire health professionals is through online applications. The military has a website dedicated to health professional recruitment, where you can submit your application and resume. Once you've submitted your application, a recruiter will contact you to discuss your qualifications and answer any questions you may have.
3. Medical Professional Associations
Military recruiters also attend medical professional associations and conferences to recruit health professionals. These events provide a great opportunity for recruiters to meet with health professionals who are interested in a military career. Some examples of medical professional associations that military recruiters attend include the American Medical Association (AMA) and the American Nurses Association (ANA).

4. Social Media and Online Advertising
In addition to traditional recruiting methods, military recruiters also use social media and online advertising to reach health professionals. They use platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn to post job ads and engage with potential candidates. They also use targeted online advertising to reach health professionals who are searching for job opportunities online.
5. Referrals and Word of Mouth
Finally, military recruiters also rely on referrals and word of mouth to hire health professionals. They encourage current military health professionals to refer their colleagues and friends who may be interested in a military career. They also offer incentives for referrals, such as bonuses and recognition.

Benefits of Joining the Military as a Health Professional
Joining the military as a health professional can be a rewarding and challenging career path. Some of the benefits of joining the military as a health professional include:
- Competitive salary and benefits package
- Opportunity to serve your country and make a difference in the lives of others
- Professional development and advancement opportunities
- Access to state-of-the-art medical equipment and technology
- Opportunities for deployment and travel

Conclusion
Joining the military as a health professional can be a fulfilling and rewarding career path. If you're a health professional considering a career in the military, we hope this article has provided you with valuable information and insights. Remember to research the different ways military recruiters hire health professionals and to consider the benefits of joining the military as a health professional.
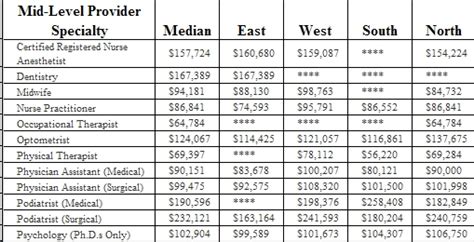
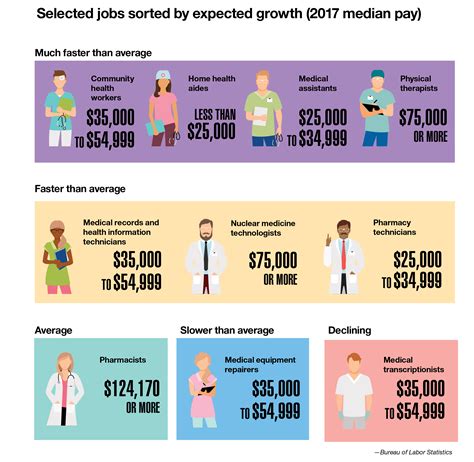
Military Health Professionals Image Gallery





What are the benefits of joining the military as a health professional?
+The benefits of joining the military as a health professional include a competitive salary and benefits package, opportunity to serve your country and make a difference in the lives of others, professional development and advancement opportunities, access to state-of-the-art medical equipment and technology, and opportunities for deployment and travel.
What are the education and certification requirements for health professionals in the military?
+To be considered for a health professional role in the military, you typically need to have a degree from an accredited institution and be licensed and certified in your field. For example, if you're a nurse, you'll need to have a Bachelor's degree in nursing and be licensed as a registered nurse (RN). If you're a doctor, you'll need to have a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree and be licensed to practice medicine.
How do military recruiters hire health professionals?
+Military recruiters hire health professionals through a variety of methods, including military recruiting offices, online applications, medical professional associations, social media and online advertising, and referrals and word of mouth.
