Intro
Master the art of naming angles in geometry with our comprehensive guide. Learn about acute, right, obtuse, and straight angles, as well as complementary, supplementary, and corresponding angles. Understand the definitions, properties, and examples of each angle type, and discover how to identify and name angles in various geometric shapes.
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, sizes, and positions of objects. It involves understanding and working with various concepts, including points, lines, angles, and planes. Angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, and naming them correctly is essential for accurate communication and problem-solving. In this article, we will explore the different types of angles, their definitions, and how to name them.
What is an Angle?

An angle is formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex. The angle is measured in degrees, with 360 degrees making a full circle. Angles can be classified into different types based on their measure and position.
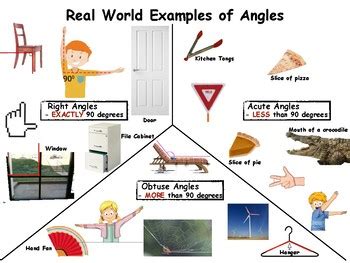
Types of Angles
There are several types of angles, including:
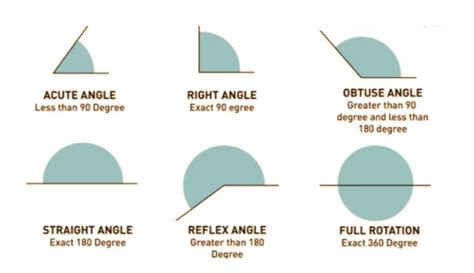
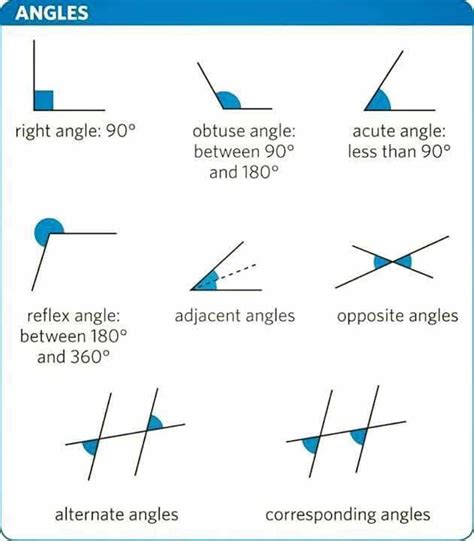
- Acute Angle: An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 degrees.
- Right Angle: An angle whose measure is exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Angle: An angle whose measure is between 90 and 180 degrees.
- Straight Angle: An angle whose measure is exactly 180 degrees.
- Reflex Angle: An angle whose measure is between 180 and 360 degrees.
Naming Angles
Angles can be named in different ways, depending on the context and the type of angle. Here are some common ways to name angles:
- Vertex Angle: An angle is named by its vertex, which is the common endpoint of the two rays that form the angle. For example, angle A, where A is the vertex.
- Three-Point Angle: An angle can be named by three points, where the first point is the vertex, and the other two points are on the rays that form the angle. For example, angle ABC, where A is the vertex, B is on one ray, and C is on the other ray.
- Angle Notation: Angles can also be named using notation, such as ∠A or ∠ABC.
Properties of Angles
Angles have several important properties, including:
- Angle Addition Postulate: The sum of the measures of two adjacent angles is equal to the measure of the larger angle.
- Angle Subtraction Postulate: The difference of the measures of two adjacent angles is equal to the measure of the smaller angle.
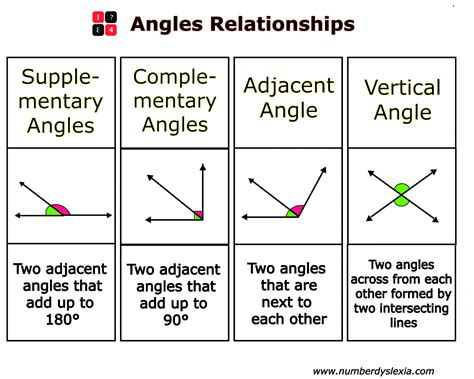
- Vertical Angles: Two angles that are opposite each other and share the same vertex are called vertical angles.
- Supplementary Angles: Two angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees are called supplementary angles.
- Complementary Angles: Two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees are called complementary angles.
Angle Relationships
Angles can be related in different ways, including:
- Congruent Angles: Two angles that have the same measure are called congruent angles.
- Similar Angles: Two angles that have the same shape, but not necessarily the same measure, are called similar angles.
- Angle Bisectors: A line or ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles is called an angle bisector.
Applications of Angles
Angles have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Architecture: Angles are used to design buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering: Angles are used to design and build machines, mechanisms, and other devices.
- Art: Angles are used to create perspective, proportion, and balance in art.
- Science: Angles are used to describe the motion of objects, the position of celestial bodies, and the structure of molecules.
Real-World Examples
Angles are used in various real-world applications, including:
- Construction: Angles are used to build stairs, roofs, and other structures.
- Surveying: Angles are used to measure distances and angles between landmarks.
- Navigation: Angles are used to determine the position and direction of ships, planes, and other vehicles.
Conclusion
Angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, and naming them correctly is essential for accurate communication and problem-solving. In this article, we have explored the different types of angles, their definitions, and how to name them. We have also discussed the properties of angles, angle relationships, and their applications in various fields. Understanding angles is crucial for solving problems in mathematics, science, engineering, and other disciplines.
Angle Image Gallery



What is an angle in geometry?
+An angle in geometry is formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex.
What are the different types of angles?
+Angles can be classified into acute, right, obtuse, straight, and reflex angles.
How are angles named?
+Angles can be named by their vertex, using three points, or using notation.
