Intro
Unlock the benefits of the GI Bill for veterans. Discover how this iconic education assistance program works, covering tuition, fees, and living expenses for degree-seeking veterans. Explore five key ways the GI Bill supports veterans educational pursuits, including on-the-job training, apprenticeships, and vocational courses.
The GI Bill is one of the most comprehensive education benefits packages available to military veterans, offering a wide range of opportunities for education, training, and career advancement. Since its inception in 1944, the GI Bill has helped millions of veterans transition back to civilian life, achieve their educational goals, and secure better-paying jobs.

In this article, we'll explore the five ways the GI Bill works for veterans, highlighting the benefits, eligibility requirements, and application processes for each program.
What is the GI Bill?
The GI Bill is a federal education benefit program designed to help military veterans, active-duty personnel, and their families achieve their educational and career goals. The program offers various benefits, including tuition assistance, housing stipends, and book allowances, to help veterans pursue higher education, vocational training, and other forms of education and training.
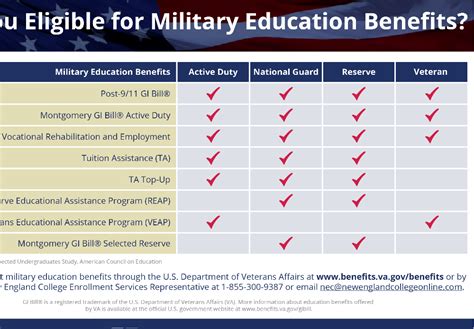
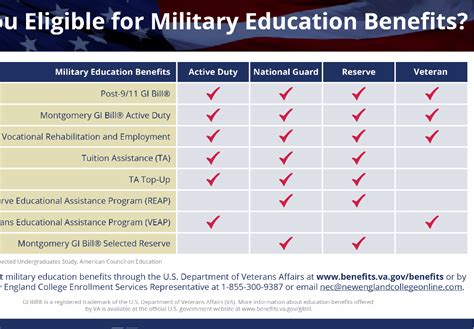
GI Bill Programs
There are several GI Bill programs available to veterans, each with its own set of benefits and eligibility requirements. The most popular programs include:
- The Post-9/11 GI Bill (Chapter 33)
- The Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD, Chapter 30)
- The Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR, Chapter 1606)
- The Reserve Educational Assistance Program (REAP, Chapter 1607)
- The Veterans' Educational Assistance Program (VEAP, Chapter 32)
1. The Post-9/11 GI Bill (Chapter 33)
The Post-9/11 GI Bill is one of the most comprehensive education benefits programs available to veterans. The program offers up to 36 months of education benefits, including:
- Tuition and fees paid directly to the school
- A monthly housing stipend based on the Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) rate for an E-5 with dependents
- A yearly book stipend of up to $1,000
- A one-time relocation stipend of up to $500
To be eligible for the Post-9/11 GI Bill, veterans must have served at least 90 days of active duty since September 10, 2001, and received an honorable discharge.

How to Apply for the Post-9/11 GI Bill
To apply for the Post-9/11 GI Bill, veterans must submit an application through the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) website. The application process typically takes 30-60 days, and veterans can expect to receive a Certificate of Eligibility (COE) once their application is approved.
2. The Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD, Chapter 30)
The Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD) program offers education benefits to active-duty personnel who have served at least two years of active duty. The program provides up to 36 months of education benefits, including:
- A monthly stipend based on the veteran's enrollment status and type of training
- A tuition and fees reimbursement of up to $600 per month
To be eligible for the MGIB-AD program, veterans must have served at least two years of active duty and received an honorable discharge.

How to Apply for the MGIB-AD Program
To apply for the MGIB-AD program, veterans must submit an application through the VA website. The application process typically takes 30-60 days, and veterans can expect to receive a COE once their application is approved.
3. The Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR, Chapter 1606)
The Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) program offers education benefits to members of the Selected Reserve, including the Army Reserve, Navy Reserve, Air Force Reserve, Marine Corps Reserve, Coast Guard Reserve, and the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. The program provides up to 36 months of education benefits, including:
- A monthly stipend based on the veteran's enrollment status and type of training
- A tuition and fees reimbursement of up to $600 per month
To be eligible for the MGIB-SR program, veterans must have served at least six years of service in the Selected Reserve and received an honorable discharge.

How to Apply for the MGIB-SR Program
To apply for the MGIB-SR program, veterans must submit an application through the VA website. The application process typically takes 30-60 days, and veterans can expect to receive a COE once their application is approved.
4. The Reserve Educational Assistance Program (REAP, Chapter 1607)
The Reserve Educational Assistance Program (REAP) offers education benefits to members of the Selected Reserve who are called to active duty in response to a war or national emergency. The program provides up to 36 months of education benefits, including:
- A monthly stipend based on the veteran's enrollment status and type of training
- A tuition and fees reimbursement of up to $600 per month
To be eligible for the REAP program, veterans must have served at least 90 days of active duty in response to a war or national emergency and received an honorable discharge.

How to Apply for the REAP Program
To apply for the REAP program, veterans must submit an application through the VA website. The application process typically takes 30-60 days, and veterans can expect to receive a COE once their application is approved.
5. The Veterans' Educational Assistance Program (VEAP, Chapter 32)
The Veterans' Educational Assistance Program (VEAP) offers education benefits to veterans who have contributed to the program through payroll deductions while serving on active duty. The program provides up to 36 months of education benefits, including:
- A monthly stipend based on the veteran's enrollment status and type of training
- A tuition and fees reimbursement of up to $600 per month
To be eligible for the VEAP program, veterans must have contributed to the program through payroll deductions while serving on active duty and received an honorable discharge.

How to Apply for the VEAP Program
To apply for the VEAP program, veterans must submit an application through the VA website. The application process typically takes 30-60 days, and veterans can expect to receive a COE once their application is approved.
GI Bill Image Gallery









What is the GI Bill?
+The GI Bill is a federal education benefit program designed to help military veterans, active-duty personnel, and their families achieve their educational and career goals.
What are the different types of GI Bill programs?
+There are several GI Bill programs available, including the Post-9/11 GI Bill, the Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty, the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve, the Reserve Educational Assistance Program, and the Veterans' Educational Assistance Program.
How do I apply for the GI Bill?
+To apply for the GI Bill, veterans must submit an application through the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) website. The application process typically takes 30-60 days, and veterans can expect to receive a Certificate of Eligibility (COE) once their application is approved.
What are the eligibility requirements for the GI Bill?
+The eligibility requirements for the GI Bill vary depending on the program. Generally, veterans must have served at least 90 days of active duty and received an honorable discharge to be eligible for the Post-9/11 GI Bill and other programs.
How much does the GI Bill pay?
+The amount of money the GI Bill pays varies depending on the program and the type of training. Generally, the GI Bill pays up to 36 months of education benefits, including tuition and fees, a housing stipend, and a book allowance.
In conclusion, the GI Bill is a comprehensive education benefits program designed to help military veterans, active-duty personnel, and their families achieve their educational and career goals. With its various programs and benefits, the GI Bill provides opportunities for education, training, and career advancement, helping veterans transition back to civilian life and secure better-paying jobs.
