Intro
Unlock the secrets of incredible speed with Mach 6, six times the speed of sound. Discover what it means to reach Mach 6, its applications in aerospace and defense, and the technological advancements making it possible. Explore the science behind supersonic flight, sonic booms, and the future of high-speed travel.
The concept of speed has always fascinated humans, and the idea of Mach 6, or six times the speed of sound, is particularly intriguing. But what exactly does Mach 6 mean, and how fast is it?

To understand Mach 6, we first need to grasp the basics of the Mach number, which is a dimensionless quantity representing the ratio of an object's speed to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. In other words, Mach 1 is equivalent to the speed of sound, while Mach 2 is twice the speed of sound, and so on.
The speed of sound varies depending on the medium, temperature, and pressure. At sea level and room temperature, the speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h). Therefore, Mach 6 would be equivalent to six times this speed, or around 4,608 mph (7,416 km/h).
History of Supersonic Flight
Supersonic flight has been a subject of interest for decades, with the first supersonic aircraft, the Bell X-1, breaking the sound barrier in 1947. The X-1 was a rocket-powered aircraft that reached a top speed of Mach 1.06. Since then, numerous aircraft have been designed to operate at supersonic speeds, including military jets and experimental vehicles.
However, as speeds increase, so do the challenges associated with supersonic flight. One of the primary concerns is the formation of shockwaves, which can generate intense heat and friction, potentially damaging the aircraft. Additionally, supersonic flight requires significant amounts of energy, making it inefficient for long-range flights.
Challenges of Mach 6
Achieving Mach 6 speeds is an incredibly complex task, requiring the development of advanced materials and technologies. Some of the key challenges include:
- Heat management: At supersonic speeds, friction generates intense heat, which can cause damage to the aircraft's structure and electronics.
- Aerodynamic stability: Maintaining stability at high speeds is crucial to prevent loss of control and ensure safe flight.
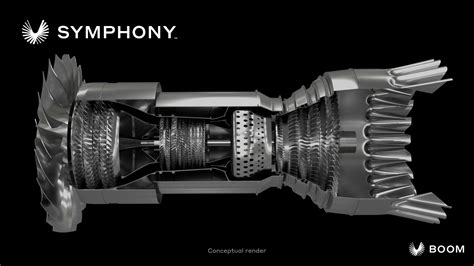
- Propulsion systems: Developing efficient propulsion systems capable of producing the necessary thrust to achieve Mach 6 speeds is a significant challenge.
- Materials science: Creating materials that can withstand the extreme conditions associated with supersonic flight is essential for building a reliable aircraft.

Current Research and Development
Despite the challenges, researchers and engineers continue to explore the possibilities of supersonic flight. Some of the current projects and initiatives include:
- NASA's X-59 QueSST: An experimental aircraft designed to reduce sonic booms and achieve supersonic speeds.
- Lockheed Martin's SR-72: A proposed reconnaissance aircraft capable of reaching speeds up to Mach 6.
- The European Union's HEXAFLY-INT: A research project focused on developing a supersonic aircraft capable of carrying passengers.
Future Applications
If Mach 6 speeds can be achieved safely and efficiently, the potential applications are vast. Some possible uses include:
- High-speed transportation: Supersonic aircraft could revolutionize air travel, reducing travel times between continents.
- Space exploration: Mach 6 speeds could be used to launch spacecraft into orbit or beyond.
- Military applications: Supersonic aircraft could provide a significant advantage in military operations, enabling rapid deployment and response times.

Conclusion
Mach 6 speeds represent a significant challenge, but the potential rewards are substantial. As researchers and engineers continue to push the boundaries of supersonic flight, we may see the development of new technologies and applications that transform the way we travel and explore the world.
Gallery of Supersonic Flight









What is the speed of sound?
+The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level and room temperature.
What is Mach 6?
+Mach 6 is six times the speed of sound, equivalent to approximately 4,608 mph (7,416 km/h).
What are the challenges of supersonic flight?
+Some of the key challenges include heat management, aerodynamic stability, propulsion systems, and materials science.
