Intro
Unlock the intricacies of cyber security with our comprehensive guide. Discover the various difficulty levels of cyber threats, from beginner-friendly to expert-level attacks. Learn how to assess and address vulnerabilities, and explore the nuances of threat analysis, penetration testing, and security posture. Elevate your cyber security knowledge and stay ahead of emerging threats.
The ever-evolving world of cyber security has become a crucial concern for individuals, organizations, and governments alike. As technology advances, the threat landscape expands, and the need for robust security measures grows. But have you ever wondered about the various difficulty levels involved in cyber security? In this article, we'll delve into the world of cyber security difficulty levels, exploring the different types of threats, their complexity, and the skills required to tackle them.
Understanding Cyber Security Difficulty Levels
Cyber security difficulty levels refer to the complexity and severity of various threats, attacks, and vulnerabilities. These levels help security professionals assess the risks and allocate resources accordingly. The difficulty levels range from basic to advanced, with each level requiring a different set of skills, knowledge, and expertise.
Cyber Security Difficulty Levels: A Breakdown
- Basic: Basic cyber security threats include phishing attacks, malware infections, and simple password cracking. These threats are relatively easy to mitigate and require minimal expertise. However, neglecting basic security measures can still lead to significant consequences.
Example: A phishing email attempting to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Intermediate: Intermediate threats involve more sophisticated attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and network scanning. These threats require a moderate level of expertise to detect and respond to.
Example: A SQL injection attack targeting a vulnerable web application.
- Advanced: Advanced threats are highly sophisticated and often involve nation-state actors, organized crime groups, or advanced persistent threats (APTs). These threats require specialized skills, knowledge, and expertise to detect and mitigate.
Example: A highly targeted and customized malware attack designed to evade detection.
- Expert: Expert-level threats involve highly complex and innovative attacks, such as artificial intelligence (AI)-powered malware, quantum computing attacks, or advanced threat simulations. These threats require top-tier expertise and cutting-edge technologies to detect and respond to.
Example: An AI-powered malware attack that adapts and evolves to evade detection.
Skills and Knowledge Required for Each Difficulty Level
To tackle cyber security threats effectively, security professionals need to possess a range of skills and knowledge. Here's a breakdown of the skills required for each difficulty level:
- Basic:
- Familiarity with security fundamentals (e.g., password management, firewalls)
- Basic networking knowledge
- Understanding of common threats (e.g., phishing, malware)
- Intermediate:
- Programming skills (e.g., Python, C++)
- Knowledge of operating systems (e.g., Windows, Linux)
- Familiarity with security tools and technologies (e.g., antivirus software, intrusion detection systems)
- Understanding of web application security
- Advanced:
- In-depth knowledge of computer systems and networks
- Advanced programming skills (e.g., assembly language, exploit development)
- Familiarity with threat intelligence and incident response
- Understanding of advanced security technologies (e.g., sandboxing, threat hunting)
- Expert:
- Expert-level programming skills (e.g., AI, machine learning)
- In-depth knowledge of emerging technologies (e.g., quantum computing, IoT security)
- Advanced threat analysis and mitigation skills
- Familiarity with cutting-edge security tools and technologies
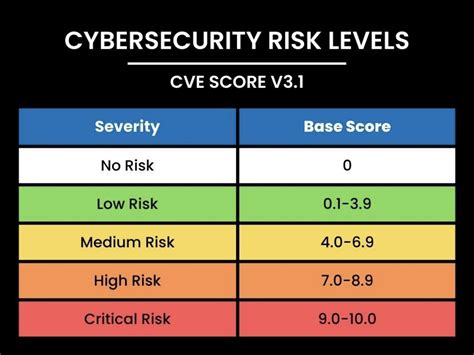
Real-World Examples of Cyber Security Difficulty Levels
- Basic: A small business experiences a phishing attack, resulting in the compromise of employee login credentials.
- Intermediate: A mid-sized organization discovers a SQL injection vulnerability in their web application, leading to unauthorized data access.
- Advanced: A large corporation falls victim to a highly targeted and customized malware attack, requiring specialized expertise to detect and respond to.
- Expert: A nation-state actor launches an AI-powered malware attack against a critical infrastructure organization, requiring top-tier expertise and cutting-edge technologies to detect and mitigate.

Conclusion
Cyber security difficulty levels are a crucial aspect of the ever-evolving threat landscape. Understanding these levels helps security professionals assess risks, allocate resources, and develop strategies to mitigate threats. By possessing the necessary skills and knowledge, security professionals can effectively tackle cyber security threats and protect their organizations from the ever-present danger of cyber attacks.
Call to Action: Share your thoughts on cyber security difficulty levels in the comments below. What do you think is the most pressing cyber security concern facing organizations today?
Gallery of Cyber Security Images
Cyber Security Image Gallery





FAQs
What are the different cyber security difficulty levels?
+The cyber security difficulty levels include basic, intermediate, advanced, and expert.
What skills and knowledge are required for each difficulty level?
+The skills and knowledge required for each difficulty level vary, but generally include programming skills, knowledge of operating systems, and familiarity with security tools and technologies.
How can organizations protect themselves from cyber attacks?
+Organizations can protect themselves from cyber attacks by implementing robust security measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems, and by providing regular training and awareness programs for employees.
