Intro
Revolutionizing farming in the field of agriculture with innovative techniques and technologies. Discover how precision farming, sustainable agriculture, and agricultural technology are transforming the industry. Learn about the benefits of crop monitoring, irrigation management, and farm automation, and explore the future of farming and its impact on food production and environmental sustainability.
The world of agriculture is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the need for sustainable practices. As the global population continues to grow, the pressure on farmers to produce more food while minimizing their environmental footprint has never been greater. In this context, innovative farming practices and technologies are emerging as game-changers, revolutionizing the field of agriculture.
One of the most significant trends in modern agriculture is the adoption of precision farming techniques. This approach involves using advanced technologies such as drones, satellite imaging, and sensor systems to collect and analyze data on soil health, crop growth, and weather patterns. By leveraging this data, farmers can optimize their farming practices, reducing waste and improving yields.
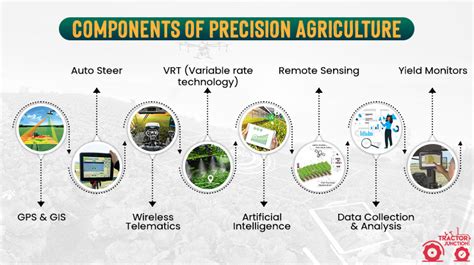
For example, precision irrigation systems use sensors and drones to monitor soil moisture levels, allowing farmers to apply exactly the right amount of water to their crops. This not only saves water but also reduces the energy required to pump and treat it. Similarly, precision fertilizer application uses GPS and sensor data to apply fertilizers only where they are needed, minimizing waste and reducing the environmental impact of fertilizer runoff.
Another area where technology is transforming agriculture is in the development of vertical farming systems. These systems involve growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in indoor environments, using hydroponics or aeroponics. By using LED lighting and carefully controlled climate conditions, vertical farmers can produce high yields of fresh produce year-round, regardless of weather conditions or season.
The Benefits of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming offers a range of benefits, including:
- Increased yields: By growing crops in vertically stacked layers, farmers can produce more food per square foot than traditional farming methods.
- Water efficiency: Vertical farming systems use significantly less water than traditional farming methods, making them ideal for water-scarce regions.
- Year-round production: By controlling climate conditions and using LED lighting, vertical farmers can produce fresh produce 365 days a year, regardless of weather conditions or season.
- Reduced land use: Vertical farming systems can be used to produce food in urban areas, reducing the need for arable land and preserving natural habitats.

In addition to precision farming and vertical farming, other innovative technologies are emerging to support sustainable agriculture practices. For example, precision livestock farming uses sensors and data analytics to monitor the health and behavior of livestock, allowing farmers to optimize their feeding and breeding practices. Similarly, autonomous farming systems use robots and artificial intelligence to automate tasks such as planting, pruning, and harvesting.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in modern agriculture, from precision farming to autonomous farming systems. AI algorithms can be used to analyze data from sensors and drones, providing insights on soil health, crop growth, and weather patterns. This information can be used to optimize farming practices, reducing waste and improving yields.

AI can also be used to develop autonomous farming systems, where robots and drones are used to automate tasks such as planting, pruning, and harvesting. These systems have the potential to significantly improve efficiency and reduce labor costs, making farming more sustainable and profitable.
Steps to Implement AI in Agriculture
- Collect and analyze data: Use sensors and drones to collect data on soil health, crop growth, and weather patterns.
- Develop AI algorithms: Use machine learning algorithms to analyze data and provide insights on optimal farming practices.
- Implement autonomous systems: Use robots and drones to automate tasks such as planting, pruning, and harvesting.
- Monitor and evaluate: Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of AI systems, making adjustments as needed.
In conclusion, the field of agriculture is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the need for sustainable practices. Precision farming, vertical farming, and artificial intelligence are just a few examples of the innovative technologies emerging to support sustainable agriculture practices. By adopting these technologies, farmers can improve yields, reduce waste, and minimize their environmental footprint, ensuring a more sustainable food future for generations to come.
Agriculture Image Gallery









What is precision farming?
+Precision farming is an agricultural practice that uses advanced technology, such as drones, satellite imaging, and sensor systems, to collect and analyze data on soil health, crop growth, and weather patterns.
What is vertical farming?
+Vertical farming is a method of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in indoor environments, using hydroponics or aeroponics.
How can artificial intelligence be used in agriculture?
+Artificial intelligence can be used in agriculture to analyze data from sensors and drones, providing insights on soil health, crop growth, and weather patterns, and to develop autonomous farming systems.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the innovative technologies emerging in the field of agriculture. From precision farming to vertical farming and artificial intelligence, these technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we produce food, reducing waste and improving yields. By adopting these technologies, farmers can ensure a more sustainable food future for generations to come.
