Intro
Unlock the mysteries of power generation with our in-depth look at the inner workings of a power plant. Discover the intricacies of electricity production, from fossil fuel combustion to renewable energy sources, and explore the systems, technologies, and mechanisms that drive modern power plants, including turbines, generators, and transmission systems.
The world's increasing demand for electricity has led to a surge in the construction of power plants, which are essentially facilities that generate electricity on a large scale. Power plants play a crucial role in meeting the world's energy needs, and their inner workings are a fascinating blend of engineering, physics, and technology.

From thermal power plants that burn fossil fuels to nuclear power plants that harness the energy released from atomic reactions, each type of power plant has its unique inner workings. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of a power plant, exploring the different components, processes, and technologies that make electricity generation possible.
Types of Power Plants
There are several types of power plants, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Some of the most common types of power plants include:
- Thermal Power Plants: These power plants generate electricity by burning fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, or oil. The heat produced from the combustion process is used to produce steam, which drives a turbine to generate electricity.
- Nuclear Power Plants: These power plants use nuclear reactions to generate steam, which drives a turbine to produce electricity. Nuclear power plants are a cleaner source of energy compared to thermal power plants, as they do not produce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Hydroelectric Power Plants: These power plants harness the energy of moving water to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power plants are a renewable source of energy and do not produce any emissions.
- Geothermal Power Plants: These power plants use the heat from the Earth's core to generate steam, which drives a turbine to produce electricity.
Components of a Power Plant
A power plant consists of several components, each playing a crucial role in the electricity generation process. Some of the main components of a power plant include:
- Boiler: The boiler is the heart of a power plant, where fuel is burned to produce steam. The boiler is a massive vessel that is designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
- Turbine: The turbine is a mechanical device that converts the energy of the steam into rotational energy. The turbine is connected to a generator, which converts the rotational energy into electrical energy.
- Generator: The generator is a machine that converts the rotational energy of the turbine into electrical energy. The generator uses electromagnetic induction to produce electricity.
- Transformer: The transformer is a device that increases the voltage of the electricity produced by the generator to a level that is suitable for transmission.
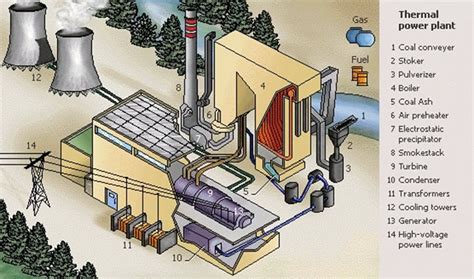
The Electricity Generation Process
The electricity generation process in a power plant involves several stages, from fuel combustion to electricity transmission. Here is an overview of the electricity generation process:
- Fuel Combustion: Fuel is burned in the boiler to produce heat, which is used to produce steam.
- Steam Generation: The heat produced from the combustion process is used to generate steam, which drives the turbine.
- Turbine: The turbine converts the energy of the steam into rotational energy, which is connected to the generator.
- Generator: The generator converts the rotational energy of the turbine into electrical energy.
- Transformer: The transformer increases the voltage of the electricity produced by the generator to a level that is suitable for transmission.
- Transmission: The electricity is transmitted to the power grid, where it is distributed to consumers.
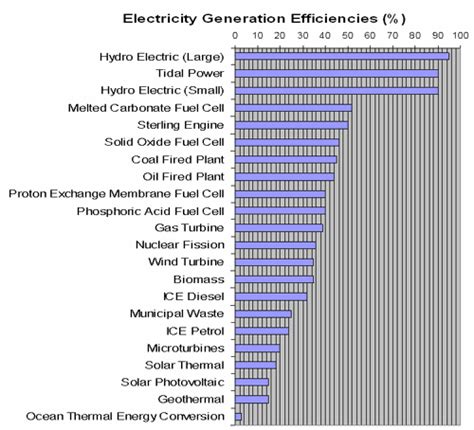
Efficiency and Performance
Power plants have varying levels of efficiency and performance, depending on the type of power plant and the technology used. Some of the key performance indicators of a power plant include:
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a power plant is measured by the amount of electricity generated per unit of fuel consumed.
- Capacity Factor: The capacity factor is the ratio of the actual output of a power plant to its maximum potential output.
- Availability: The availability of a power plant is the percentage of time that the plant is available to generate electricity.

Environmental Impact
Power plants have a significant environmental impact, depending on the type of fuel used and the technology employed. Some of the environmental impacts of power plants include:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Thermal power plants produce greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change.
- Air Pollution: Power plants produce air pollutants, such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide.
- Water Pollution: Power plants produce wastewater, which can pollute waterways and harm aquatic life.
Mitigating Environmental Impacts
There are several strategies that can be employed to mitigate the environmental impacts of power plants, including:
- Renewable Energy Sources: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Carbon capture and storage technologies can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from thermal power plants.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water conservation measures can reduce the amount of wastewater produced by power plants.

Future of Power Plants
The future of power plants is likely to be shaped by advances in technology and changes in energy policy. Some of the trends that are likely to shape the future of power plants include:
- Renewable Energy: Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are likely to become increasingly prominent in the energy mix.
- Energy Storage: Advances in energy storage technologies, such as batteries, are likely to improve the efficiency and reliability of power plants.
- Smart Grids: The development of smart grids is likely to enable greater flexibility and efficiency in the transmission and distribution of electricity.

Gallery of Power Plants
Power Plant Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is a power plant?
+A power plant is a facility that generates electricity on a large scale.
What are the different types of power plants?
+There are several types of power plants, including thermal power plants, nuclear power plants, hydroelectric power plants, and geothermal power plants.
How does a power plant generate electricity?
+A power plant generates electricity by converting the energy of a fuel source, such as coal or uranium, into electrical energy.
What are some of the environmental impacts of power plants?
+Power plants can have significant environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and water pollution.
What is the future of power plants?
+The future of power plants is likely to be shaped by advances in technology and changes in energy policy, including the increasing use of renewable energy sources and energy storage technologies.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the inner workings of a power plant. From the different types of power plants to the environmental impacts and future trends, we have covered it all. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply someone interested in learning more about power plants, we hope this article has been informative and engaging.
