Intro
Discover how Jet Assisted Take Off (JATO) technology enables aircraft to take off safely in short distances. Learn the principles, benefits, and history of JATO systems, including rocket-assisted and jet-powered units. Understand the role of thrust augmentation, runway length, and aircraft weight in JATO operations.
What is Jet Assisted Take Off (JATO)?

Jet Assisted Take Off, commonly referred to as JATO, is a system used to assist aircraft in taking off from a runway. The primary purpose of JATO is to provide an extra boost of power to the aircraft, allowing it to lift off the ground more quickly and efficiently. This is especially useful for aircraft that are heavily loaded or operating in hot and high conditions, where the air is thinner and provides less lift.
The concept of JATO has been around for several decades and has been used in various forms throughout the history of aviation. In the early days of flight, JATO was used to assist aircraft in taking off from short runways or in situations where the aircraft was heavily loaded. Today, JATO is still used in certain applications, such as military operations and space exploration.
How Does JATO Work?

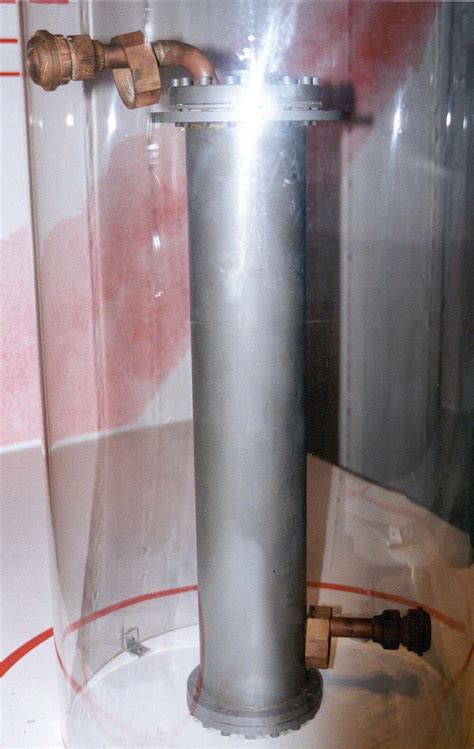
JATO works by using a small rocket engine, typically fueled by solid propellant, to provide an additional source of thrust to the aircraft. The rocket engine is usually mounted on the aircraft's fuselage or wing and is ignited during takeoff. The additional thrust provided by the JATO rocket helps to accelerate the aircraft down the runway, allowing it to lift off the ground more quickly.
The JATO system typically consists of a rocket motor, a fuel system, and an ignition system. The rocket motor is the component that produces the thrust, while the fuel system provides the necessary propellant to the motor. The ignition system is used to ignite the propellant and start the rocket motor.
Types of JATO Systems
There are several types of JATO systems that have been developed over the years. Some of the most common types include:
- Solid-Fueled JATO: This type of JATO system uses a solid propellant, such as ammonium perchlorate, to produce thrust.
- Liquid-Fueled JATO: This type of JATO system uses a liquid propellant, such as kerosene or liquid oxygen, to produce thrust.
- Hybrid JATO: This type of JATO system uses a combination of solid and liquid propellants to produce thrust.
Each type of JATO system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which system to use depends on the specific application and requirements.
Advantages of JATO

JATO systems offer several advantages over traditional aircraft propulsion systems. Some of the main advantages include:
- Increased Thrust: JATO systems can provide a significant increase in thrust, allowing aircraft to take off from shorter runways or operate in hot and high conditions.
- Improved Safety: JATO systems can improve safety by reducing the risk of engine failure during takeoff.
- Reduced Takeoff Distance: JATO systems can reduce the takeoff distance required for an aircraft, allowing it to operate from shorter runways.
Applications of JATO
JATO systems have been used in a variety of applications, including:
- Military Operations: JATO systems have been used in military operations to assist aircraft in taking off from short runways or operating in hot and high conditions.
- Space Exploration: JATO systems have been used in space exploration to assist spacecraft in escaping the Earth's atmosphere.
- Agricultural Aviation: JATO systems have been used in agricultural aviation to assist aircraft in taking off from short runways or operating in hot and high conditions.
Challenges and Limitations of JATO

While JATO systems offer several advantages, they also have some challenges and limitations. Some of the main challenges and limitations include:
- Complexity: JATO systems are complex and require sophisticated engineering and design.
- Cost: JATO systems can be expensive to develop and implement.
- Safety Concerns: JATO systems can pose safety concerns, such as the risk of rocket failure or propellant explosion.
JATO Image Gallery









What is JATO and how does it work?
+JATO is a system used to assist aircraft in taking off from a runway. It works by using a small rocket engine to provide an additional source of thrust to the aircraft.
What are the advantages of JATO?
+The advantages of JATO include increased thrust, improved safety, and reduced takeoff distance.
What are the challenges and limitations of JATO?
+The challenges and limitations of JATO include complexity, cost, and safety concerns.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of JATO and its applications. Whether you are a student of aviation or simply interested in learning more about JATO, we hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or comments, please don't hesitate to contact us.
