Intro
Discover the Lexington Class Aircraft Carrier, a WWII naval aviation pioneer that revolutionized maritime warfare. Learn about its design, capabilities, and significance in shaping the future of aircraft carriers, naval aviation, and military strategy. Explore its role in WWII, its innovations, and its lasting impact on modern naval warfare tactics.
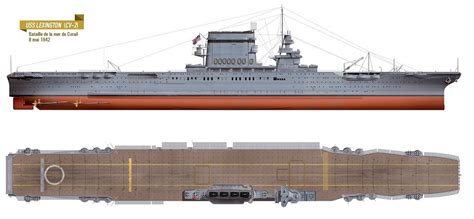
The Lexington class aircraft carrier, also known as the "Lexington-class" or "Essex-class" carriers, played a pivotal role in World War II, revolutionizing naval aviation and setting the standard for future aircraft carrier designs. The two ships of this class, USS Lexington (CV-2) and USS Saratoga (CV-3), were the largest and most advanced aircraft carriers in the world at the time, serving as the backbone of the United States Navy's naval aviation capabilities.

The Lexington class aircraft carriers were designed to accommodate a large number of aircraft, with a capacity for up to 78 planes. The ships featured a length of 888 feet (271 meters), a beam of 106 feet (32 meters), and a draft of 28 feet (8.5 meters). They had a top speed of 33.25 knots (61.58 km/h) and a range of 10,000 nautical miles (18,520 kilometers).
Design and Construction
The Lexington class aircraft carriers were designed to be fast and maneuverable, with a sleek and streamlined hull shape. The ships had a distinctive "island" superstructure, which housed the bridge, control tower, and other essential systems. The flight deck was 866 feet (264 meters) long and 83 feet (25 meters) wide, with a large hangar deck below.

The Lexington class aircraft carriers were constructed at the Fore River Shipyard in Quincy, Massachusetts, and the New York Navy Yard in Brooklyn, New York. USS Lexington (CV-2) was launched on October 3, 1925, and commissioned on December 14, 1927, while USS Saratoga (CV-3) was launched on April 7, 1925, and commissioned on November 16, 1927.
Operational History
The Lexington class aircraft carriers played a significant role in the interwar period, participating in various naval exercises and maneuvers. During World War II, the ships saw extensive service in the Pacific Theater, supporting operations against the Japanese.
USS Lexington (CV-2) was sunk on May 8, 1942, during the Battle of the Coral Sea, while USS Saratoga (CV-3) survived the war and was eventually scrapped in 1946.

Aircraft and Aviation
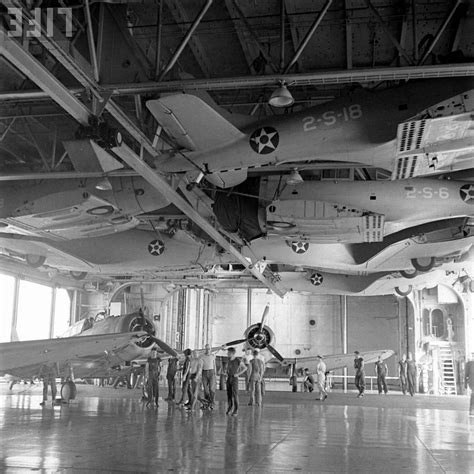
The Lexington class aircraft carriers were designed to operate a wide range of aircraft, including fighters, dive bombers, and torpedo planes. The ships had a large aircraft complement, with up to 78 planes embarked.
The primary aircraft operated from the Lexington class carriers included:
- Grumman F2F and F3F biplane fighters
- Curtiss SBC Helldiver and SB2U Vindicator dive bombers
- Douglas TBD Devastator and TBM Avenger torpedo planes

Legacy
The Lexington class aircraft carriers played a significant role in the development of naval aviation, setting the standard for future aircraft carrier designs. The ships' large size, advanced design, and impressive aircraft complement made them a formidable force in the Pacific Theater during World War II.
The legacy of the Lexington class aircraft carriers can be seen in the many Essex-class carriers that followed, which served as the backbone of the United States Navy's naval aviation capabilities for decades.

Gallery of Lexington Class Aircraft Carrier
Lexington Class Aircraft Carrier Image Gallery









What was the primary role of the Lexington class aircraft carriers?
+The primary role of the Lexington class aircraft carriers was to provide air support for naval operations, serving as a mobile airbase at sea.
How many aircraft could the Lexington class carriers embark?
+The Lexington class aircraft carriers could embark up to 78 aircraft, including fighters, dive bombers, and torpedo planes.
What was the fate of USS Lexington (CV-2)?
+USS Lexington (CV-2) was sunk on May 8, 1942, during the Battle of the Coral Sea.
The Lexington class aircraft carriers played a significant role in the development of naval aviation, setting the standard for future aircraft carrier designs. Their legacy can still be seen in the many Essex-class carriers that followed, which served as the backbone of the United States Navy's naval aviation capabilities for decades.
