Intro
Discover how welding impacts your life expectancy in 7 crucial ways. Learn about the health risks associated with welding, including respiratory problems, cancer, and neurological damage. Understand the long-term effects of welding on your overall well-being and explore ways to minimize exposure and protect your health, from proper ventilation to personal protective equipment.
Welding is a crucial process in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive repair. However, it poses significant health risks to welders, which can impact their life expectancy. Prolonged exposure to welding fumes, radiation, and other hazardous materials can lead to severe health problems, including respiratory issues, cancer, and neurological damage. In this article, we will explore the ways welding affects life expectancy and provide insights into the risks associated with this profession.

1. Respiratory Problems
Welding fumes contain toxic particles, including metals, oxides, and silicates, which can cause respiratory problems. Prolonged inhalation of these particles can lead to conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), welders are at a higher risk of developing respiratory problems due to exposure to hazardous fumes.
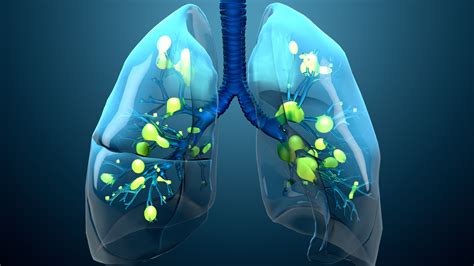
2. Cancer Risk
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified welding fumes as "possibly carcinogenic to humans." Exposure to welding fumes has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer, laryngeal cancer, and urinary tract cancer. The risk of cancer is higher for welders who work with stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals that release toxic fumes.
3. Neurological Damage
Welding fumes contain metals like manganese, copper, and lead, which can cause neurological damage. Prolonged exposure to these metals can lead to conditions like Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders. According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), welders are at a higher risk of developing neurological problems due to exposure to welding fumes.
4. Eye and Skin Problems
Welding can cause eye and skin problems due to exposure to radiation and hazardous materials. Welders are at a higher risk of developing cataracts, eye irritation, and skin conditions like dermatitis and skin cancer. According to OSHA, welders should wear personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent eye and skin problems.
5. Cardiovascular Disease
Welding can cause cardiovascular disease due to exposure to hazardous materials and radiation. According to the American Heart Association, welders are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease due to exposure to particulate matter, metals, and other pollutants.
6. Musculoskeletal Disorders
Welding can cause musculoskeletal disorders due to repetitive movements, awkward postures, and vibrations. According to OSHA, welders are at a higher risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders like back pain, shoulder strain, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
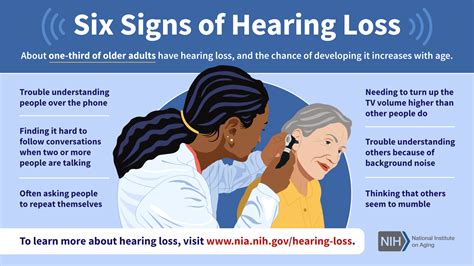
7. Hearing Loss
Welding can cause hearing loss due to exposure to loud noises. According to NIOSH, welders are at a higher risk of developing hearing loss due to exposure to noise levels above 85 decibels.
Gallery of Welding Hazards
Welding Hazards Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risks associated with welding?
+The risks associated with welding include respiratory problems, cancer, neurological damage, eye and skin problems, cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal disorders, and hearing loss.
How can welders protect themselves from hazardous materials?
+Welders can protect themselves from hazardous materials by wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), including respirators, gloves, safety glasses, and earplugs.
What are the symptoms of welding-related illnesses?
+The symptoms of welding-related illnesses include respiratory problems, skin irritation, eye irritation, hearing loss, and neurological problems like Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease.
How can welders reduce their risk of developing welding-related illnesses?
+Welders can reduce their risk of developing welding-related illnesses by following safety protocols, wearing PPE, and minimizing exposure to hazardous materials.
What are the long-term effects of welding on life expectancy?
+The long-term effects of welding on life expectancy include increased risk of respiratory problems, cancer, neurological damage, and cardiovascular disease, which can reduce life expectancy.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the ways welding affects life expectancy. By understanding the risks associated with welding, welders can take necessary precautions to minimize exposure to hazardous materials and reduce their risk of developing welding-related illnesses.
