Intro
Discover 5 essential Maple Elementary tips for improved learning, covering foundational skills, educational strategies, and classroom techniques to enhance student success and academic growth.
The world of maple syrup production is a fascinating one, filled with rich history, intricate processes, and delicious outcomes. For those venturing into this realm, whether as enthusiasts or professionals, understanding the nuances of maple syrup production is crucial. From the selection of the right maple trees to the final bottling of the syrup, every step plays a significant role in determining the quality and flavor of the final product. Here, we'll delve into five essential tips for anyone looking to engage with maple syrup production, focusing on the elementary aspects that form the foundation of this craft.
The process of making maple syrup is labor-intensive and requires patience, dedication, and a good understanding of the natural conditions that affect maple trees. It's a journey that starts with the identification of suitable maple species, primarily the sugar maple (Acer saccharum) and the black maple (Acer nigrum), due to their higher sap sugar content. The sap of these trees, which typically flows in late winter or early spring, is the raw material from which maple syrup is made.
As one begins this journey, it's essential to recognize the importance of proper tree identification and health. Only healthy trees should be tapped, as they produce better-tasting sap and are less likely to be damaged by the tapping process. The age of the tree is also a critical factor; trees should be at least 40 years old and have a diameter of about 40 inches or more to be considered suitable for tapping.
Understanding the Basics of Maple Syrup Production

To produce maple syrup, one must first understand the basics of how sap is collected and converted into syrup. This involves drilling a small hole in the trunk of the maple tree, about three to four feet off the ground, and gently hammering a spout or spigot into the hole. The spout is then connected to a collection vessel or a network of tubes that direct the sap to a central collection point. The sap, which is clear and has a slightly sweet taste, is then boiled in a large, shallow pan called an evaporator to concentrate the sugars. It takes approximately 40 gallons of sap to produce just one gallon of maple syrup, highlighting the labor and resource intensity of this process.
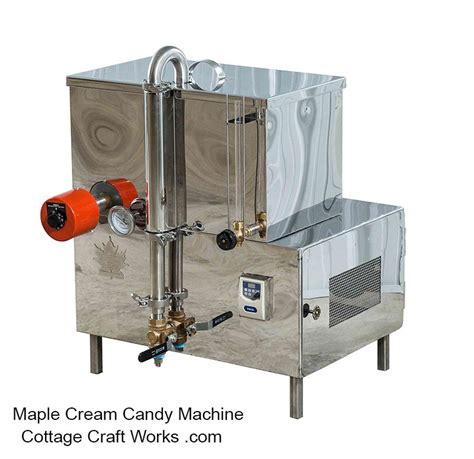
Choosing the Right Equipment
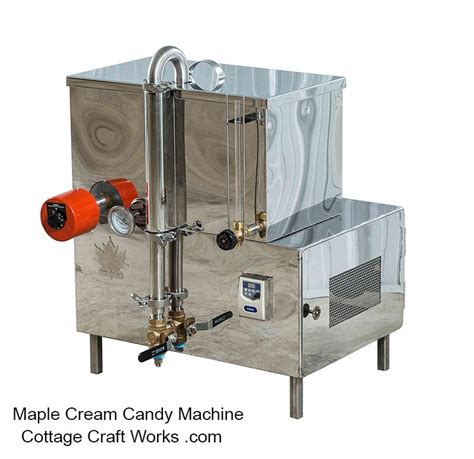

The quality and appropriateness of the equipment used can significantly impact the efficiency and success of maple syrup production. This includes everything from the taps and collection vessels to the evaporator and filtering equipment. For small-scale producers, choosing equipment that is durable, easy to clean, and suitable for the scale of operation is crucial. Larger operations may require more complex systems, including vacuum pumps to enhance sap flow and reverse osmosis machines to pre-concentrate the sap before boiling.
Boiling and Filtering
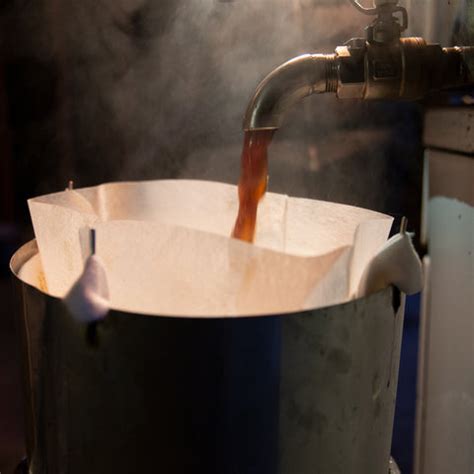
The boiling process is where the magic happens, transforming the clear, watery sap into a rich, amber-colored syrup. This process requires careful monitoring, as the sap must be boiled to exactly the right temperature (7.5 degrees Fahrenheit above the boiling point of water) to achieve the perfect consistency and sugar content. After boiling, the syrup is filtered to remove any sediment or impurities, resulting in a clear, smooth product. The filtering process typically involves passing the syrup through a series of filters, including a coarse filter to remove large particles and a finer filter, often made of diatomaceous earth or a similar material, to achieve clarity.
Grading and Bottling

Once the syrup is produced, it's graded according to its color and flavor. The grading system typically includes Grade A (further divided into light, medium, and dark amber) and Grade B, with Grade A being the most prized for its delicate flavor and light color. Grade B syrup, while still of high quality, has a stronger, more robust flavor and is often used for cooking or making other maple products. After grading, the syrup is bottled or packaged in a variety of formats, from small glass bottles to large containers for commercial or industrial use.
Maintenance and Sustainability

Finally, maintaining the health of the maple trees and ensuring the sustainability of the operation are paramount. This involves careful tapping practices to avoid damaging the trees, re-tapping in a different spot each year to allow the previous year's hole to heal, and adopting sustainable forestry practices. Additionally, producers should be mindful of environmental factors, such as climate change, which can affect sap flow and the overall health of the maple tree population. By prioritizing sustainability, maple syrup producers can help ensure the long-term viability of their operations and the continued health of the forests they depend on.
Maple Syrup Production Image Gallery










What is the best time to tap maple trees?
+The best time to tap maple trees is in late winter or early spring, when temperatures are below freezing at night and above freezing during the day. This temperature fluctuation creates positive pressure inside the tree, causing the sap to flow out through the tap.
How often should maple trees be tapped?
+Maple trees should be tapped once a year, and the tap should be placed in a different spot each year to allow the previous year's hole to heal. This practice helps maintain the health of the tree and ensures continued sap production.
What is the difference between Grade A and Grade B maple syrup?
+Grade A maple syrup is lighter in color and has a more delicate flavor, making it ideal for table use. Grade B syrup is darker and has a stronger, more robust flavor, often used for cooking and making other maple products.
In conclusion, the journey into maple syrup production is a rewarding one, filled with challenges and opportunities for those who are passionate about this traditional craft. By understanding the basics of maple syrup production, from tree selection to bottling, and by adopting sustainable practices, producers can ensure the long-term viability of their operations and the continued enjoyment of this delicious and versatile product. Whether you're a seasoned producer or just starting out, the world of maple syrup offers a unique blend of tradition, innovation, and community, making it a fascinating and rewarding pursuit for anyone interested in exploring the wonders of nature and the joys of artisanal food production. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about maple syrup production, and to explore the many resources available for those looking to delve deeper into this captivating world.
