Intro
Explore the Middle East map in 1945, a pivotal year in the regions history. This article provides a historical geographic overview, detailing the territorial landscape, political boundaries, and key events that shaped the region. Discover the geopolitical dynamics, colonial influence, and emerging nationalist movements that defined the Middle East in 1945.
The Middle East, a region of immense cultural, historical, and strategic significance, has undergone numerous transformations throughout its rich history. One pivotal moment in this narrative is the year 1945, a time marked by the aftermath of World War II and the onset of the Cold War. This era saw the emergence of new global powers, the redrawing of international borders, and the dawn of a new era for the Middle East. This article aims to provide a comprehensive historical geographic overview of the Middle East in 1945, highlighting the key events, territorial changes, and the geopolitical landscape that defined this critical juncture.
The Pre-War Landscape
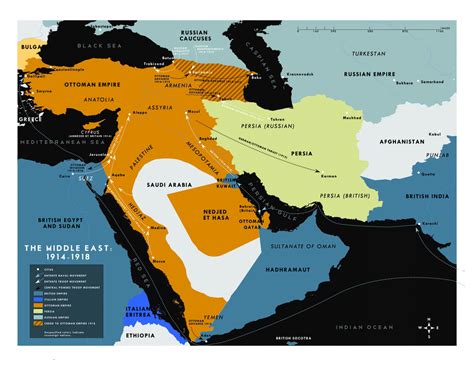
Before delving into the specifics of 1945, it's essential to understand the pre-war landscape of the Middle East. The region was primarily under colonial rule, with the British and French controlling large swaths of territory through the Sykes-Picot Agreement of 1916. This agreement divided the Ottoman Empire's Middle Eastern territories into British and French spheres of influence, laying the groundwork for modern-day borders. The interwar period saw the rise of nationalist movements across the region, pushing for independence from colonial powers.
Nationalist Movements and the Road to Independence
- Egypt: Gained independence from Britain in 1922 but remained under British influence until the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty of 1936.
- Iraq: Became an independent kingdom in 1932 after being a British mandate territory since 1920.
- Syria and Lebanon: Under French mandate, both territories struggled for independence, with Syria gaining it in 1941 and Lebanon following in 1943.
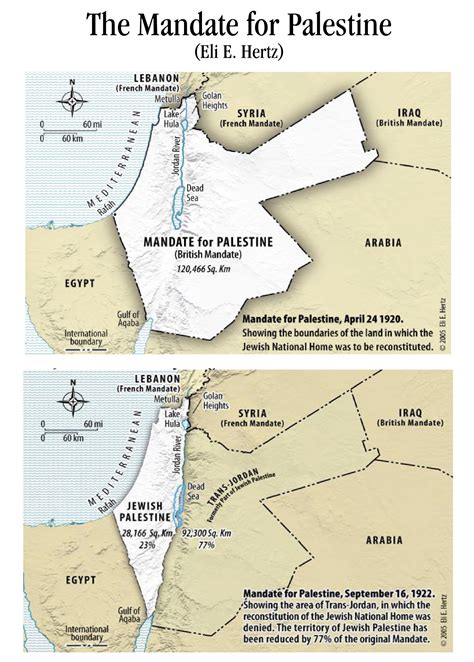
- Palestine: Was a British mandate territory, with the question of Jewish immigration and the future of the territory being contentious issues.
The Post-War Era and the Emergence of New Powers

The end of World War II marked a significant shift in the global balance of power. The United States and the Soviet Union emerged as superpowers, with the Middle East becoming a critical region in the Cold War rivalry. The Potsdam Conference in 1945 set the stage for the post-war world order, with discussions on the future of Germany, the Soviet Union's influence in Eastern Europe, and the beginning of the nuclear age.
The Impact of the Cold War on the Middle East
- US and Soviet Influence: Both superpowers vied for influence in the Middle East, often supporting opposing sides in regional conflicts and nationalist movements.
- Israel's Establishment: In 1948, Israel was established, leading to the Arab-Israeli War and a longstanding conflict that has shaped regional politics to this day.
- The Baghdad Pact: Formed in 1955 with the aim of containing Soviet expansion, it was a military alliance of Middle Eastern states that further polarized the region.
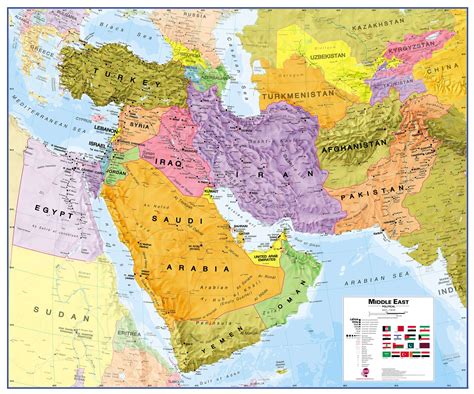
Geopolitical Landscape in 1945

In 1945, the Middle East was a cauldron of nationalist aspirations, colonial legacies, and emerging superpower rivalries. The regional map was dotted with newly independent states, mandated territories, and areas of influence controlled by the great powers. The Palestine question remained unresolved, setting the stage for future conflicts.
Territorial Changes and Emerging Borders
- Redrawing of Borders: The end of World War II led to the redrawing of some borders in the Middle East, primarily affecting territories controlled by the defeated Axis powers and their allies.
- Independence Movements: Many Middle Eastern countries were in the midst of independence movements, with some achieving sovereignty in the immediate post-war period.
Gallery of Middle East Maps
Middle East Historical Maps
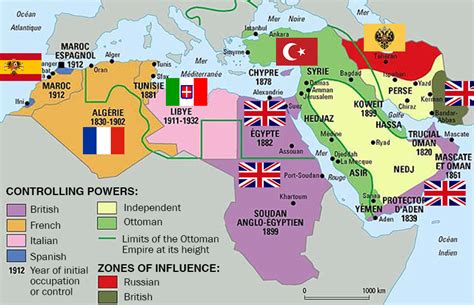
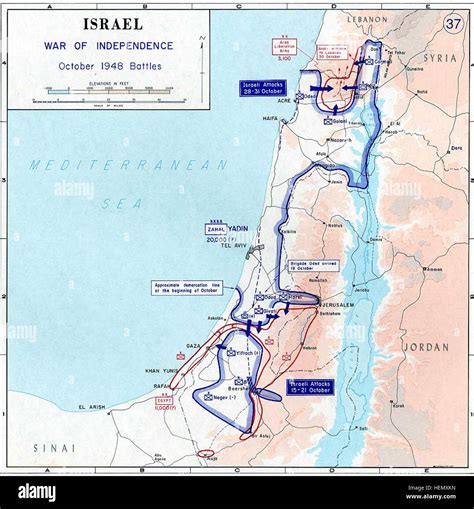
What was the Middle East like in 1945?
+The Middle East in 1945 was characterized by the aftermath of World War II, with the region experiencing a mix of colonial legacy, nationalist movements, and emerging superpower influence.
How did the Cold War affect the Middle East?
+The Cold War polarized the Middle East, with the US and Soviet Union vying for influence, often through proxy states and alliances, leading to regional conflicts and the establishment of Israel.
What were the key geopolitical changes in the Middle East post-1945?
+The establishment of Israel, the Baghdad Pact, and the redrawing of borders following World War II were among the key geopolitical changes that defined the post-1945 Middle East.
The Middle East in 1945 was a complex tapestry of colonial legacies, nationalist aspirations, and emerging superpower rivalries. The post-war era set the stage for the region's future, marked by conflicts, alliances, and the pursuit of independence and sovereignty. Understanding this period is crucial for grasping the complexities of modern Middle Eastern politics and international relations.
If you found this article informative and insightful, we encourage you to share it with others interested in historical geography and the Middle East. Your comments and questions are also welcome, providing an opportunity for further discussion and exploration of this fascinating topic.
