Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of military ranks with our simplified officer rankings chart. Understand the difference between O-1 to O-10 ranks, from Second Lieutenant to General. Learn about rank insignia, pay grades, and responsibilities. Discover how military officer rankings work and advance your knowledge of the armed forces.
Military Officer Rankings Chart Explained Simply
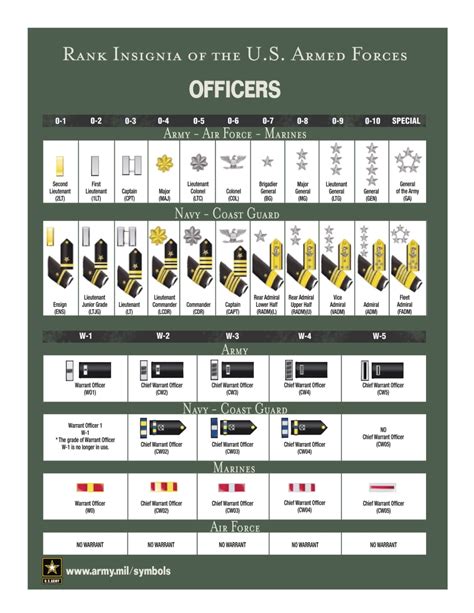
Understanding military officer rankings can be a daunting task, especially for those without prior knowledge or experience. With various branches and ranks, it's easy to get lost in the hierarchy. However, grasping the basics of military officer rankings is crucial for anyone interested in joining the armed forces or simply wanting to understand the structure.
The military is divided into several branches, including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Each branch has its own ranking system, but they share a similar structure. In this article, we'll break down the military officer rankings chart, explaining each rank and its responsibilities in simple terms.
What is the Military Officer Rankings Chart?
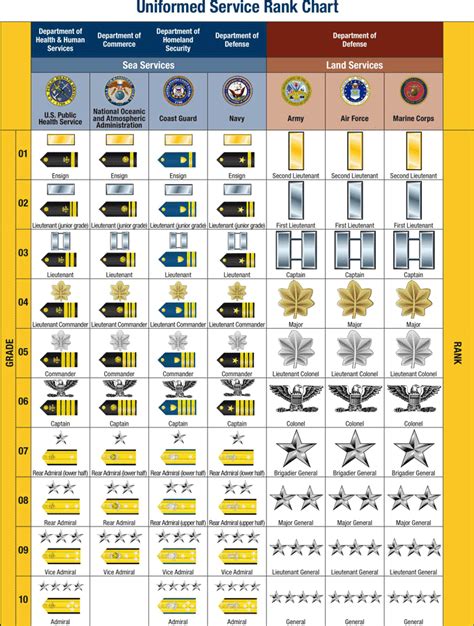
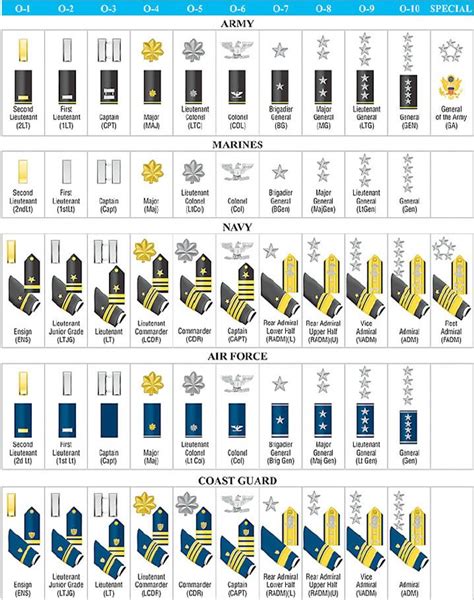
The military officer rankings chart is a hierarchical system that outlines the various ranks within the armed forces. The chart displays the ranks in order of seniority, from lowest to highest. The chart is divided into several sections, including:
- Commissioned Officers: These are the leaders of the military, responsible for making strategic decisions and overseeing operations.
- Warrant Officers: These are technical experts who specialize in specific areas, such as aviation or cybersecurity.
- Enlisted Personnel: These are the backbone of the military, responsible for carrying out day-to-day tasks and operations.
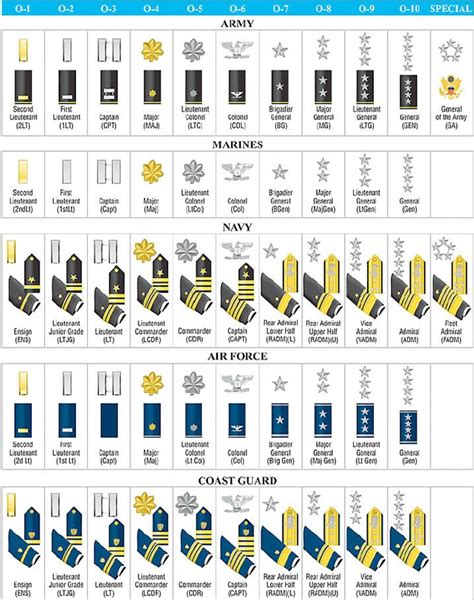
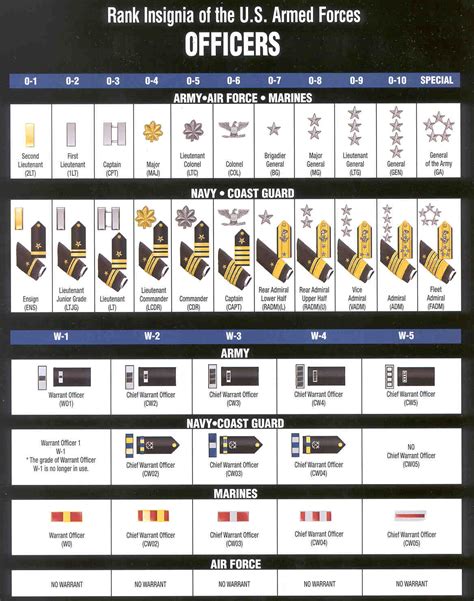
Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers are the highest-ranking individuals in the military. They hold positions of authority and are responsible for making strategic decisions.
- Second Lieutenant (O-1): The lowest commissioned officer rank, typically held by new officers.
- First Lieutenant (O-2): A junior officer rank, often serving as a platoon leader or executive officer.
- Captain (O-3): A mid-level officer rank, responsible for leading companies or battalions.
- Major (O-4): A senior officer rank, often serving as an executive officer or battalion commander.
- Lieutenant Colonel (O-5): A high-ranking officer, responsible for leading battalions or brigades.
- Colonel (O-6): A senior officer rank, often serving as a brigade commander or executive officer.
- Brigadier General (O-7): A one-star general officer rank, responsible for leading brigades or divisions.
- Major General (O-8): A two-star general officer rank, often serving as a division commander.
- Lieutenant General (O-9): A three-star general officer rank, responsible for leading corps or armies.
- General (O-10): The highest commissioned officer rank, responsible for leading entire branches or the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
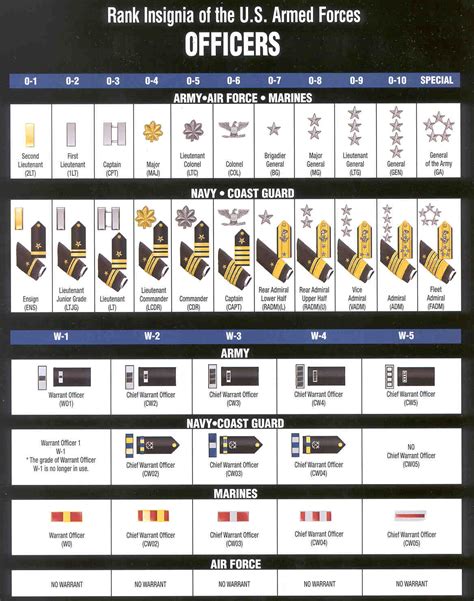
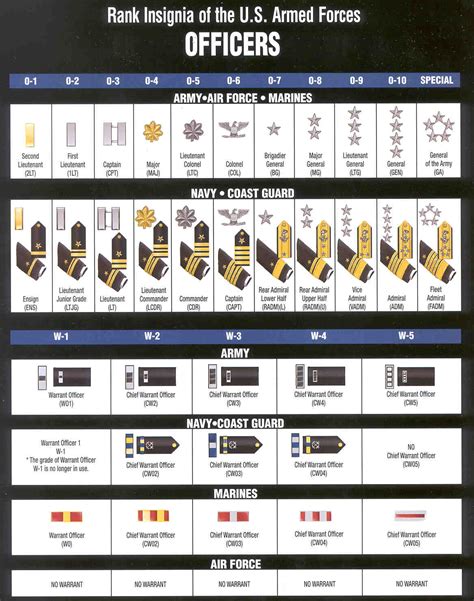
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts who specialize in specific areas. They hold a unique position, ranking above enlisted personnel but below commissioned officers.
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): The lowest warrant officer rank, typically held by new warrant officers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): A junior warrant officer rank, often serving as a technical expert or advisor.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): A mid-level warrant officer rank, responsible for leading teams or serving as a senior advisor.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): A senior warrant officer rank, often serving as a senior technical expert or leader.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): The highest warrant officer rank, responsible for leading teams or serving as a senior advisor.
Enlisted Personnel Ranks
Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the military, responsible for carrying out day-to-day tasks and operations.
- Private (E-1): The lowest enlisted rank, typically held by new recruits.
- Private First Class (E-2): A junior enlisted rank, often serving as a team member or assistant.
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4): A mid-level enlisted rank, responsible for leading teams or serving as a technical expert.
- Sergeant (E-5): A senior enlisted rank, often serving as a team leader or senior advisor.
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): A high-ranking enlisted rank, responsible for leading teams or serving as a senior advisor.
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): A senior enlisted rank, often serving as a platoon sergeant or senior advisor.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8): A high-ranking enlisted rank, responsible for leading teams or serving as a senior advisor.
- Sergeant Major (E-9): The highest enlisted rank, often serving as a senior advisor or leader.

Military Officer Rankings Chart: Key Takeaways
- The military officer rankings chart is a hierarchical system that outlines the various ranks within the armed forces.
- Commissioned officers hold positions of authority and are responsible for making strategic decisions.
- Warrant officers are technical experts who specialize in specific areas.
- Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the military, responsible for carrying out day-to-day tasks and operations.
By understanding the military officer rankings chart, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the structure and hierarchy of the armed forces. Whether you're interested in joining the military or simply want to understand the rankings, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of the military officer rankings chart.
Military Officer Rankings Chart Image Gallery
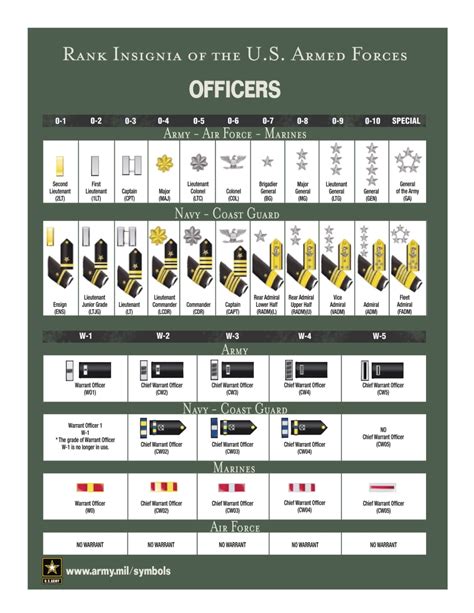
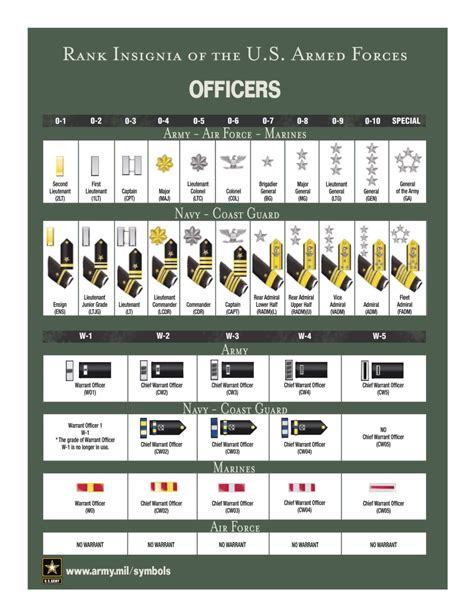
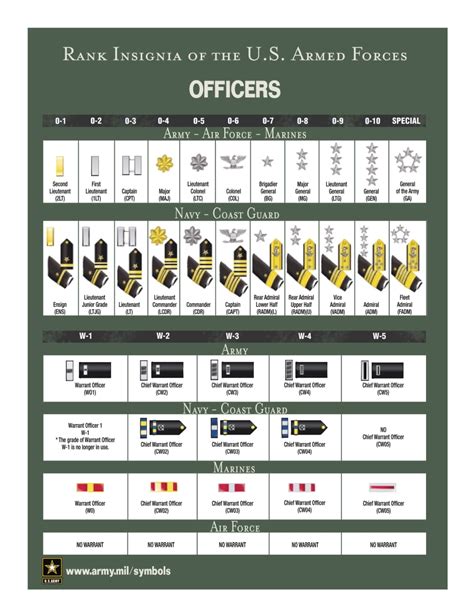

What is the highest rank in the military?
+The highest rank in the military is General (O-10), which is the highest commissioned officer rank.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?
+A commissioned officer is a leader who holds a position of authority, while a warrant officer is a technical expert who specializes in a specific area.
What is the lowest rank in the military?
+The lowest rank in the military is Private (E-1), which is the lowest enlisted rank.
How do I become a commissioned officer in the military?
+To become a commissioned officer, you typically need to complete a four-year degree and attend Officer Candidate School (OCS) or receive a commission through a service academy.
What is the purpose of the military officer rankings chart?
+The military officer rankings chart is used to outline the various ranks within the armed forces and provide a clear understanding of the hierarchy and structure of the military.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the military officer rankings chart is essential for anyone interested in joining the armed forces or simply wanting to understand the structure and hierarchy of the military. By grasping the basics of the chart, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the roles and responsibilities of each rank. Whether you're a seasoned veteran or a new recruit, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of the military officer rankings chart.
