Intro
Discover how military pay fares after taxes with our in-depth analysis. Learn about the 5 key ways military compensation is affected, including tax-free allowances, deductions, and exemptions. Understand how BAH, BAS, and special pays impact your take-home pay and explore strategies to maximize your military income after taxes.
Serving in the military comes with a unique set of financial benefits and challenges. One of the most significant advantages is the tax-free allowances and benefits that military personnel receive. Understanding how military pay looks after taxes can help service members and their families make informed decisions about their finances.
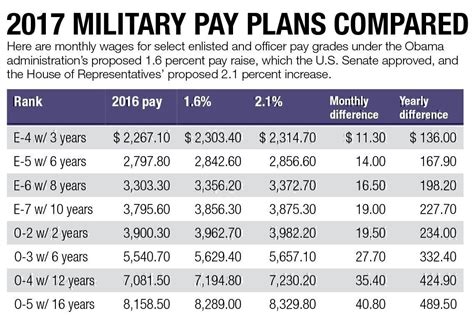
Military pay is composed of basic pay, allowances, and special pays. The tax implications of these different components can vary significantly. In this article, we will explore five ways military pay looks after taxes, including the tax-free nature of certain allowances, the impact of the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act (SCRA), and the role of the military's tax-free shopping privileges.
1. Tax-Free Allowances

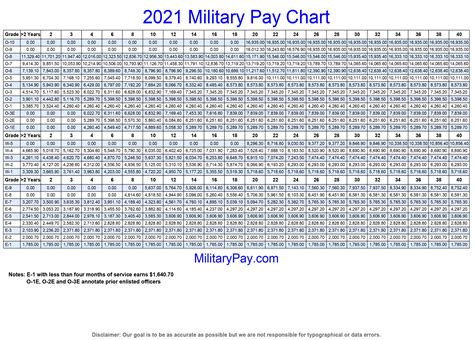
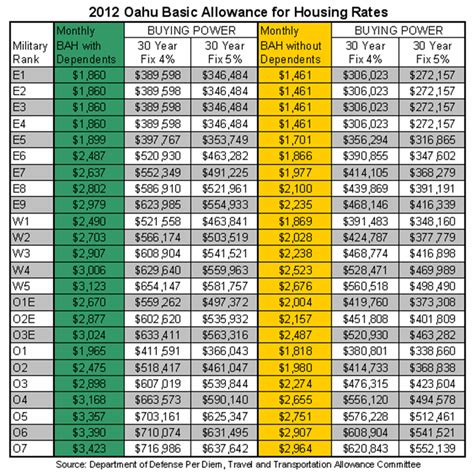
One of the most significant advantages of military pay is the tax-free nature of certain allowances. The Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) and the Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS) are two examples of tax-free allowances. These allowances are designed to help service members offset the cost of living expenses, such as housing and food.
According to the IRS, BAH and BAS are not considered taxable income. This means that service members do not have to pay federal income tax on these allowances. The tax-free nature of these allowances can result in significant savings for service members, especially those who are stationed in high-cost areas.
Types of Tax-Free Allowances
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH)
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS)
- Cost of Living Allowance (COLA)
- Hazardous Duty Pay
- Special Duty Pay
2. Servicemembers Civil Relief Act (SCRA)

The Servicemembers Civil Relief Act (SCRA) is a federal law that provides financial relief to service members who are called to active duty. One of the key provisions of the SCRA is the reduction of interest rates on certain debts, such as credit cards and mortgages.
Under the SCRA, service members may be eligible for a reduced interest rate of 6% on certain debts. This can result in significant savings for service members who are struggling to make ends meet. Additionally, the SCRA prohibits creditors from taking certain actions, such as foreclosing on a home or repossessing a car, while a service member is on active duty.
Benefits of SCRA
- Reduced interest rates on certain debts
- Protection from foreclosure and repossession
- Suspension of court proceedings
- Reduction of insurance premiums
3. Tax-Free Shopping Privileges

Military personnel and their families are eligible for tax-free shopping privileges at military bases. This includes shopping at commissaries, exchanges, and other military stores.
The tax-free shopping privileges can result in significant savings for service members and their families. According to the Defense Commissary Agency, service members can save up to 30% on their grocery bills by shopping at commissaries.
Types of Tax-Free Shopping Privileges
- Commissary shopping
- Exchange shopping
- Military clothing and gear
- Fuel and other household essentials
4. Combat Zone Tax Exclusion

Service members who serve in combat zones may be eligible for a tax exclusion on their income. This means that service members do not have to pay federal income tax on their income earned while serving in a combat zone.
The combat zone tax exclusion can result in significant savings for service members who serve in combat zones. According to the IRS, the tax exclusion can apply to both active duty and reserve personnel.
Eligibility for Combat Zone Tax Exclusion
- Service in a designated combat zone
- Income earned while serving in a combat zone
- Both active duty and reserve personnel are eligible
5. Special Tax Credits

Service members may be eligible for special tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the Child Tax Credit. These credits can result in significant savings for service members who meet the eligibility requirements.
According to the IRS, the EITC is a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income working individuals and families. The Child Tax Credit is a tax credit of up to $2,000 per child for families with qualifying children.
Types of Special Tax Credits
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Dependent Care Credit
- Education Credits
Military Pay Image Gallery







What is the difference between military pay and allowances?
+Military pay refers to the basic pay that service members receive, while allowances are additional forms of compensation that are designed to help service members offset the cost of living expenses.
Are military allowances taxable?
+No, military allowances, such as BAH and BAS, are not considered taxable income.
What is the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act (SCRA)?
+The SCRA is a federal law that provides financial relief to service members who are called to active duty. It includes provisions such as reduced interest rates on certain debts and protection from foreclosure and repossession.
In conclusion, military pay is a complex system that includes both taxable and non-taxable forms of compensation. Understanding how military pay looks after taxes can help service members and their families make informed decisions about their finances. Whether it's taking advantage of tax-free allowances, shopping at commissaries, or claiming special tax credits, there are many ways that service members can reduce their tax liability and increase their take-home pay.
