Intro
Discover the Muslim Holiday Calendar Guide, featuring Islamic dates, Ramadan timings, Eid celebrations, and Hijri calendar events, to plan your religious observances and cultural festivities with accuracy and devotion.
The Muslim holiday calendar is a vital part of Islamic culture and tradition, marking important dates and events that are significant to Muslims around the world. These holidays and celebrations are based on the Islamic lunar calendar, which is approximately 11 days shorter than the solar calendar used in the Western world. Understanding the Muslim holiday calendar is essential for building bridges of cultural understanding and fostering respect between different communities. In this article, we will delve into the significance of the Muslim holiday calendar, its key dates, and how it is observed by Muslims globally.
The Muslim holiday calendar is filled with significant events that commemorate important moments in Islamic history, the life of the Prophet Muhammad, and the principles of the Islamic faith. From the holy month of Ramadan to the festive celebrations of Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, each holiday has its unique traditions, practices, and spiritual significance. For Muslims, these holidays are not just occasions for celebration but also times for reflection, prayer, and strengthening one's faith and connection with the community.
Observing the Muslim holiday calendar is a way for Muslims to connect with their heritage and with the global Muslim community, known as the Ummah. It provides a shared sense of identity and belonging, transcending geographical boundaries and cultural differences. The calendar's events are a reminder of the importance of compassion, forgiveness, and the pursuit of peace and justice, values that are at the heart of Islamic teachings. By understanding and respecting these holidays, individuals from other faiths and backgrounds can foster greater harmony and cooperation, recognizing the common human values that underpin all religious traditions.
Introduction to the Muslim Holiday Calendar
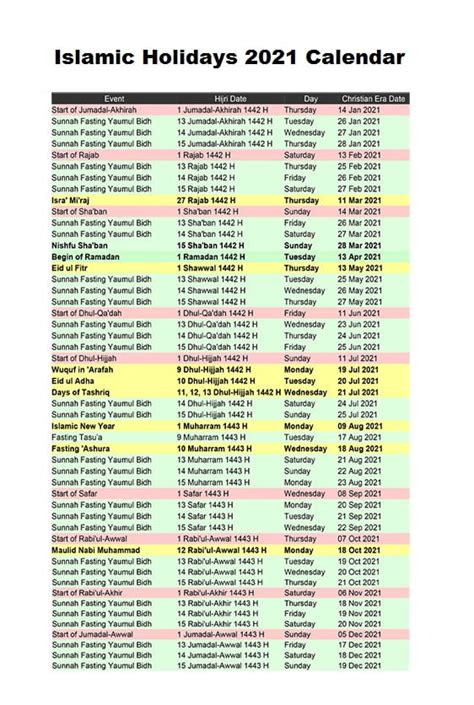
The Muslim holiday calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, is based on the lunar cycle. It consists of 12 months, with each month beginning on the new moon. The most significant months in the Islamic calendar are Ramadan, the month of fasting, and the months of Dhu al-Hijjah and Dhu al-Qadah, during which the Hajj pilgrimage takes place. Understanding the structure and key dates of the Muslim holiday calendar is essential for grasping the rhythm of Islamic life and the spiritual practices that define Muslim communities worldwide.
Key Holidays in the Muslim Calendar
The Muslim calendar is marked by several key holidays and celebrations, each with its unique significance and traditions. These include: - **Mawlid al-Nabi**: Celebrating the birthday of the Prophet Muhammad, which falls on the 12th day of the month of Rabi' al-awwal. It is a time for Muslims to reflect on the life and teachings of the Prophet. - **Laylat al-Mi'raj**: Commemorating the Prophet's journey from Mecca to Jerusalem and his ascension to heaven, which occurs on the 27th of Rajab. This event is seen as a pivotal moment in Islamic history. - **Laylat al-Bara'ah**: Observed on the 15th of Sha'ban, it is a night of forgiveness and is considered an opportunity for Muslims to seek pardon for their sins. - **Ramadan**: The ninth month of the Islamic calendar, during which Muslims fast from dawn to sunset. It is a period of intense spiritual reflection, prayer, and charity. - **Eid al-Fitr**: Celebrated on the first day of Shawwal, marking the end of Ramadan. It is a joyous occasion where Muslims gather with family and friends, exchange gifts, and participate in communal prayers. - **Eid al-Adha**: Falling on the 10th day of Dhu al-Hijjah, it commemorates the willingness of the Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God. It is a time of great festivity and sacrifice, where Muslims slaughter animals and distribute the meat to the poor.The Significance of Ramadan

Ramadan is perhaps the most significant month in the Islamic calendar, a period of fasting, known as Sawm, which is one of the Five Pillars of Islam. During Ramadan, Muslims abstain from food and drink from dawn to sunset, a practice that is meant to foster self-control, empathy for those less fortunate, and a deeper connection with God. The fast is broken each evening with a meal called Iftar, often shared with family and friends, and the night is filled with special prayers known as Tarawih. Ramadan concludes with the celebration of Eid al-Fitr, a day of feasting, gift-giving, and communal prayer.
Practices During Ramadan
Some of the key practices during Ramadan include: - **Fasting (Sawm)**: Abstaining from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn to sunset. - **Tarawih Prayers**: Special nighttime prayers performed in congregation, which involve the recitation of the Quran. - **Recitation of the Quran**: Muslims strive to complete the recitation of the entire Quran during Ramadan. - **Charity (Zakat)**: Giving to the poor and needy, which is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is especially emphasized during Ramadan. - **I'tikaf**: Spending the last ten days of Ramadan in seclusion in the mosque for prayer and contemplation.Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha

Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are the two major festivals in the Islamic calendar, each marking significant events and principles of the Islamic faith. Eid al-Fitr, or the "Festival of Breaking the Fast," is a celebration of the completion of Ramadan, acknowledging the self-control and devotion exhibited during the month of fasting. Eid al-Adha, or the "Festival of Sacrifice," commemorates the willingness of the Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son Ismail as an act of obedience to God, symbolizing the submission and trust in God's will.
Traditions of Eid Celebrations
Some of the traditions associated with Eid celebrations include: - **Eid Prayer**: A special congregational prayer performed in the morning. - **Charity (Sadaqah al-Fitr)**: Giving to the poor to ensure everyone can celebrate Eid. - **Gift-Giving**: Exchanging gifts with family and friends. - **Feasting**: Enjoying special meals with loved ones. - **Sacrifice**: During Eid al-Adha, Muslims who can afford it sacrifice an animal, usually a sheep or a goat, and distribute the meat among family, friends, and the poor.Observing the Muslim Holidays

Observing the Muslim holidays is a meaningful way for Muslims to express their faith, connect with their community, and honor the principles of Islam. These holidays are not just about celebration but also about reflection, prayer, and acts of kindness and charity. For non-Muslims, learning about and respecting these holidays can foster greater understanding and mutual respect, highlighting the shared human values that underpin all religious traditions.
Building Bridges of Understanding
To build bridges of understanding, it is essential to: - **Learn About Muslim Holidays**: Educate oneself about the significance and traditions of Muslim holidays. - **Show Respect**: Acknowledge and respect the observance of these holidays by Muslims. - **Engage in Dialogue**: Openly communicate with Muslims to understand their perspectives and experiences. - **Participate in Interfaith Events**: Join events and activities that promote interfaith understanding and cooperation.Muslim Holiday Image Gallery










What is the significance of Ramadan in the Muslim calendar?
+Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar and is observed as a month of fasting (Sawm), one of the Five Pillars of Islam. It is a period of spiritual reflection, prayer, and charity, commemorating the revelation of the Quran to the Prophet Muhammad.
How do Muslims celebrate Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha?
+Eid al-Fitr is celebrated at the end of Ramadan, marking the completion of the fasting period, with special prayers, feasting, and gift-giving. Eid al-Adha commemorates the willingness of the Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son, involving the sacrifice of an animal and the distribution of its meat among family, friends, and the poor.
What is the importance of the Hajj pilgrimage in the Muslim holiday calendar?
+The Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is a once-in-a-lifetime obligation for Muslims who are physically and financially able. It takes place during the month of Dhu al-Hijjah and involves a series of rituals that commemorate the life of the Prophet Ibrahim and the early history of Islam.
As we conclude this journey through the Muslim holiday calendar, it is clear that these celebrations and commemorations are not just events but are deeply intertwined with the spiritual, cultural, and social fabric of Muslim communities worldwide. By embracing the diversity of religious traditions and practices, we can foster a more inclusive and compassionate global community. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about the Muslim holiday calendar, and to explore the rich tapestry of Islamic culture and tradition. Together, let us build bridges of understanding and respect, celebrating our shared humanity and the values that unite us across cultures and faiths.
