Intro
Discover the medical requirements for joining the National Guard. Learn about the physical health standards, medical disqualifications, and exemptions. Understand how to prepare for the medical exam and what to expect during the enlistment process. Get informed on the National Guards medical requirements and start your service journey today.
The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces that consists of citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to serve in times of war or national emergency. To join the National Guard, individuals must meet certain medical requirements to ensure they are fit for service. In this article, we will explore the medical requirements for joining the National Guard, including the standards for enlistment, commissioning, and deployment.
Why Medical Requirements Matter
Medical requirements are an essential part of the National Guard enlistment process. The goal is to ensure that individuals are physically and mentally fit to perform their duties, which can include combat, humanitarian missions, and disaster response. Meeting medical requirements also helps prevent injuries and illnesses that could compromise an individual's ability to serve.
Medical Standards for Enlistment
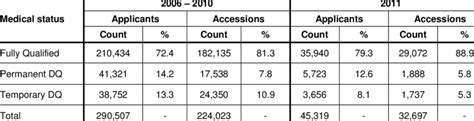
To enlist in the National Guard, individuals must meet the medical standards outlined in Army Regulation 40-501, Chapter 2. These standards cover a range of medical conditions, including:
- Vision: Individuals must have a minimum visual acuity of 20/40 in each eye, with or without corrective lenses.
- Hearing: Individuals must have a minimum hearing threshold of 30 decibels in each ear.
- Blood pressure: Individuals must have a blood pressure reading below 140/90 mmHg.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): Individuals must have a BMI between 19 and 40.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, epilepsy, and asthma, may be disqualifying or require a waiver.
Commissioning Medical Requirements
Commissioned officers in the National Guard must meet more stringent medical standards than enlisted personnel. These standards include:
- Physical fitness: Commissioned officers must meet the Army's physical fitness standards, which include a 2-mile run, push-ups, and sit-ups.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as herniated disks, may be disqualifying or require a waiver.
- Mental health: Commissioned officers must undergo a mental health evaluation to ensure they are fit for command.
Deployment Medical Requirements
National Guard personnel who deploy overseas must meet additional medical requirements, including:
- Vaccinations: Deploying personnel must be up-to-date on all recommended vaccinations, including those for hepatitis A, typhoid, and rabies.
- Medications: Deploying personnel must be free from medications that could interfere with their duties, such as sedatives or narcotics.
- Medical equipment: Deploying personnel must be able to use medical equipment, such as a tourniquet and bandages.
How to Prepare for a Medical Exam
If you are interested in joining the National Guard, it is essential to prepare for the medical exam. Here are some tips:
- Get a physical: Schedule a physical exam with your doctor to ensure you meet the medical standards.
- Gather medical records: Collect any relevant medical records, including vaccination records and medical history.
- Be honest: Be truthful about your medical history and any conditions you may have.
Common Medical Disqualifications
Certain medical conditions may be disqualifying for National Guard service, including:
- Chronic illnesses: Conditions such as diabetes, epilepsy, and asthma may be disqualifying.
- Injuries: Serious injuries, such as those requiring surgery or hospitalization, may be disqualifying.
- Mental health conditions: Certain mental health conditions, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), may be disqualifying.
Waivers and Appeals
If you are disqualified from National Guard service due to a medical condition, you may be eligible for a waiver or appeal. Here are the steps to follow:
- Submit a waiver request: If you believe your medical condition does not preclude you from serving, you can submit a waiver request.
- Provide medical documentation: You must provide medical documentation to support your waiver request.
- Appeal the decision: If your waiver request is denied, you can appeal the decision to the Army Board for the Correction of Military Records.
Gallery of National Guard Medical Requirements
National Guard Medical Requirements Gallery


FAQs
What are the medical requirements for joining the National Guard?
+The medical requirements for joining the National Guard include meeting the Army's medical standards, which cover a range of medical conditions, including vision, hearing, blood pressure, and body mass index (BMI).
Can I join the National Guard if I have a medical condition?
+It depends on the medical condition. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or epilepsy, may be disqualifying or require a waiver. It is best to consult with a medical professional and a National Guard recruiter to determine your eligibility.
How do I prepare for a National Guard medical exam?
+To prepare for a National Guard medical exam, schedule a physical exam with your doctor, gather any relevant medical records, and be honest about your medical history and any conditions you may have.
In conclusion, the National Guard has strict medical requirements to ensure that individuals are physically and mentally fit to serve. Understanding these requirements is essential for anyone interested in joining the National Guard. By meeting these requirements, individuals can ensure they are eligible to serve and perform their duties to the best of their ability.
