Intro
Discover the 5 key differences between National Guard and Army Reserve. Learn how these two reserve components differ in mission, deployment, training, benefits, and service requirements. Understand the unique aspects of each and make an informed decision about your military career. Get the inside scoop on National Guard vs Army Reserve.
When considering a career in the military, many individuals are drawn to the flexibility and part-time nature of serving in the National Guard or Army Reserve. While both components share similarities, there are distinct differences between the two. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision about which path to pursue. In this article, we'll delve into the 5 key differences between the National Guard and Army Reserve, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and benefits.
Role and Responsibilities

One of the primary differences between the National Guard and Army Reserve is their role and responsibilities. The National Guard is a dual-mission force, meaning they have both federal and state responsibilities. When not deployed federally, National Guard units can be called upon by their respective state governors to assist with domestic emergencies, such as natural disasters or civil unrest. In contrast, the Army Reserve is a federal force that primarily supports the active duty Army. Army Reserve units can be deployed alongside active duty units, but they do not have the same state-level responsibilities as the National Guard.
Deployments and Training
In terms of deployments, both the National Guard and Army Reserve can be deployed overseas in support of federal missions. However, National Guard units are more likely to be deployed for state-level emergencies. When it comes to training, both components require their members to participate in regular drills and annual training exercises. However, National Guard units may also conduct training exercises at the state level, focusing on domestic emergency response and homeland security.
Benefits and Pay
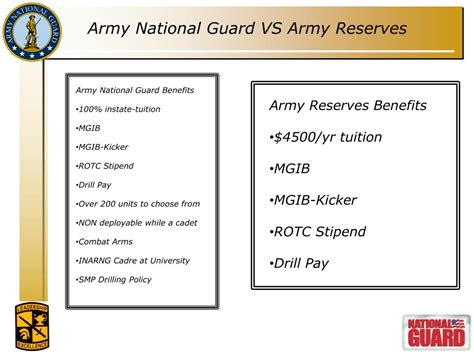
Both the National Guard and Army Reserve offer similar benefits, including access to the GI Bill, education assistance, and medical benefits. However, there are some differences in pay and allowances. National Guard members are typically paid by their state, whereas Army Reserve members are paid by the federal government. Additionally, National Guard members may be eligible for state-specific benefits, such as tuition reimbursement or student loan forgiveness programs.
Time Commitment
Another key difference is the time commitment required for each component. National Guard members typically drill one weekend per month and attend an annual training exercise for two weeks. Army Reserve members also drill one weekend per month, but their annual training exercises can last up to three weeks. However, Army Reserve members may also be required to participate in additional training exercises or deployments, which can impact their time commitment.
Service Requirements

Both the National Guard and Army Reserve require their members to serve for a minimum of six years. However, National Guard members can choose to serve for a shorter period, typically three to four years, depending on the state and their role. Army Reserve members, on the other hand, typically serve for the full six years.
Education Opportunities
Finally, both components offer education opportunities, including access to the GI Bill and tuition assistance programs. However, National Guard members may have additional education benefits available to them, depending on their state. For example, some states offer free tuition to National Guard members who attend in-state colleges or universities.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Path

When deciding between the National Guard and Army Reserve, it's essential to consider your personal goals, priorities, and circumstances. If you're interested in serving your community and state, while also supporting federal missions, the National Guard may be the right choice for you. On the other hand, if you're looking for a more traditional military experience with a focus on federal deployments, the Army Reserve may be the better fit.
Gallery Section:
National Guard vs Army Reserve Image Gallery









FAQ Section:
What is the main difference between the National Guard and Army Reserve?
+The main difference between the National Guard and Army Reserve is their role and responsibilities. The National Guard is a dual-mission force with both federal and state responsibilities, while the Army Reserve is a federal force that primarily supports the active duty Army.
How often do National Guard and Army Reserve members drill?
+Both National Guard and Army Reserve members typically drill one weekend per month and attend an annual training exercise.
What benefits do National Guard and Army Reserve members receive?
+Both National Guard and Army Reserve members receive similar benefits, including access to the GI Bill, education assistance, and medical benefits. However, National Guard members may also be eligible for state-specific benefits.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the differences between the National Guard and Army Reserve. Whether you're considering a career in the military or simply want to learn more about these two components, we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.
