Intro
Discover the differences between National Guard and Army. Learn about the 5 key distinctions in mission, deployment, training, and lifestyle. Understand the unique aspects of serving in the National Guard versus active duty Army, including state vs federal control, deployment frequency, and education benefits.
The National Guard and the Army are two distinct branches of the US military, each with its own unique mission, responsibilities, and characteristics. While both branches are part of the US Armed Forces, they have different roles, requirements, and benefits. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between the National Guard and the Army.
The National Guard and the Army have been integral parts of the US military for centuries, with the National Guard dating back to 1636 and the Army to 1775. Both branches have a rich history, but they have distinct differences in their purpose, structure, and operations.

1. Mission and Purpose
One of the primary differences between the National Guard and the Army is their mission and purpose. The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces that can be called upon to support both state and federal authorities. The National Guard's primary mission is to provide support during natural disasters, civil unrest, and other domestic emergencies. In contrast, the Army's primary mission is to protect the country from external threats and to defend its interests abroad.
The National Guard is often referred to as the " Citizen-Soldier" because its members are part-time soldiers who can be called upon to serve in a variety of roles, including homeland security, disaster response, and community support. The Army, on the other hand, is a full-time military force that is responsible for defending the country against external threats.
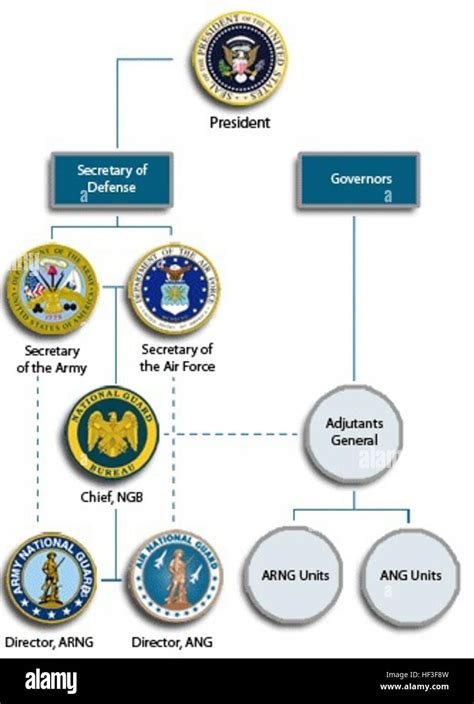
Structure and Organization
Another key difference between the National Guard and the Army is their structure and organization. The National Guard is a decentralized force that is organized at the state level, with each state having its own National Guard unit. This means that National Guard units are often tied to specific geographic regions and are responsible for supporting local communities.
In contrast, the Army is a centralized force that is organized at the federal level. The Army is divided into different branches, including the Active Component, the Reserve Component, and the National Guard. The Army's organizational structure is more complex, with a clear chain of command and a centralized command structure.
Training and Deployment
The National Guard and the Army also have different training and deployment requirements. National Guard members typically train one weekend a month and two weeks a year, known as Annual Training (AT). During this time, they may participate in a variety of training exercises, including combat training, first aid, and leadership development.
In contrast, Army soldiers typically train full-time, with a focus on developing their combat skills and preparing for deployment. Army soldiers may deploy to combat zones or other areas of operation for extended periods, often for 6-12 months or more.

2. Service Requirements
The National Guard and the Army have different service requirements. National Guard members typically serve part-time, with a minimum commitment of 6 years. During this time, they may be called upon to serve in a variety of roles, including homeland security, disaster response, and community support.
In contrast, Army soldiers typically serve full-time, with a minimum commitment of 2-4 years. Army soldiers may also be required to serve for longer periods, depending on their Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) and the needs of the Army.
Benefits and Compensation
The National Guard and the Army offer different benefits and compensation packages. National Guard members are eligible for a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare, and retirement benefits. They may also be eligible for state-specific benefits, such as tuition reimbursement and student loan forgiveness.
In contrast, Army soldiers are eligible for a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare, and retirement benefits. They may also be eligible for special pay and allowances, such as hazardous duty pay and combat pay.

3. Career Opportunities
The National Guard and the Army offer different career opportunities. National Guard members can pursue a range of careers, including careers in law enforcement, emergency management, and healthcare. They may also be eligible for promotion to leadership positions within the National Guard.
In contrast, Army soldiers can pursue a range of careers, including careers in combat, logistics, and administration. They may also be eligible for promotion to leadership positions within the Army.
Education and Training Opportunities
The National Guard and the Army offer different education and training opportunities. National Guard members may be eligible for education assistance, including tuition reimbursement and student loan forgiveness. They may also be eligible for training and certification programs, such as Emergency Management and Homeland Security.
In contrast, Army soldiers may be eligible for education assistance, including tuition reimbursement and student loan forgiveness. They may also be eligible for training and certification programs, such as combat training and leadership development.

4. Deployment and Service Overseas
The National Guard and the Army have different deployment and service overseas requirements. National Guard members may be deployed overseas, but this is relatively rare. When deployed, National Guard members typically serve in support roles, such as logistics and administration.
In contrast, Army soldiers may be deployed overseas more frequently, often in combat roles. Army soldiers may serve in a variety of countries, including Iraq, Afghanistan, and Syria.
Community Involvement
The National Guard and the Army have different levels of community involvement. National Guard members are often involved in their local communities, participating in events and activities such as parades, festivals, and disaster response.
In contrast, Army soldiers may not have as much community involvement, as they are often deployed overseas or serving in remote areas. However, Army soldiers may still participate in community events and activities, such as Veterans Day parades and Memorial Day ceremonies.

5. Retention and Promotion
The National Guard and the Army have different retention and promotion requirements. National Guard members typically serve part-time, with a minimum commitment of 6 years. During this time, they may be eligible for promotion to leadership positions within the National Guard.
In contrast, Army soldiers typically serve full-time, with a minimum commitment of 2-4 years. Army soldiers may be eligible for promotion to leadership positions within the Army, but this often requires additional training and education.

In conclusion, the National Guard and the Army are two distinct branches of the US military, each with its own unique mission, responsibilities, and characteristics. While both branches are part of the US Armed Forces, they have different roles, requirements, and benefits. Whether you are considering joining the National Guard or the Army, it is essential to understand the differences between these two branches and to choose the one that best aligns with your goals, values, and aspirations.
National Guard vs Army Image Gallery










What is the main difference between the National Guard and the Army?
+The main difference between the National Guard and the Army is their mission and purpose. The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces that can be called upon to support both state and federal authorities, while the Army is a full-time military force that is responsible for defending the country against external threats.
What are the benefits of joining the National Guard?
+The benefits of joining the National Guard include education assistance, healthcare, and retirement benefits. National Guard members may also be eligible for state-specific benefits, such as tuition reimbursement and student loan forgiveness.
What are the benefits of joining the Army?
+The benefits of joining the Army include education assistance, healthcare, and retirement benefits. Army soldiers may also be eligible for special pay and allowances, such as hazardous duty pay and combat pay.
How long do National Guard members typically serve?
+National Guard members typically serve part-time, with a minimum commitment of 6 years.
How long do Army soldiers typically serve?
+Army soldiers typically serve full-time, with a minimum commitment of 2-4 years.
