Intro
Discover the differences between National Guard and Military service. Learn about the 5 key distinctions in roles, responsibilities, deployment, training, and benefits. Understand the unique aspects of each and make an informed decision about your service. Get the inside scoop on National Guard vs Military and find your path to serving your country.
The National Guard and the military are two entities that are often confused with one another, but they have distinct differences in terms of their purpose, structure, and deployment. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between the National Guard and the military, helping you understand the unique roles each plays in defending the country and serving the community.

1. Purpose and Mission
The primary purpose of the military is to protect the country from external threats and to defend its interests abroad. The military is responsible for carrying out a wide range of missions, including combat operations, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance. In contrast, the National Guard has a dual mission. Its primary role is to provide support to the states and communities during times of natural disasters, civil unrest, and other domestic emergencies. Additionally, the National Guard can be deployed overseas to support military operations.
Key Statistics:
- The military has approximately 1.3 million active-duty personnel.
- The National Guard has around 450,000 personnel.

2. Structure and Organization
The military is a federal force, with its personnel and resources managed by the Department of Defense. The military is divided into five branches: the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Each branch has its own unique mission, structure, and culture.
The National Guard, on the other hand, is a reserve component of the military, with its personnel and resources managed by the individual states. The National Guard is composed of two branches: the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. While the National Guard is a federal force, it can be called upon to support state and local authorities during domestic emergencies.
Key Facts:
- The National Guard is the oldest component of the US military, dating back to 1636.
- The National Guard has units in all 50 states, as well as in several territories.
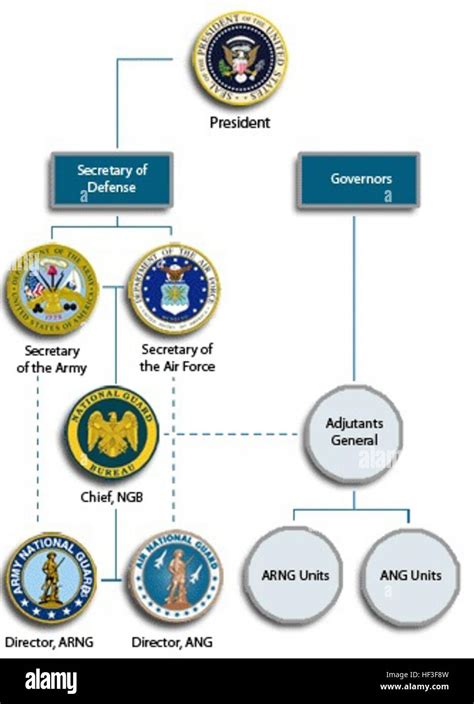
3. Deployment and Training
The military is deployed overseas to carry out a wide range of missions, including combat operations, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance. Military personnel can be deployed for extended periods, often for 12-18 months or more.
The National Guard, on the other hand, can be deployed overseas to support military operations, but it is also deployed domestically to support state and local authorities during emergencies. National Guard personnel typically train one weekend a month and two weeks a year, with the option to attend annual training exercises.
Key Statistics:
- The military has deployed over 200,000 personnel overseas since 2001.
- The National Guard has deployed over 100,000 personnel overseas since 2001.

4. Benefits and Compensation
Military personnel receive a wide range of benefits, including access to healthcare, education, and retirement benefits. Military personnel also receive a competitive salary, with the opportunity to advance in rank and receive promotions.
National Guard personnel also receive benefits, including access to healthcare and education benefits. However, the compensation for National Guard personnel is typically lower than for military personnel, with the exception of those who are deployed overseas.
Key Facts:
- Military personnel can receive up to 100% tuition assistance for education.
- National Guard personnel can receive up to 100% tuition assistance for education.

5. Career Opportunities
The military offers a wide range of career opportunities, from enlisted personnel to officers. Military personnel can choose from a variety of Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), including infantry, engineering, and healthcare.
The National Guard also offers a wide range of career opportunities, with personnel able to choose from a variety of MOS. However, the National Guard typically has fewer career opportunities than the military, with a greater emphasis on part-time service.
Key Statistics:
- The military has over 150 different MOS.
- The National Guard has over 100 different MOS.

National Guard Vs Military Image Gallery









What is the main difference between the National Guard and the military?
+The main difference between the National Guard and the military is their purpose and mission. The military is a federal force responsible for defending the country from external threats, while the National Guard is a reserve component that can be deployed overseas to support military operations and domestically to support state and local authorities during emergencies.
Can National Guard personnel be deployed overseas?
+Yes, National Guard personnel can be deployed overseas to support military operations. However, they can also be deployed domestically to support state and local authorities during emergencies.
What are the benefits of joining the National Guard?
+The National Guard offers a wide range of benefits, including access to healthcare, education benefits, and retirement benefits. Additionally, National Guard personnel can receive competitive pay and benefits, as well as opportunities for career advancement.
We hope this article has helped you understand the key differences between the National Guard and the military. Whether you are considering a career in the military or the National Guard, it is essential to understand the unique roles each plays in defending the country and serving the community.
