Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the US Navys commissioned officer ranks. Discover the 7 key ranks, from Ensign to Captain, and understand the responsibilities, requirements, and career progression. Learn about the roles of junior and senior officers, and how they contribute to the Navys mission. Explore the path to becoming a commissioned officer and advancing through the ranks.
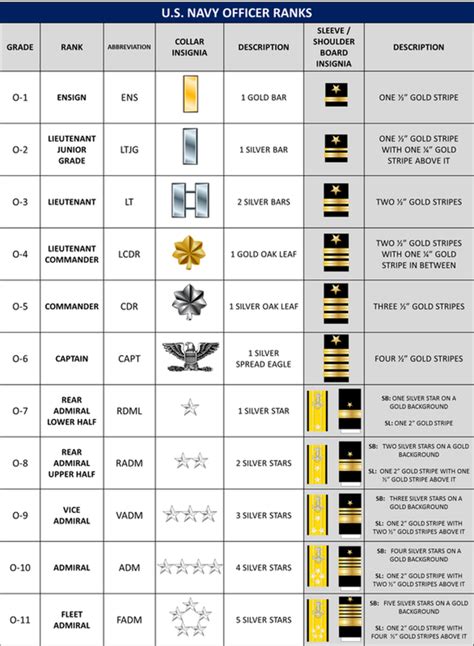
The United States Navy is a prestigious branch of the US military, with a rich history and a complex hierarchy of ranks. Commissioned officers play a crucial role in the Navy, holding leadership positions and making important decisions that impact the entire organization. In this article, we will explore the seven Navy commissioned officer ranks, explaining their responsibilities, requirements, and insignia.

Understanding Navy Commissioned Officer Ranks
The Navy commissioned officer ranks are divided into three main categories: junior officers, senior officers, and flag officers. Each rank has its unique responsibilities, requirements, and insignia. The ranks are also divided into pay grades, which determine the officer's salary and benefits.
Navy Commissioned Officer Rank Structure
The Navy commissioned officer rank structure is as follows:
- Junior Officers: O-1 to O-3
- Senior Officers: O-4 to O-6
- Flag Officers: O-7 to O-10
Junior Officers: O-1 to O-3
Junior officers are the entry-level commissioned officers in the Navy. They hold leadership positions and are responsible for leading small teams and making tactical decisions.

Ensign (O-1)
The Ensign is the most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy. Ensigns typically serve as division officers, leading small teams of sailors and making tactical decisions.
- Requirements: Bachelor's degree, completion of Officer Candidate School (OCS), or commissioning through the United States Naval Academy
- Insignia: One gold bar
Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2)
The Lieutenant Junior Grade is the second most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy. Lieutenants Junior Grade typically serve as department heads or executive officers.
- Requirements: 2-3 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: One gold bar with a silver bar above
Lieutenant (O-3)
The Lieutenant is a junior officer rank in the Navy. Lieutenants typically serve as department heads, executive officers, or commanding officers of small units.
- Requirements: 4-6 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: Two gold bars
Senior Officers: O-4 to O-6
Senior officers are more experienced and hold higher leadership positions in the Navy. They are responsible for leading larger teams and making strategic decisions.

Lieutenant Commander (O-4)
The Lieutenant Commander is a senior officer rank in the Navy. Lieutenant Commanders typically serve as executive officers, department heads, or commanding officers of small units.
- Requirements: 8-12 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: Three gold bars
Commander (O-5)
The Commander is a senior officer rank in the Navy. Commanders typically serve as commanding officers of small units, executive officers, or department heads.
- Requirements: 12-16 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: Four gold bars
Captain (O-6)
The Captain is the most senior officer rank below the flag officer ranks. Captains typically serve as commanding officers of large units, executive officers, or department heads.
- Requirements: 16-20 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: Five gold bars
Flag Officers: O-7 to O-10
Flag officers are the most senior officers in the Navy, holding the highest leadership positions and making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization.

Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (O-7)
The Rear Admiral (Lower Half) is the most junior flag officer rank in the Navy. Rear Admirals (Lower Half) typically serve as deputy commanders of large units or as department heads.
- Requirements: 20-24 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: One gold star on a blue background
Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (O-8)
The Rear Admiral (Upper Half) is a flag officer rank in the Navy. Rear Admirals (Upper Half) typically serve as commanders of large units or as department heads.
- Requirements: 24-28 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: Two gold stars on a blue background
Vice Admiral (O-9)
The Vice Admiral is a flag officer rank in the Navy. Vice Admirals typically serve as deputy commanders of major commands or as department heads.
- Requirements: 28-32 years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: Three gold stars on a blue background
Admiral (O-10)
The Admiral is the most senior flag officer rank in the Navy. Admirals typically serve as commanders of major commands or as department heads.
- Requirements: 32+ years of service, completion of a warfare qualification, and a bachelor's degree
- Insignia: Four gold stars on a blue background
Navy Commissioned Officer Ranks Gallery









What are the different types of Navy commissioned officer ranks?
+The Navy commissioned officer ranks are divided into three main categories: junior officers (O-1 to O-3), senior officers (O-4 to O-6), and flag officers (O-7 to O-10).
What is the most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy?
+The Ensign is the most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy.
What is the highest commissioned officer rank in the Navy?
+The Admiral is the highest commissioned officer rank in the Navy.
In conclusion, the Navy commissioned officer ranks are a complex hierarchy of leadership positions that require different levels of experience, education, and training. Understanding these ranks can help individuals who are interested in joining the Navy or advancing their careers within the organization.
