Intro
Unlock a prestigious career as a Navy Commissioned Officer with our 6-step guide. Learn the requirements, qualifications, and application process to join the esteemed ranks of Navy officers. Discover how to navigate the Naval Academy, Officer Candidate School, and other pathways to achieve a commission and serve as a leader in the US Navy.
Serving in the Navy as a commissioned officer is a prestigious and rewarding career goal that requires dedication, hard work, and a strong passion for serving one's country. The process of becoming a Navy commissioned officer can be complex and challenging, but with the right guidance, anyone can achieve this esteemed position. In this article, we will outline the six steps to become a Navy commissioned officer, providing valuable insights and practical advice for those who aspire to serve in this role.
Step 1: Meet the Basic Requirements
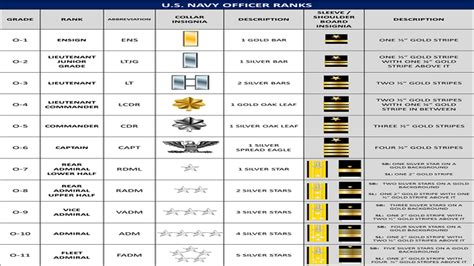
To be eligible to become a Navy commissioned officer, candidates must meet certain basic requirements. These include:
- Being a U.S. citizen
- Being between the ages of 19 and 29 (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Having a high school diploma or equivalent
- Having a minimum GPA of 2.5 (although a GPA of 3.0 or higher is preferred)
- Passing the Navy's physical fitness test
- Passing a background check
- Being willing to serve for a minimum of four years on active duty
In addition to these basic requirements, candidates must also choose a specific career path or designator, which will determine their role in the Navy.
Choosing a Career Path
The Navy offers a wide range of career paths, each with its own unique challenges and rewards. Some of the most popular career paths for commissioned officers include:
- Aviation: Pilots, naval flight officers, and other aviation professionals
- Surface Warfare: Officers who serve on ships and other surface vessels
- Submarine Warfare: Officers who serve on submarines
- Special Warfare: Officers who serve in special operations forces, such as Navy SEALs
- Nuclear Power: Officers who serve on nuclear-powered ships and submarines
Candidates should carefully consider their interests, skills, and strengths when choosing a career path.
Step 2: Earn a Bachelor's Degree

While a bachelor's degree is not strictly necessary to become a Navy commissioned officer, it is highly recommended. In fact, the Navy requires candidates to have a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution in order to be eligible for most officer commissioning programs.
Candidates should choose a degree program that is relevant to their chosen career path, and that will provide them with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed as a Navy officer. Some popular degree programs for Navy officers include:
- Engineering
- Computer science
- Business administration
- International relations
- Physics
In addition to earning a bachelor's degree, candidates should also maintain a high GPA and participate in extracurricular activities that demonstrate their leadership and teamwork skills.
Leadership and Teamwork Skills
The Navy values leadership and teamwork skills highly, and candidates should strive to develop these skills through their academic and extracurricular activities. Some ways to develop leadership and teamwork skills include:
- Joining a ROTC program or other military organization
- Participating in team sports or other group activities
- Holding leadership positions in clubs or other organizations
- Volunteering for community service projects
By developing strong leadership and teamwork skills, candidates can demonstrate their potential to succeed as a Navy commissioned officer.
Step 3: Take the Officer Candidate Test (OCT)

The Officer Candidate Test (OCT) is a standardized test that is used to evaluate candidates for Navy officer commissioning programs. The test assesses a candidate's knowledge, skills, and abilities in areas such as:
- Verbal comprehension
- Quantitative reasoning
- Leadership and teamwork
- Communication skills
Candidates should prepare thoroughly for the OCT by studying and practicing with sample questions and other study materials.
Preparing for the OCT
To prepare for the OCT, candidates should:
- Study the test format and content
- Practice with sample questions
- Review relevant subjects such as math, science, and English
- Develop strong communication and leadership skills
By preparing thoroughly for the OCT, candidates can increase their chances of passing the test and being selected for a Navy officer commissioning program.
Step 4: Apply for a Commissioning Program

Once candidates have met the basic requirements, earned a bachelor's degree, and passed the OCT, they can apply for a Navy officer commissioning program. The Navy offers several commissioning programs, each with its own unique requirements and benefits. Some of the most popular commissioning programs include:
- Officer Candidate School (OCS)
- Naval Reserve Officers' Training Corps (NROTC)
- United States Naval Academy (USNA)
- Direct Commission Officer (DCO) programs
Candidates should carefully review the requirements and benefits of each commissioning program and choose the one that best fits their needs and goals.
Commissioning Program Options
Each commissioning program has its own unique requirements and benefits. For example:
- OCS is a 12-week training program that is designed for candidates who have a bachelor's degree and want to become a Navy officer.
- NROTC is a four-year scholarship program that provides tuition and fees to students who attend a participating university and agree to serve in the Navy after graduation.
- USNA is a four-year service academy that provides a free education to students who agree to serve in the Navy after graduation.
- DCO programs are designed for candidates who have specialized skills or experience, such as doctors or lawyers.
By choosing the right commissioning program, candidates can increase their chances of becoming a Navy commissioned officer.
Step 5: Complete Officer Training

Once candidates have been selected for a commissioning program, they will attend officer training. Officer training is designed to teach candidates the skills and knowledge they need to become a Navy commissioned officer. The training program includes:
- Classroom instruction
- Practical training
- Physical fitness training
- Leadership and teamwork training
Candidates should be prepared to work hard and learn quickly during officer training.
Officer Training Curriculum
The officer training curriculum includes a wide range of topics, such as:
- Naval history and tradition
- Leadership and management
- Communication skills
- Tactics and strategy
- Physical fitness and first aid
By completing officer training, candidates can gain the skills and knowledge they need to succeed as a Navy commissioned officer.
Step 6: Receive a Commission

After completing officer training, candidates will receive a commission as a Navy commissioned officer. A commission is a formal appointment to the rank of ensign, which is the lowest rank of commissioned officer in the Navy.
Candidates should be proud of their achievement and be prepared to serve their country as a Navy commissioned officer.
Life as a Navy Commissioned Officer
As a Navy commissioned officer, candidates can expect to serve in a wide range of roles and responsibilities. They may be stationed on a ship, submarine, or other naval vessel, or they may serve in a shore-based assignment.
Regardless of their assignment, Navy commissioned officers are expected to demonstrate strong leadership and teamwork skills, as well as a commitment to serving their country.
By following these six steps, candidates can become a Navy commissioned officer and serve their country with pride.
Navy Commissioned Officer Image Gallery










What are the basic requirements to become a Navy commissioned officer?
+The basic requirements to become a Navy commissioned officer include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 19 and 29, having a high school diploma or equivalent, having a minimum GPA of 2.5, passing the Navy's physical fitness test, and passing a background check.
What is the Officer Candidate Test (OCT)?
+The Officer Candidate Test (OCT) is a standardized test that is used to evaluate candidates for Navy officer commissioning programs. The test assesses a candidate's knowledge, skills, and abilities in areas such as verbal comprehension, quantitative reasoning, leadership and teamwork, and communication skills.
What are the different types of commissioning programs offered by the Navy?
+The Navy offers several commissioning programs, including Officer Candidate School (OCS), Naval Reserve Officers' Training Corps (NROTC), United States Naval Academy (USNA), and Direct Commission Officer (DCO) programs.
