Intro
Explore the 13 Navy ranks, from Enlisted to Officer, and understand the hierarchy, responsibilities, and requirements for each. Learn about Seaman, Petty Officer, and Chief ranks, as well as Commissioned Officers, Warrant Officers, and Admiral ranks. Discover the path to advancement and the qualifications needed for a successful Navy career.
The United States Navy is one of the largest and most prestigious naval forces in the world, with a long history of protecting American interests and defending freedom. The Navy is composed of two main categories of personnel: enlisted and officers. Within these categories, there are 13 distinct ranks, each with its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and levels of authority.
Understanding the different Navy ranks is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or simply wanting to learn more about the inner workings of the Navy. In this article, we will delve into the 13 Navy ranks, exploring the differences between enlisted and officer ranks, as well as the specific responsibilities and requirements associated with each rank.
Enlisted Ranks
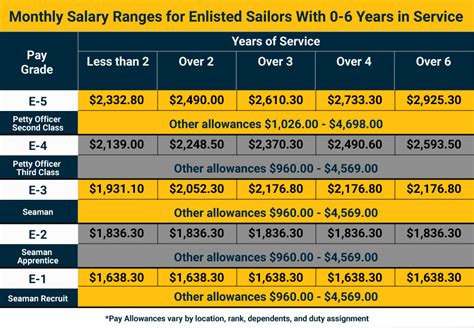
Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the Navy's workforce. They are the backbone of the organization, performing a wide range of critical tasks that keep the Navy running smoothly. Enlisted personnel can be divided into nine distinct ranks, each with its own set of responsibilities and requirements.

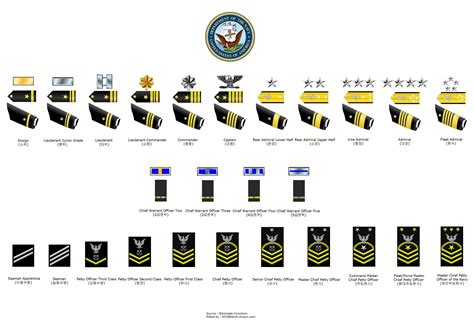
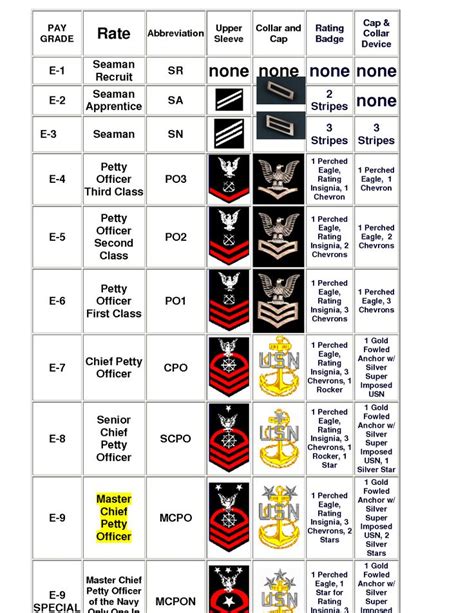
The nine enlisted ranks in the Navy are:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): The lowest rank in the Navy, Seaman Recruit is the entry-level position for new enlistees. Seaman Recruits are typically in training and are not yet assigned to a specific job or duty station.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): Seaman Apprentices are in training and are learning the skills necessary to perform their specific job or rating.
- Seaman (E-3): Seamen are trained and experienced personnel who perform a variety of tasks, including maintenance, repair, and operation of naval equipment.
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): Petty Officers are non-commissioned officers who have demonstrated leadership potential and are responsible for leading and mentoring junior personnel.
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): Petty Officers Second Class are experienced leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical expertise and are responsible for leading and managing teams.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): Petty Officers First Class are senior leaders who have demonstrated exceptional technical expertise and leadership abilities.
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): Chief Petty Officers are senior enlisted leaders who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical expertise.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): Senior Chief Petty Officers are senior enlisted leaders who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical expertise, and are responsible for leading and managing large teams.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): Master Chief Petty Officers are the highest-ranking enlisted personnel in the Navy, and are responsible for leading and managing entire departments or divisions.
Officer Ranks
Officer ranks in the Navy are divided into four categories: Warrant Officers, Limited Duty Officers, Line Officers, and Staff Corps Officers. Officers are responsible for leading and managing enlisted personnel, as well as making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization.
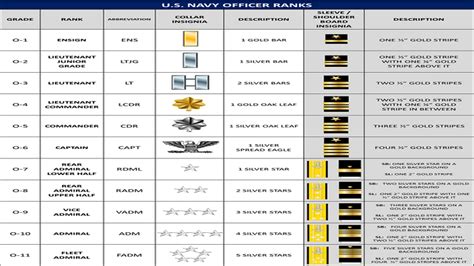
The four officer ranks in the Navy are:
- Ensign (O-1): Ensigns are the lowest-ranking officers in the Navy, and are typically recent graduates of the United States Naval Academy or other officer commissioning programs.
- Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2): Lieutenants Junior Grade are junior officers who have completed their initial training and are assigned to a specific job or duty station.
- Lieutenant (O-3): Lieutenants are experienced officers who have demonstrated leadership potential and are responsible for leading and managing teams.
- Lieutenant Commander (O-4): Lieutenant Commanders are senior officers who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical expertise, and are responsible for leading and managing large teams.
Warrant Officers
Warrant Officers are technical experts who have demonstrated exceptional expertise in a specific area. They are responsible for providing technical guidance and support to officers and enlisted personnel.

The five Warrant Officer ranks in the Navy are:
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): Warrant Officer 1 is the lowest-ranking Warrant Officer, and is responsible for providing technical guidance and support to officers and enlisted personnel.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): Chief Warrant Officer 2 is a senior Warrant Officer who has demonstrated exceptional technical expertise and is responsible for leading and managing teams.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): Chief Warrant Officer 3 is a senior Warrant Officer who has demonstrated exceptional technical expertise and is responsible for leading and managing large teams.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): Chief Warrant Officer 4 is a senior Warrant Officer who has demonstrated exceptional technical expertise and is responsible for leading and managing entire departments or divisions.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): Chief Warrant Officer 5 is the highest-ranking Warrant Officer, and is responsible for providing technical guidance and support to senior officers and enlisted personnel.
Gallery of Navy Ranks
Navy Ranks Image Gallery







FAQs
What are the different types of Navy ranks?
+The Navy has two main categories of personnel: enlisted and officers. Within these categories, there are 13 distinct ranks, each with its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and levels of authority.
What is the highest-ranking enlisted personnel in the Navy?
+The highest-ranking enlisted personnel in the Navy is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
What is the difference between a Warrant Officer and a Commissioned Officer?
+A Warrant Officer is a technical expert who has demonstrated exceptional expertise in a specific area, while a Commissioned Officer is a leader who has completed a four-year degree and has demonstrated leadership potential.
In conclusion, understanding the different Navy ranks is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or simply wanting to learn more about the inner workings of the Navy. By exploring the enlisted and officer ranks, as well as the specific responsibilities and requirements associated with each rank, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and nuance of the Navy's organizational structure.
