Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the US Air Force with our in-depth guide to Non Commissioned Air Force Ranks. Discover the roles, responsibilities, and insignia of each NCO rank, from Airman to Command Chief Master Sergeant. Understand the promotion process, rank structures, and Air Force enlisted rank progression. Enlisted air force ranks explained, from the basics to mastery.
The United States Air Force (USAF) is a branch of the US military that relies heavily on a clear hierarchy and rank structure to maintain order, discipline, and effectiveness. Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) play a vital role in the Air Force, serving as leaders, trainers, and mentors to junior airmen. In this article, we will delve into the world of non-commissioned Air Force ranks, exploring their responsibilities, requirements, and the various ranks that make up the NCO corps.
Understanding the Air Force Rank Structure
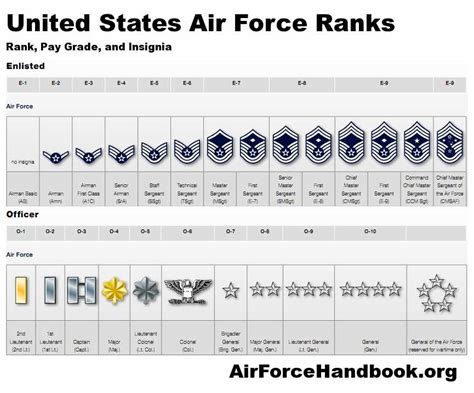
The Air Force rank structure is divided into several categories: enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), senior non-commissioned officers (SNCOs), and officers. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the Air Force, while NCOs and SNCOs are responsible for leading and mentoring these individuals. The rank structure is designed to provide a clear progression path for airmen to advance through the ranks as they gain experience, training, and leadership skills.
The Role of Non-Commissioned Officers in the Air Force
Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) are the backbone of the Air Force, providing leadership, guidance, and support to junior airmen. NCOs are responsible for:
- Leading and mentoring airmen in their unit
- Providing training and guidance on job-specific skills
- Conducting performance evaluations and providing feedback
- Maintaining unit discipline and enforcing Air Force regulations
- Advising senior leaders on issues affecting their unit
Air Force Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks
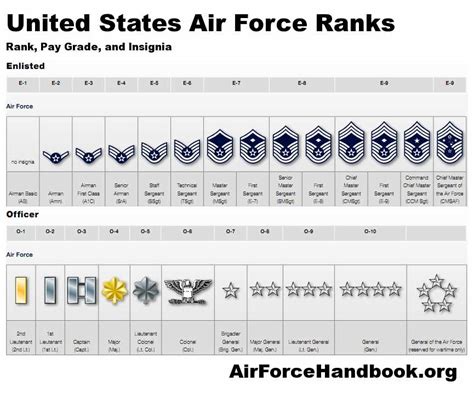
The Air Force has several non-commissioned officer ranks, each with its own set of responsibilities and requirements. Here are the NCO ranks in the Air Force, listed in order of rank:
-
Airman (E-1 to E-3)
Airmen are the most junior enlisted personnel in the Air Force. They are responsible for completing basic training and gaining job-specific skills. Airmen are not considered NCOs, but rather the foundation of the Air Force enlisted corps.
-
Staff Sergeant (E-5)
Staff sergeants are the first NCO rank in the Air Force. They are responsible for leading small teams and providing guidance to junior airmen. Staff sergeants typically have 5-10 years of service and have demonstrated leadership potential.
-
Technical Sergeant (E-6)
Technical sergeants are skilled leaders who have demonstrated expertise in their job specialty. They are responsible for leading larger teams and providing technical guidance to junior airmen. Technical sergeants typically have 10-15 years of service.
-
Master Sergeant (E-7)
Master sergeants are senior NCOs who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical skills. They are responsible for leading large teams and providing guidance to junior NCOs. Master sergeants typically have 15-20 years of service.
-
Senior Master Sergeant (E-8)
Senior master sergeants are highly experienced NCOs who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical skills. They are responsible for leading large teams and providing guidance to junior NCOs. Senior master sergeants typically have 20-25 years of service.
-
Chief Master Sergeant (E-9)
Chief master sergeants are the most senior NCOs in the Air Force. They are responsible for leading large teams and providing guidance to junior NCOs. Chief master sergeants typically have 25+ years of service and are considered experts in their job specialty.
Requirements for Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks

To advance through the NCO ranks, airmen must meet specific requirements, including:
- Time-in-grade: Airmen must have a certain amount of time in their current rank before being eligible for promotion.
- Time-in-service: Airmen must have a certain amount of time in the Air Force before being eligible for promotion.
- Performance evaluations: Airmen must receive positive performance evaluations to demonstrate their leadership potential.
- Training and education: Airmen must complete specific training and education courses to demonstrate their technical skills.
- Leadership experience: Airmen must demonstrate leadership experience, such as leading teams or mentoring junior airmen.
Conclusion
The non-commissioned officer ranks in the Air Force are a vital part of the military hierarchy. NCOs provide leadership, guidance, and support to junior airmen, and are responsible for maintaining unit discipline and enforcing Air Force regulations. By understanding the various NCO ranks and their requirements, airmen can set clear goals for advancement and develop the skills needed to succeed in their careers.
Gallery of Air Force NCOs
Air Force NCOs Image Gallery






What is the role of a non-commissioned officer in the Air Force?
+Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) are responsible for leading and mentoring junior airmen, providing training and guidance, and maintaining unit discipline and enforcing Air Force regulations.
How do I become a non-commissioned officer in the Air Force?
+To become an NCO, airmen must meet specific requirements, including time-in-grade, time-in-service, performance evaluations, training and education, and leadership experience.
What are the different non-commissioned officer ranks in the Air Force?
+The Air Force has several NCO ranks, including staff sergeant, technical sergeant, master sergeant, senior master sergeant, and chief master sergeant.
