Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the US Navys Officer Ranks, from Ensign to Admiral. Discover the responsibilities, requirements, and career paths of O-1 Officers, including Lieutenants, Lieutenant Commanders, and Commanders. Learn about the roles, duties, and expertise required for each rank, and how they contribute to the Navys mission and operations.
In the United States Navy, officers play a vital role in leading and managing the fleet, as well as making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization. From ensigns to admirals, each officer rank has its own unique responsibilities and requirements. In this article, we will delve into the world of Navy officer ranks, exploring the different levels, responsibilities, and qualifications required for each position.
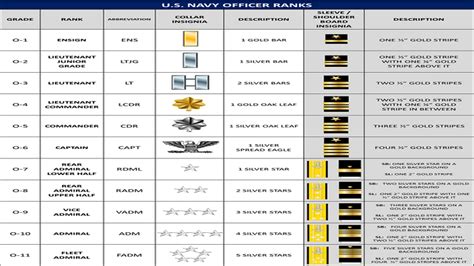
Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers in the Navy are leaders who have completed a four-year degree and have been commissioned through one of several programs, including the United States Naval Academy, Navy Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC), or Officer Candidate School (OCS).
Ensign (O-1)
The ensign is the most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy. Ensigns typically serve as division officers, leading a team of sailors and overseeing the day-to-day operations of a ship or shore-based unit. To become an ensign, one must complete a four-year degree and commissioning program.

Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2)
Lieutenant junior grade is the second-most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy. Lieutenants junior grade typically serve as department heads or assistant department heads, overseeing specific areas of a ship or shore-based unit. To become a lieutenant junior grade, one must complete a minimum of two years of commissioned service.

Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers in the Navy are technical experts who have advanced training and experience in a specific field. Warrant officers are typically recruited from the enlisted ranks and must complete a warrant officer commissioning program.
Warrant Officer 1 (W-1)
The warrant officer 1 is the most junior warrant officer rank in the Navy. Warrant officers 1 typically serve as technical experts in a specific field, providing guidance and oversight to junior sailors. To become a warrant officer 1, one must complete a warrant officer commissioning program and have a minimum of four years of enlisted service.

Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2)
The chief warrant officer 2 is a mid-level warrant officer rank in the Navy. Chief warrant officers 2 typically serve as senior technical experts, providing guidance and oversight to junior sailors and warrant officers. To become a chief warrant officer 2, one must complete a minimum of six years of warrant officer service.

Senior Officer Ranks
Senior officers in the Navy are leaders who have advanced training and experience, as well as a strong track record of performance. Senior officers typically serve in command or senior staff positions, making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization.
Lieutenant Commander (O-4)
The lieutenant commander is a mid-level senior officer rank in the Navy. Lieutenant commanders typically serve as department heads or executive officers, overseeing the day-to-day operations of a ship or shore-based unit. To become a lieutenant commander, one must complete a minimum of eight years of commissioned service.

Commander (O-5)
The commander is a senior officer rank in the Navy. Commanders typically serve as commanding officers or senior staff officers, making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization. To become a commander, one must complete a minimum of 11 years of commissioned service.

Flag Officer Ranks
Flag officers in the Navy are senior leaders who have advanced training and experience, as well as a strong track record of performance. Flag officers typically serve in senior command or staff positions, making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization.
Captain (O-6)
The captain is a flag officer rank in the Navy. Captains typically serve as commanding officers or senior staff officers, making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization. To become a captain, one must complete a minimum of 15 years of commissioned service.

Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (O-7)
The rear admiral (lower half) is a flag officer rank in the Navy. Rear admirals (lower half) typically serve as senior staff officers or commanders of smaller units, making strategic decisions that impact the entire organization. To become a rear admiral (lower half), one must complete a minimum of 20 years of commissioned service.

Navy Officer Ranks Image Gallery










What is the most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy?
+The most junior commissioned officer rank in the Navy is Ensign (O-1).
What is the difference between a warrant officer and a commissioned officer?
+A warrant officer is a technical expert who has advanced training and experience in a specific field, while a commissioned officer is a leader who has completed a four-year degree and has been commissioned through one of several programs.
What is the highest rank in the Navy?
+The highest rank in the Navy is Admiral (O-10).
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the different officer ranks in the Navy, as well as their responsibilities and requirements. Whether you're considering a career in the Navy or simply interested in learning more about the organization, we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.
