Intro
Discover the rewarding careers of Army officers, exploring leadership roles and opportunities that foster personal growth and service. Learn about various officer ranks, duties, and requirements, as well as paths for advancement, education, and specialized fields, offering a life of purpose and challenge in the armed forces.
Serving as an army officer is a prestigious and challenging career path that offers a wide range of leadership roles and opportunities. Army officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of soldiers, making critical decisions, and executing complex missions. In this article, we will explore the different types of army officer careers, the qualifications and requirements needed to become an army officer, and the benefits and opportunities that come with this career path.
What is an Army Officer?
An army officer is a member of the armed forces who holds a position of authority and leadership within the military. Army officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of soldiers, making tactical decisions, and executing missions. They are also responsible for ensuring the safety and well-being of their troops, as well as the successful completion of their assigned missions.
Types of Army Officer Careers
There are several types of army officer careers, each with its own unique set of responsibilities and requirements. Some of the most common types of army officer careers include:
- Infantry Officer: Infantry officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of infantry soldiers, who are trained to fight on foot. Infantry officers are responsible for making tactical decisions and executing missions in a variety of environments, from urban to rural settings.
- Armor Officer: Armor officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of armor soldiers, who are trained to operate and maintain tanks and other armored vehicles. Armor officers are responsible for making tactical decisions and executing missions in a variety of environments, from urban to rural settings.
- Artillery Officer: Artillery officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of artillery soldiers, who are trained to operate and maintain artillery systems. Artillery officers are responsible for making tactical decisions and executing missions in a variety of environments, from urban to rural settings.
- Aviation Officer: Aviation officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of aviation soldiers, who are trained to operate and maintain aircraft. Aviation officers are responsible for making tactical decisions and executing missions in a variety of environments, from urban to rural settings.
- Engineering Officer: Engineering officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of engineering soldiers, who are trained to design, build, and maintain infrastructure and equipment. Engineering officers are responsible for making tactical decisions and executing missions in a variety of environments, from urban to rural settings.

Qualifications and Requirements
To become an army officer, you must meet certain qualifications and requirements. These include:
- Age: You must be between the ages of 17 and 35 to enlist in the army.
- Citizenship: You must be a U.S. citizen to enlist in the army.
- Education: You must have a high school diploma or equivalent to enlist in the army. Some army officer careers may require a college degree.
- Physical Fitness: You must meet the army's physical fitness standards, which include passing a physical fitness test and meeting certain body fat percentage requirements.
- Background Check: You must pass a background check to enlist in the army.
Benefits and Opportunities
Serving as an army officer comes with a wide range of benefits and opportunities. Some of the most significant benefits and opportunities include:
- Leadership Development: As an army officer, you will have the opportunity to develop your leadership skills and experience.
- Career Advancement: The army offers a wide range of career advancement opportunities, from promotions to new assignments and deployments.
- Education Benefits: The army offers education benefits, including the GI Bill, which can help you pay for college or vocational training.
- Healthcare Benefits: The army offers comprehensive healthcare benefits, including medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Travel Opportunities: As an army officer, you will have the opportunity to travel and experience new cultures and environments.
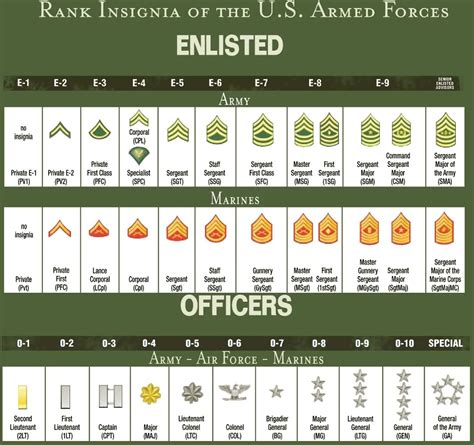
Army Officer Ranks and Responsibilities
Army officers are ranked according to their level of experience and responsibility. The most common army officer ranks include:
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): A second lieutenant is the lowest rank of army officer. Second lieutenants are typically responsible for leading small teams of soldiers and making tactical decisions.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A first lieutenant is the next highest rank of army officer. First lieutenants are typically responsible for leading larger teams of soldiers and making more complex tactical decisions.
- Captain (CPT): A captain is a mid-level rank of army officer. Captains are typically responsible for leading companies of soldiers and making strategic decisions.
- Major (MAJ): A major is a senior rank of army officer. Majors are typically responsible for leading battalions of soldiers and making high-level strategic decisions.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A lieutenant colonel is a senior rank of army officer. Lieutenant colonels are typically responsible for leading brigades of soldiers and making high-level strategic decisions.
Army Officer Training and Education
Army officers must complete a variety of training and education programs to prepare them for their roles. Some of the most common training and education programs include:
- Officer Candidate School (OCS): OCS is a 12-week training program that prepares new officers for their roles.
- West Point: West Point is a four-year college that prepares officers for their roles.
- Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC): ROTC is a college program that prepares officers for their roles.
- Officer Basic Leadership Course (OBC): OBC is a training program that prepares new officers for their roles.

Army Officer Specializations
Army officers can specialize in a variety of areas, including:
- Infantry: Infantry officers are trained to fight on foot and lead teams of infantry soldiers.
- Armor: Armor officers are trained to operate and maintain tanks and other armored vehicles.
- Artillery: Artillery officers are trained to operate and maintain artillery systems.
- Aviation: Aviation officers are trained to operate and maintain aircraft.
- Engineering: Engineering officers are trained to design, build, and maintain infrastructure and equipment.

Army Officer Career Paths
Army officers can pursue a variety of career paths, including:
- Combat Arms: Combat arms officers are trained to fight on the front lines and lead teams of soldiers in combat.
- Combat Support: Combat support officers are trained to provide support to combat units, including logistics, maintenance, and medical support.
- Combat Service Support: Combat service support officers are trained to provide support to combat units, including food, water, and shelter.
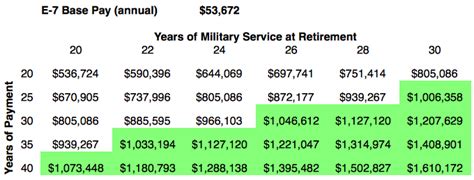
Army Officer Retirement Benefits
Army officers are eligible for a variety of retirement benefits, including:
- Pension: Army officers are eligible for a pension after 20 years of service.
- Healthcare Benefits: Army officers are eligible for comprehensive healthcare benefits, including medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Education Benefits: Army officers are eligible for education benefits, including the GI Bill, which can help them pay for college or vocational training.
Gallery of Army Officer Careers
Army Officer Careers Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is an army officer?
+An army officer is a member of the armed forces who holds a position of authority and leadership within the military.
What are the different types of army officer careers?
+There are several types of army officer careers, including infantry, armor, artillery, aviation, and engineering.
What are the qualifications and requirements to become an army officer?
+To become an army officer, you must meet certain qualifications and requirements, including age, citizenship, education, physical fitness, and background check.
What are the benefits and opportunities of serving as an army officer?
+Serving as an army officer comes with a wide range of benefits and opportunities, including leadership development, career advancement, education benefits, healthcare benefits, and travel opportunities.
What are the different ranks of army officers?
+The most common army officer ranks include second lieutenant, first lieutenant, captain, major, and lieutenant colonel.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of army officer careers, including the different types of careers, qualifications and requirements, benefits and opportunities, and ranks and responsibilities. Serving as an army officer is a challenging and rewarding career path that offers a wide range of opportunities for leadership development, career advancement, and personal growth.
